Ecg Of Evolution Step By Step Of Stemi St Elevation Myocardial
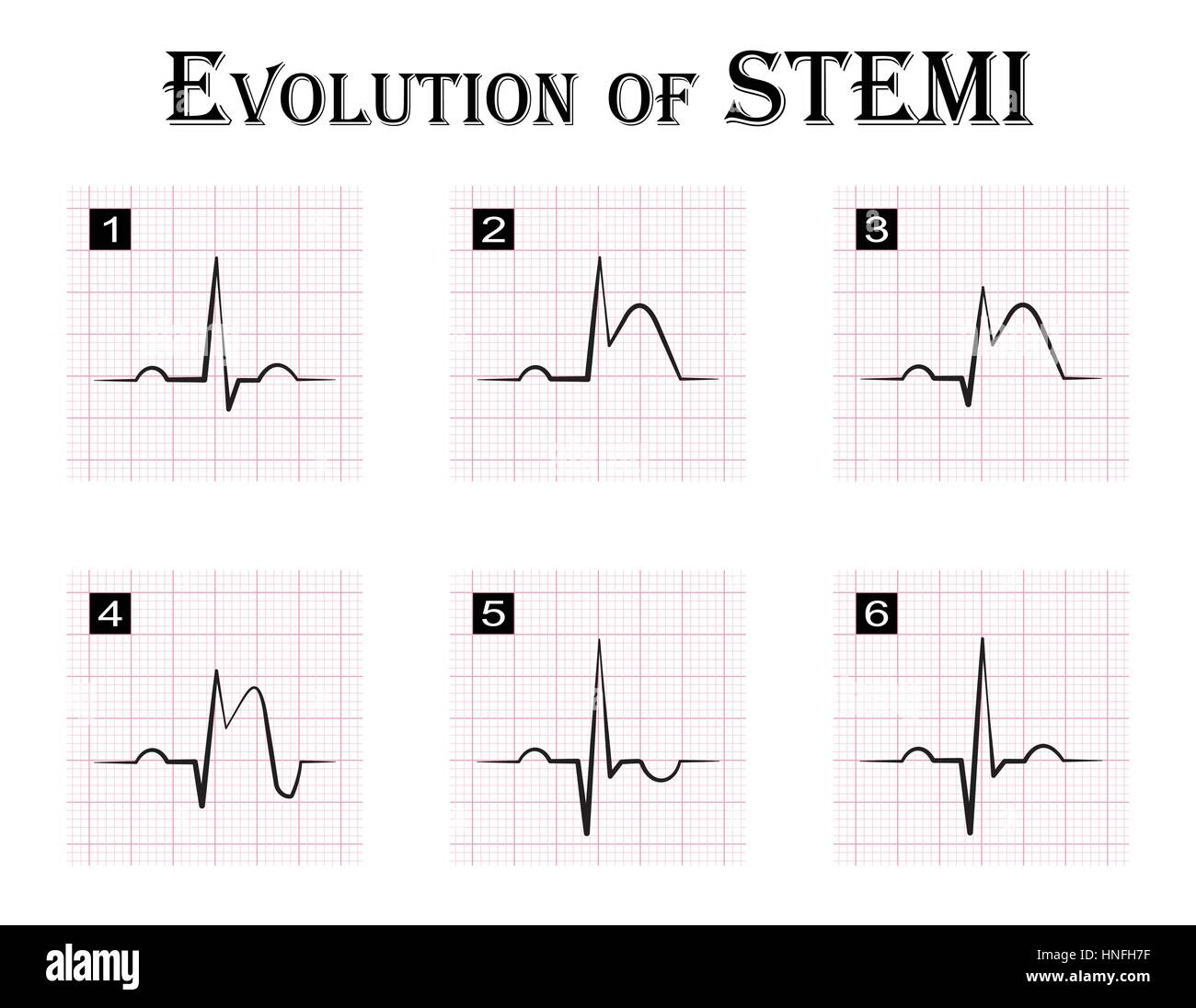
Ecg Of Evolution Step By Step Of Stemi St Elevation Myocardial An acute st elevation myocardial infarction (stemi) is a clinical event characterised by transmural myocardial ischaemia resulting in myocardial injury or necrosis. it is one of three types of acute coronary syndrome. the other forms include unstable angina and non st elevation myocardial infarction (nstemi). the diagnosis of stemi requires the. Ecg (ekg) in acute stemi (st elevation myocardial infarction) the ecg is the key to diagnosing stemi. ecg criteria for stemi are not used in the presence of left bundle branch block or left ventricular hypertrophy (lvh) because these conditions cause secondary st t changes which may mask or simulate ischemic st t changes.
