Determining The Limit Of The Difference Of Two Functions Calculus

Determining The Limit Of The Difference Of Two Functions Calculus X <a) x <a) approach the number a, then we say that the limit as x approaches a from the left is negative infinity and we write. lim x → a − f (x) = − ∞. lim x → a − f (x) = − ∞. (2.9) infinite limits from the right: let f (x) be a function defined at all values in an open interval of the form (a, c). if the values of. The next theorem, called the squeeze theorem, proves very useful for establishing basic trigonometric limits. this theorem allows us to calculate limits by “squeezing” a function, with a limit at a point \(a\) that is unknown, between two functions having a common known limit at \(a\). figure \(\pageindex{4}\) illustrates this idea.

Determining The Limit Of The Function By Rearranging Expressions Into The next theorem, called the squeeze theorem, proves very useful for establishing basic trigonometric limits. this theorem allows us to calculate limits by “squeezing” a function, with a limit at a point a that is unknown, between two functions having a common known limit at a. figure 2.27 illustrates this idea. The next theorem, called the squeeze theorem, proves very useful for establishing basic trigonometric limits. this theorem allows us to calculate limits by “squeezing” a function, with a limit at a point a that is unknown, between two functions having a common known limit at a. [link] illustrates this idea. The next theorem, called the squeeze theorem, proves very useful for establishing basic trigonometric limits. this theorem allows us to calculate limits by “squeezing” a function, with a limit at a point a that is unknown, between two functions having a common known limit at \(a\). figure \(\pageindex{4}\) illustrates this idea. The next theorem, called the squeeze theorem, proves very useful for establishing basic trigonometric limits. this theorem allows us to calculate limits by “squeezing” a function, with a limit at a point [latex]a[ latex] that is unknown, between two functions having a common known limit at [latex]a[ latex]. illustrates this idea.

Determining The Limit Of The Product Of Two Functions Calculus The next theorem, called the squeeze theorem, proves very useful for establishing basic trigonometric limits. this theorem allows us to calculate limits by “squeezing” a function, with a limit at a point a that is unknown, between two functions having a common known limit at \(a\). figure \(\pageindex{4}\) illustrates this idea. The next theorem, called the squeeze theorem, proves very useful for establishing basic trigonometric limits. this theorem allows us to calculate limits by “squeezing” a function, with a limit at a point [latex]a[ latex] that is unknown, between two functions having a common known limit at [latex]a[ latex]. illustrates this idea. So, do these two different functions also have different limits as \(x\) approaches 7? not necessarily. remember, in determining a limit of a function as \(x\) approaches \(a\), what matters is whether the output approaches a real number as we get close to \(x=a\). the existence of a limit does not depend on what happens when \(x\) equals \(a\). Use a table of values to estimate the limit of a function or to identify when the limit does not exist. use a graph to estimate the limit of a function or to identify when the limit does not exist. define one sided limits and provide examples. explain the relationship between one sided and two sided limits.
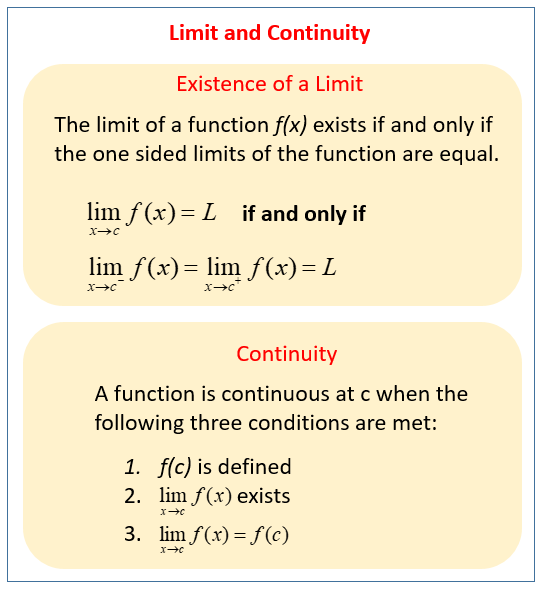
Calculus Limits Of Functions Video Lessons Examples Solutions So, do these two different functions also have different limits as \(x\) approaches 7? not necessarily. remember, in determining a limit of a function as \(x\) approaches \(a\), what matters is whether the output approaches a real number as we get close to \(x=a\). the existence of a limit does not depend on what happens when \(x\) equals \(a\). Use a table of values to estimate the limit of a function or to identify when the limit does not exist. use a graph to estimate the limit of a function or to identify when the limit does not exist. define one sided limits and provide examples. explain the relationship between one sided and two sided limits.

Piecewise Functions Limits And Continuity Calculus Youtube

Comments are closed.