Divisibility Rules From 1 To 30 Basics Of Mathematics

Free Printable Divisibility Rules Chart Divisibility rules and examples showing how to use the rules rule #1: divisibility by 2. a number is divisible by 2 if its last digit is an even number or the last digit is 0,2,4,6,or 8. for instance, 8596742 is divisible by 2 because the last digit is 2. rule #2: divisibility by 3. a number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is. Divisibility rule of 12. if the number is divisible by both 3 and 4, then the number is divisible by 12 exactly. example: 5864. sum of the digits = 5 8 6 4 = 23 (not a multiple of 3) last two digits = 64 (divisible by 4) the given number 5864 is divisible by 4 but not by 3; hence, it is not divisible by 12.

Divisibility Rules For Math Divisibility rules from 1 to 30 in one shot | learn divisibility rules by sunaina mam | mathematics |divisibility rules from 1 to 30 divisibility rules are a. Or use the "3" rule: 7 2 3=12, and 12 ÷ 3 = 4 exactly yes. note: zero is divisible by any number (except by itself), so gets a "yes" to all these tests. any integer (not a fraction) is divisible by 1. the last digit is even (0,2,4,6,8) the sum of the digits is divisible by 3. this rule can be repeated when needed:. Divisibility rule of 10. any number whose last digit is 0 is divisible by 10. example: 10, 20, 30, 100, 2000, 40,000, etc. divisibility rule for 11. if the difference of the sum of alternative digits of a number is divisible by 11, then that number is divisible by 11. example 1: consider the number. 2846767. first, understand the digit positions. 425 is divisible by 1. 13.8 is not divisible by 1. 2. any even integer a number whose last digit is 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8. 12 6 is divisible by 2. 327 5 is not divisible by 2. 3. any integer where the sum of the digits is a multiple of 3. 4365 is divisible by 2 because 4 3 6 5=18 which is divisible by 3.
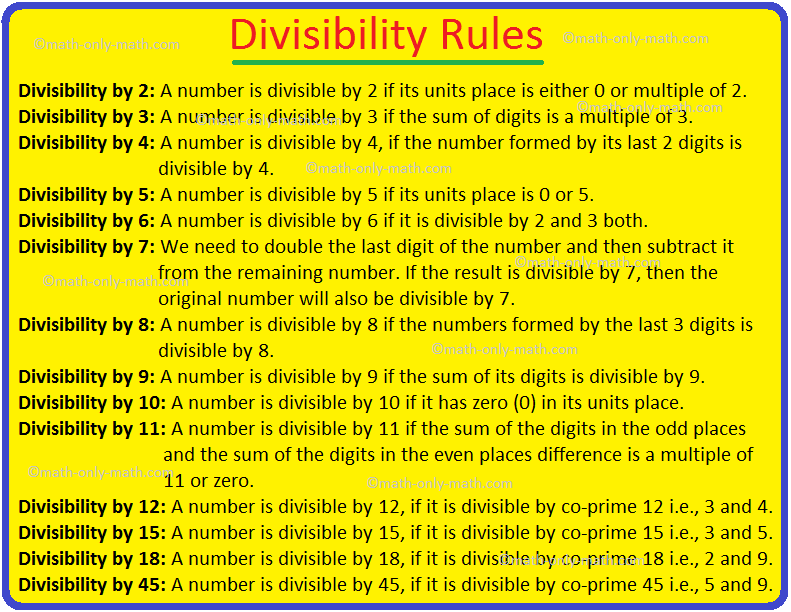
Chart Of Divisibility Rules Divisibility rule of 10. any number whose last digit is 0 is divisible by 10. example: 10, 20, 30, 100, 2000, 40,000, etc. divisibility rule for 11. if the difference of the sum of alternative digits of a number is divisible by 11, then that number is divisible by 11. example 1: consider the number. 2846767. first, understand the digit positions. 425 is divisible by 1. 13.8 is not divisible by 1. 2. any even integer a number whose last digit is 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8. 12 6 is divisible by 2. 327 5 is not divisible by 2. 3. any integer where the sum of the digits is a multiple of 3. 4365 is divisible by 2 because 4 3 6 5=18 which is divisible by 3. The divisibility rule of 9 9 tells us that 1 2 a b 1 2 a b is a multiple of 9. 9. since it is a number from 3 3 to 21, 21, it must be either 9 9 or 18. 18. now, the divisibility rule of 11 11 tells us that 1 2 a b 1 −2 a− b is a multiple of 11. 11. since it is a number from 10 −10 to 8, 8, it must be 0. Basic divisibility rules divisibility rules explained more lessons for arithmetic free math worksheets. the multiple of a number is always divisible by the number. the word “divisible” means that it can be divided exactly. example: 144 ÷ 4 = 36 (remainder = 0). so, 144 is divisible by 4 and is a multiple of 4. 144 ÷ 5 = 28 (remainder = 4).

Divisibility Rules 2 To 16 Maths Basics Tutorial Youtube The divisibility rule of 9 9 tells us that 1 2 a b 1 2 a b is a multiple of 9. 9. since it is a number from 3 3 to 21, 21, it must be either 9 9 or 18. 18. now, the divisibility rule of 11 11 tells us that 1 2 a b 1 −2 a− b is a multiple of 11. 11. since it is a number from 10 −10 to 8, 8, it must be 0. Basic divisibility rules divisibility rules explained more lessons for arithmetic free math worksheets. the multiple of a number is always divisible by the number. the word “divisible” means that it can be divided exactly. example: 144 ÷ 4 = 36 (remainder = 0). so, 144 is divisible by 4 and is a multiple of 4. 144 ÷ 5 = 28 (remainder = 4).

Comments are closed.