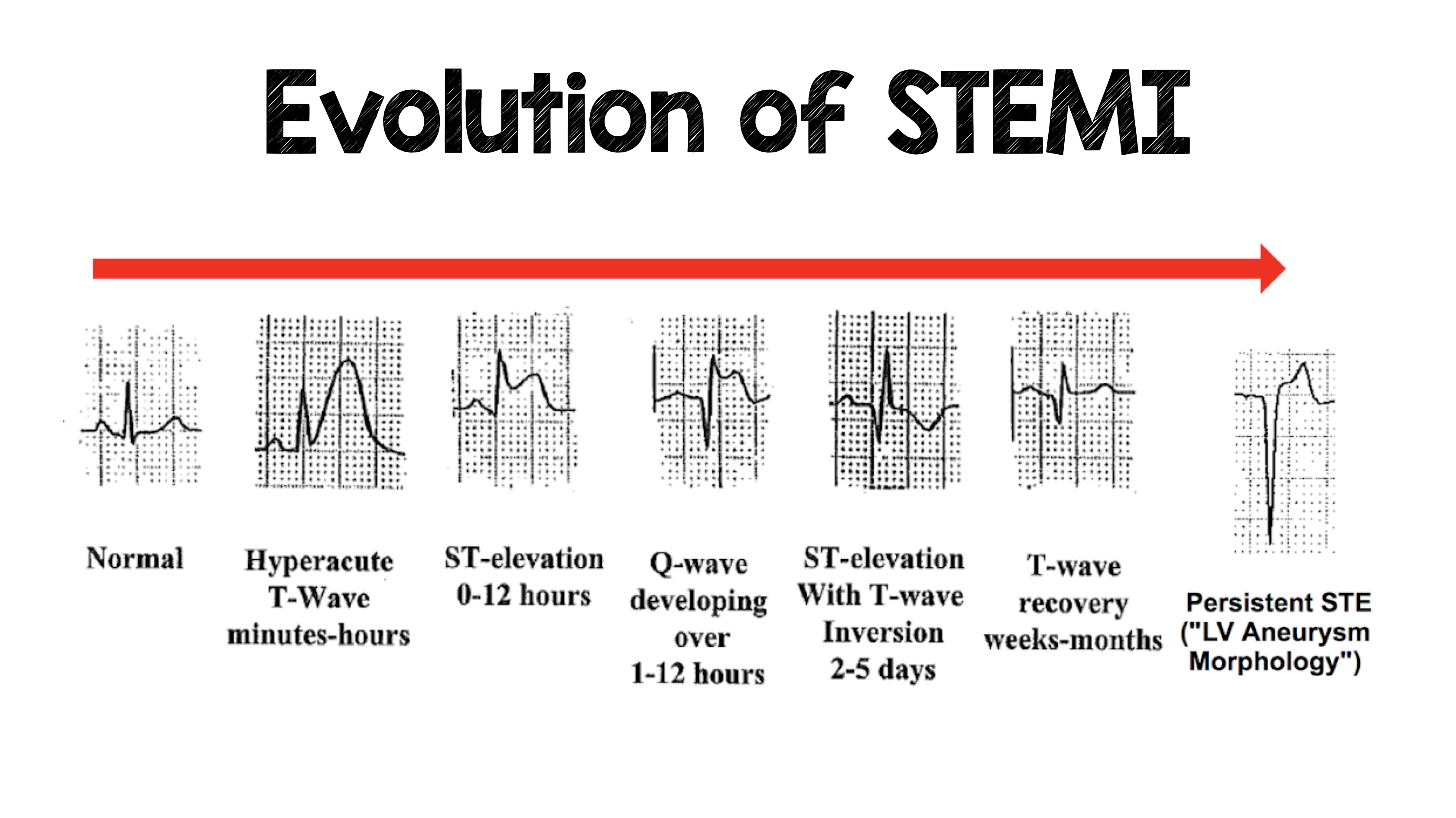
Ecg Of Evolution Step By Step Of Stemi St Elevation Myocardial Sexiz Pix Women consistently display less st segment elevation than men. the st segment elevations are less pronounced in the lateral chest leads, and rarely exceed 1 mm in leads v5–v6. the st segment has a concave appearance. the t wave apex is substantially higher than the j point. the greater the qrs amplitude, the greater the st segment elevation. A 12 lead ecg should be interpreted immediately (within 10 minutes) at first medical contact. ecg monitoring should start immediately and a defibrillator must be ready. consider connecting leads v7, v8 and v9 in patients with high suspicion of posterior acute myocardial infarction (e.g due to reciprocal st segment depressions in v1, v2, v3). It provides real time information about the heart’s electrical activity and identifies characteristic changes associated with myocardial ischemia. in stemi, the ecg typically shows st segment elevation of at least 1 mm (0.1 mv) in 2 contiguous leads, accompanied by t wave inversion or development of pathological q waves in the corresponding. Consideration of typical ekg patterns in stemi and stemi mimickers. stemi –ekg criteria. •diagnostic elevation (in absence of lvh and lbbb) defined as: new st elevation at j point in at least 2 contiguous leads in leads v2 v3, men >2mm, women > 1.5mm in other chest leads or limb leads, > 1mm. alternative causes of st–t changes.
