Ectopic Pregnancy Radiology Key
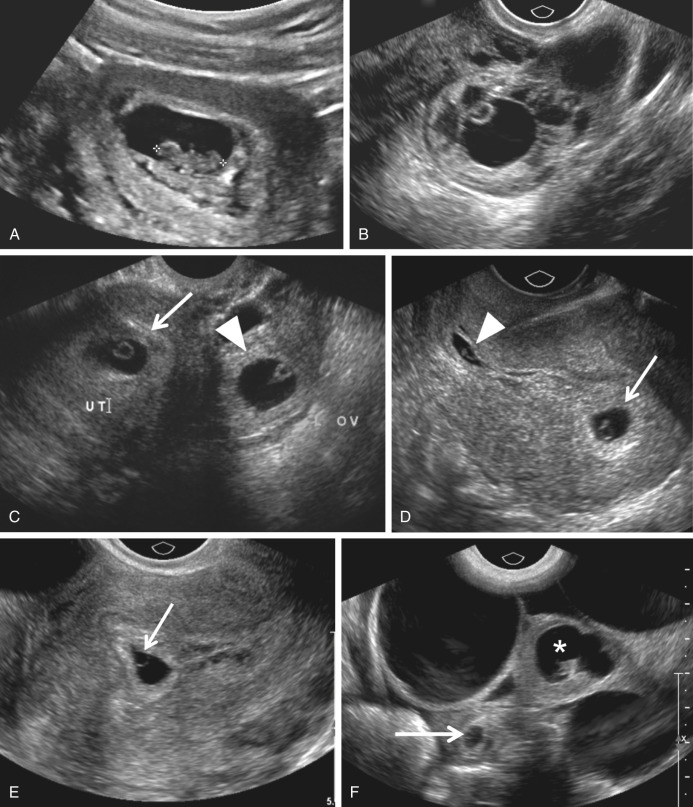
Ectopic Pregnancy Radiology Key Ectopic pregnancy in the ampullary portion of a fallopian tube. the patient presented with vaginal bleeding and a positive serum human chorionic gonadotropin (hcg). a, transvaginal longitudinal scan of the ampullary portion of the fallopian tube shows that it is surrounded by free pelvic fluid and contains a gestational sac with a yolk sac. Ectopic pregnancy. ectopic pregnancy (ep) represents an important cause of acute pelvic pain in women of reproductive age. the incidence of ep has increased more than threefold since the 1970s, likely the result of a combination of factors, including an increase in the number of patients with risk factors for ep but also earlier detection and.
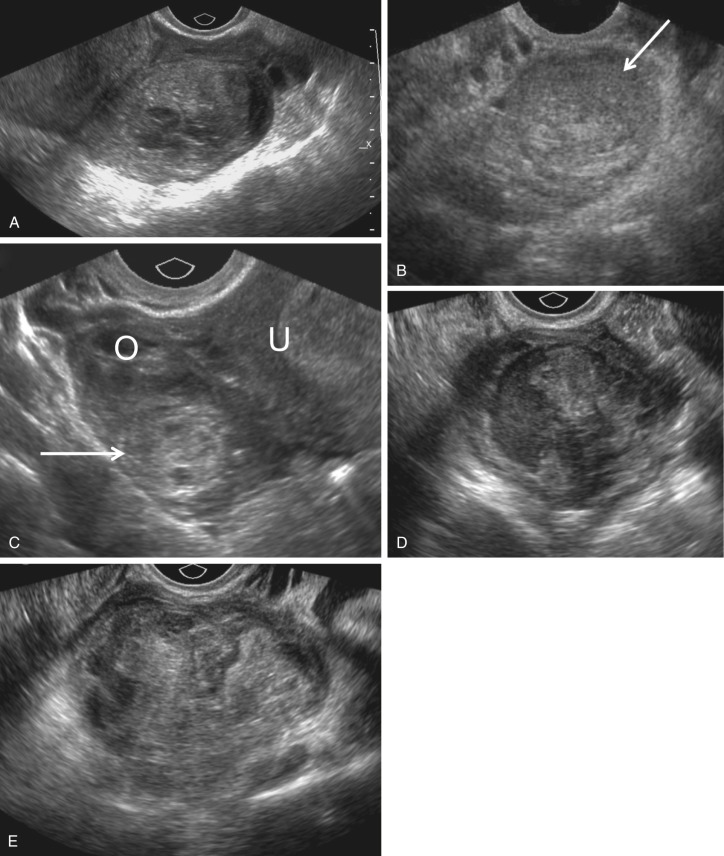
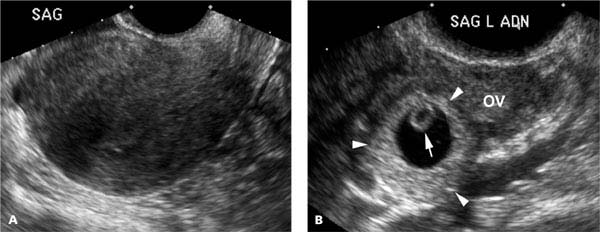
Ectopic Pregnancy Radiology Key Ectopic pregnancy. ectopic pregnancy with an extrauterine gestational sac containing a live embryo. a: transvaginal view of the uterus and left adnexa demonstrates a gestational sac (calipers) containing an embryo (arrow), located between the uterus (ut) and left ovary (ov). b: the embryo (arrow) has cardiac activity, at a rate of 150 beats per. Ectopic pregnancy accounts for approximately 2% of all pregnancies and is the most common cause of pregnancy related mortality in the first trimester. initial evaluation consists of hormonal assays and pelvic ultrasonography (us). a history of pelvic pain along with an abnormal β human chorionic gonadotropin level should trigger an evaluation for an ectopic pregnancy. the fallopian tube is. Ectopic pregnancy is a diagnosis that is quite challenging to make. it has been estimated that 40% of ectopic pregnancies go undiagnosed on initial presentation.[1] ectopic pregnancy is also a very difficult condition to identify based on history and physical, with both the history and physical examination features being neither sensitive nor specific for the diagnosis. data suggests that even. Rarely the urinary and or serum b hcg will be negative despite an ectopic pregnancy 13. serum progesterone levels are generally lower in a non viable (including ectopic) pregnancy 6; progesterone of 5 ng ml or less is strongly associated with pregnancy failure, whereas in a viable pregnancy, progesterone is usually 20 ng ml or more 5. clearly.
