Ecology Levels Of Organization Powerpoint With Notes Vrogue Co

Ecology Levels Of Organization Powerpoint With Notes Vrogue Co Ecology: levels of organization. the ecological model of levels of organization being represented as circles within circles makes intuitive sense because each level contains and is contained by the next level. individuals make up populations populations make up communities communities make up ecosystems ecosystems make up the biosphere. Ecology is the scientific study of the interactions between organisms and their environment. it was coined in 1866 by ernst haeckel from the greek words "oikos" meaning house or environment, and "logos" meaning study. ecology studies the distribution and abundance of organisms and the interactions between organisms and their physical and.

Ecology Levels Of Organization Powerpoint With Notes Vrogue Co Atom. molecule. cell. tissue. organ. organ system. organism. population. community. ecosystem. Use this ecology mini bundle to introduce your ecology unit using differentiated vocabulary lessons and a creative drawing lesson as students create the levels of ecological organization. what's included in this 1 2 day mini bundle: • 15 slide fully editable powerpoint presentation with title slides, objectives, bell work and guided notes. Main idea 1: ecologists study environments at different levels of organization. ecology is the study of the interactions (relationships) among living things, and between living things and their surroundings. studying how life interacts within the biosphere. scientists used to study each organism separately. Biotic vs. abiotic factors levels of ecological organization: individual → population → community → ecosystem → biosphere, with clear definitions, illustrations, and examples for each level. effects of resource availability on organisms and populations. analyzing resource availability and its impact. total pages: 34 pages answer key.
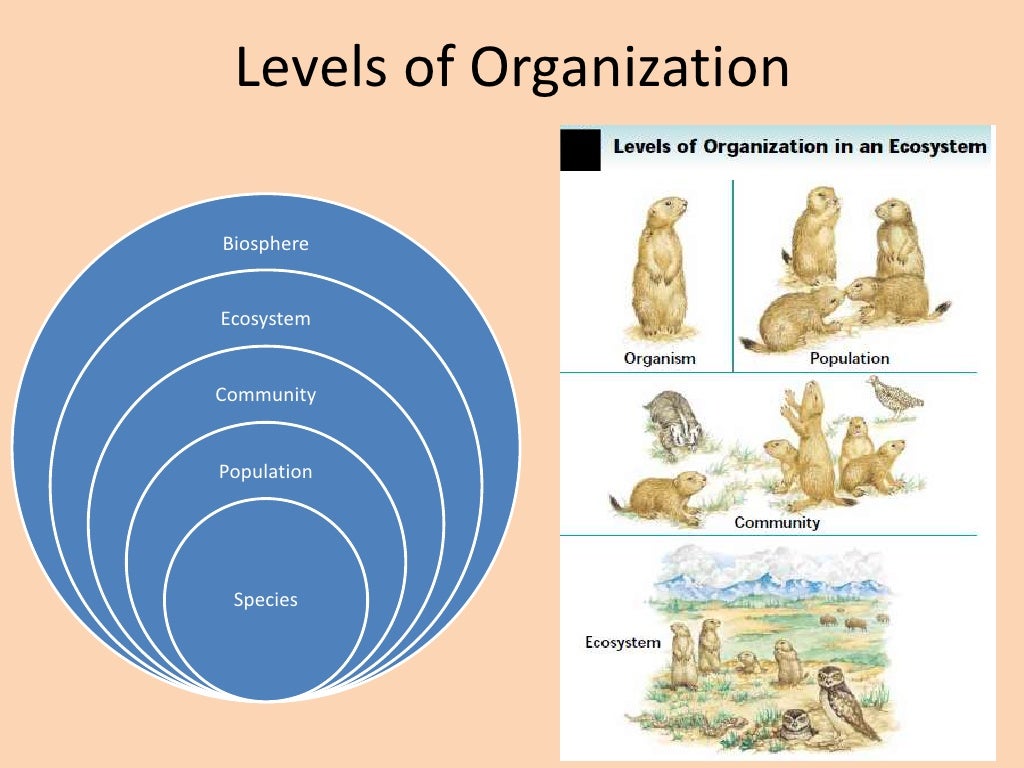
Ecology Levels Of Organization Powerpoint With Notes Vrogue Co Main idea 1: ecologists study environments at different levels of organization. ecology is the study of the interactions (relationships) among living things, and between living things and their surroundings. studying how life interacts within the biosphere. scientists used to study each organism separately. Biotic vs. abiotic factors levels of ecological organization: individual → population → community → ecosystem → biosphere, with clear definitions, illustrations, and examples for each level. effects of resource availability on organisms and populations. analyzing resource availability and its impact. total pages: 34 pages answer key. A bundled homework package and detailed unit notes chronologically follow the powerpoint slideshow. areas of focus within the ecology interactions unit: levels of biological organization (ecology), parts of the biosphere, habitat, ecological niche, types of competition, competitive exclusion theory, animal interactions, food webs, predator prey. Levels of organization in biology. from the simplest to the most complex, the levels of organization in biology are: atoms, molecules, macromolecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, populations, communities, and the biosphere. eukaryotic cells (plants, animals, fungi) display all of these levels, while prokaryotic cells.

Ecology Levels Of Organization Powerpoint With Notes Vrogue Co A bundled homework package and detailed unit notes chronologically follow the powerpoint slideshow. areas of focus within the ecology interactions unit: levels of biological organization (ecology), parts of the biosphere, habitat, ecological niche, types of competition, competitive exclusion theory, animal interactions, food webs, predator prey. Levels of organization in biology. from the simplest to the most complex, the levels of organization in biology are: atoms, molecules, macromolecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, populations, communities, and the biosphere. eukaryotic cells (plants, animals, fungi) display all of these levels, while prokaryotic cells.

Comments are closed.