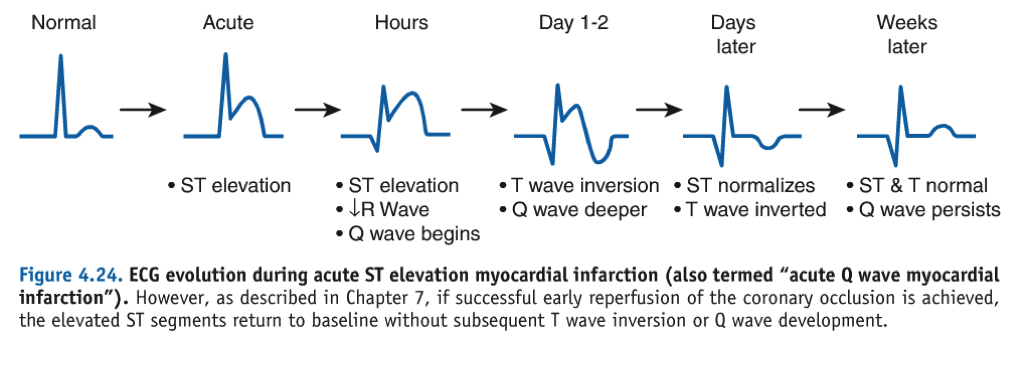
Acute Stemi Management Mnemonic Based Approach Epomedicine It provides real time information about the heart’s electrical activity and identifies characteristic changes associated with myocardial ischemia. in stemi, the ecg typically shows st segment elevation of at least 1 mm (0.1 mv) in 2 contiguous leads, accompanied by t wave inversion or development of pathological q waves in the corresponding. Consideration of typical ekg patterns in stemi and stemi mimickers. stemi –ekg criteria. •diagnostic elevation (in absence of lvh and lbbb) defined as: new st elevation at j point in at least 2 contiguous leads in leads v2 v3, men >2mm, women > 1.5mm in other chest leads or limb leads, > 1mm. alternative causes of st–t changes. The st segment is the flat, isoelectric section of the ecg between the end of the s wave (the j point) and the beginning of the t wave. the st segment represents the interval between ventricular depolarization and repolarization. the most important cause of st segment abnormality (elevation or depression) is myocardial ischaemia or infarction. Introduction. patients with severe and acute myocardial infarction (ie, st elevation myocardial infarction [stemi]) require rapid diagnosis and treatment to reduce the risk of death and permanent myocardial injury [1]. this topic provides an overview of stemi management from presentation to the period immediately after revascularization.

Comments are closed.