Earth Science Chapter 16 The Atmosphere Composition Structure And Temperature

Chapter 16 The Atmosphere Composition Structure And Temp Flashcards The warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of earth that occurs when carbon dioxide, water vapor, and other gases in the air absorb and reradiate infrared radiation. heat. the total amount of kinetic energy due to the random motion of atoms or molecules in a body of matter; also called thermal energy. inclination of the axis. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what are the three branches of earth science that will be studied in this course?, how do scientists study the atmosphere?, the prevailing conditions of the atmosphere over a short period of tie such as hourly or daily is called and more.

Earth Atmosphere Structure With Clouds Royalty Free Vector Chapter 16 the atmosphere: composition, structure & temperature. albedo. click the card to flip 👆. the reflectivity of a surface, usually expressed as a % of the incident radiation reflected. click the card to flip 👆. 1 33. This page titled 3.1: structure and composition of the atmosphere is shared under a cc by nc 3.0 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by stephen lower via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the libretexts platform. the atmosphere acts as a compressible fluid tied to the earth by gravitation; as a receptor. Earth’s atmosphere is divided into four distinct layers based on thermal characteristics (temperature changes), chemical composition, movement, and density (figure 6.1). the troposphere is the lowest layer extending from the surface up to roughly 18 km above the surface depending on location (varies from as low as 6 km to as high as 20 km. 4. carbon dioxide: ~0.036%. originally present in earth's early atmosphere in much higher concentration, but was converted to o 2 and other carbon compounds through photosynthesis by plants. b. other components of the atmosphere are present in variable concentrations. 1. water vapor (h 2 o): 0 4%.

Layers Of юааthe Atmosphereюаб юааstructureюаб Of юааearthюабтащs юааatmosphereюаб Earth’s atmosphere is divided into four distinct layers based on thermal characteristics (temperature changes), chemical composition, movement, and density (figure 6.1). the troposphere is the lowest layer extending from the surface up to roughly 18 km above the surface depending on location (varies from as low as 6 km to as high as 20 km. 4. carbon dioxide: ~0.036%. originally present in earth's early atmosphere in much higher concentration, but was converted to o 2 and other carbon compounds through photosynthesis by plants. b. other components of the atmosphere are present in variable concentrations. 1. water vapor (h 2 o): 0 4%. 0.033 0.036% carbon dioxide (co 2) together with water vapor is responsible for greenhouse effect. the atmosphere is also composed of water, ice and dust particles (aerosols). aerosols are found most frequently near their sources, for example, cities, sea coasts or active volcanoes. however, particles can be carried a great distance. One of the main components of earth’s interdependent physical systems is the atmosphere. an atmosphere is made of the layers of gases surrounding a planet or other celestial body. composition: earth’s atmosphere is composed of about 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% other gases. nitrogen (n2): it is the most plentiful gas in the air.

Describe The Composition Of The Earth S Atmosphere Earth Reminder 0.033 0.036% carbon dioxide (co 2) together with water vapor is responsible for greenhouse effect. the atmosphere is also composed of water, ice and dust particles (aerosols). aerosols are found most frequently near their sources, for example, cities, sea coasts or active volcanoes. however, particles can be carried a great distance. One of the main components of earth’s interdependent physical systems is the atmosphere. an atmosphere is made of the layers of gases surrounding a planet or other celestial body. composition: earth’s atmosphere is composed of about 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% other gases. nitrogen (n2): it is the most plentiful gas in the air.
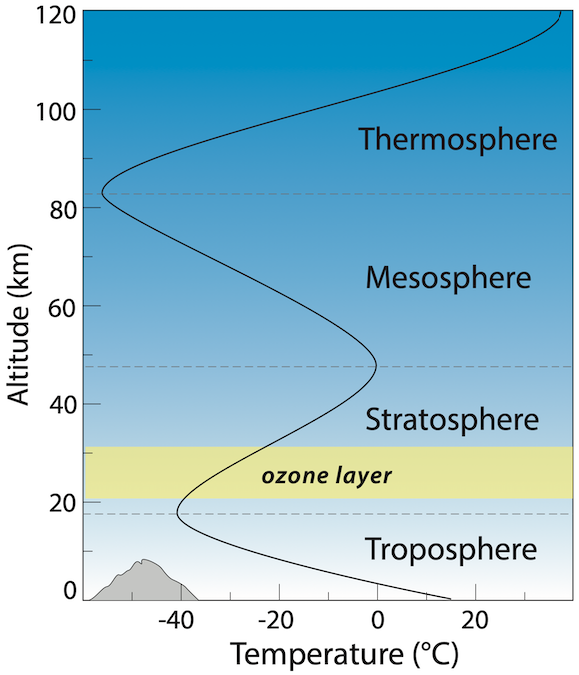
Composition Of Earth S Atmosphere Earth Science Visionlearning

Comments are closed.