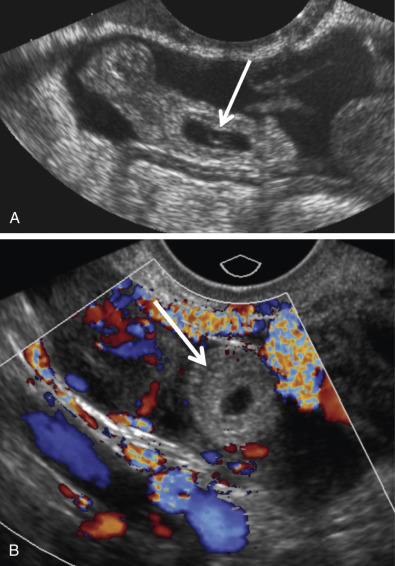
Ectopic Pregnancy Radiology Key Ectopic pregnancy is a diagnosis that is quite challenging to make. it has been estimated that 40% of ectopic pregnancies go undiagnosed on initial presentation.[1] ectopic pregnancy is also a very difficult condition to identify based on history and physical, with both the history and physical examination features being neither sensitive nor specific for the diagnosis. data suggests that even. Rarely the urinary and or serum b hcg will be negative despite an ectopic pregnancy 13. serum progesterone levels are generally lower in a non viable (including ectopic) pregnancy 6; progesterone of 5 ng ml or less is strongly associated with pregnancy failure, whereas in a viable pregnancy, progesterone is usually 20 ng ml or more 5. clearly. Ectopic pregnancy (ep) is a term used to describe any pregnancy which does not implant into the uterine cavity. there are several types of eps: tubal, interstitial, ovarian, abdominal, heterotopic, cervical, and cesarean scar. ectopic pregnancies can acutely rupture and are the number one cause of maternal death in the first trimester of pregnancy. therefore, prompt recognition and accurate. Ectopic pregnancy. deborah levine. author affiliations. from the department of radiology, beth israel deaconess medical center, 330 brookline ave, boston, ma 02215. received june 14, 2006; revision requested august 17; revision received august 28; accepted september 28; final review by the author, may 17, 2007.
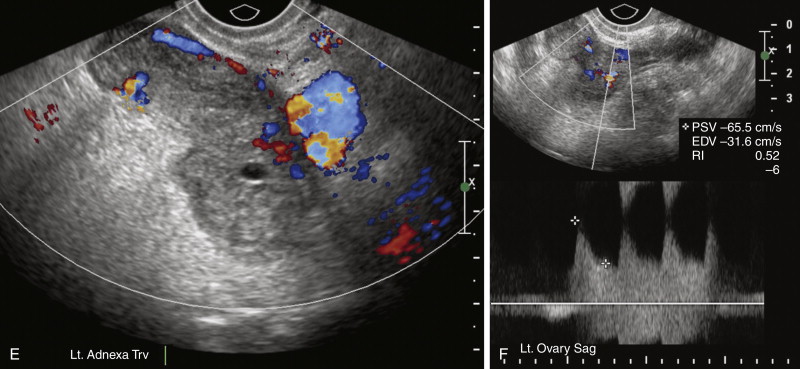
Ectopic Pregnancy Radiology Key Ectopic pregnancy (ep) is a term used to describe any pregnancy which does not implant into the uterine cavity. there are several types of eps: tubal, interstitial, ovarian, abdominal, heterotopic, cervical, and cesarean scar. ectopic pregnancies can acutely rupture and are the number one cause of maternal death in the first trimester of pregnancy. therefore, prompt recognition and accurate. Ectopic pregnancy. deborah levine. author affiliations. from the department of radiology, beth israel deaconess medical center, 330 brookline ave, boston, ma 02215. received june 14, 2006; revision requested august 17; revision received august 28; accepted september 28; final review by the author, may 17, 2007.
Ectopic Pregnancy Radiology Key

Comments are closed.