Ectothermic Vs Endothermic Cold Blooded Vs Warm Blooded Animals

Ectothermic Vs Endothermic Cold Blooded Vs Warm Blooded Animals The temperature of cold blooded or ectothermic animals varies with the environment, while warm blooded or endothermic animals maintain a relatively stable temperature. the animal kingdom falls into two categories based on how species regulate their body temperature: ectothermic and endothermic. this distinction plays a crucial role in how. Ectotherms are colloquially referred to as “cold blooded” even though their body temperatures often stay within the same temperature ranges as warm blooded animals. ectotherm an ectotherm, from the greek (ektós) “outside” and (thermós) “hot,” is an organism in which internal physiological sources of heat are of relatively small or.
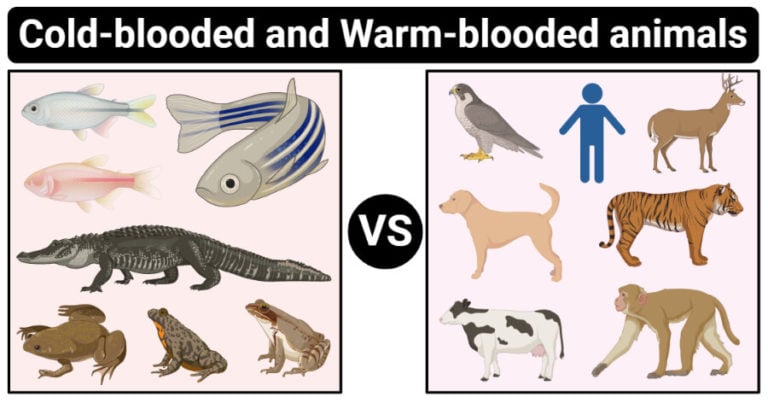
Cold Blooded Vs Warm Blooded Animals 16 Differences Examples Endothermic animals (endotherms) have an almost constantly warm body temperature, no matter how hot or cold the air temperature is. they can control their body temperature by keeping warm or cooling down. they can control the inside heat of their bodies. in cold weather they can keep warm, and in hot weather they keep cool. mammals are endotherms. For example, warm blooded mammals often maintain an internal body temperature between 97 °f to 103 °f, and birds have a slightly higher average body temperature closer to 105 °f. cold blooded animals do not have the means to keep a constant body temperature, so their body temperature is essentially controlled by their environment. The downside is that warm blooded organisms have to use a large amount of energy obtained from food for heat. warm blooded animals, therefore, consume a relatively large amount of food (usually up to five to ten times larger) than cold blooded animals. in that respect, warm blooded animals are comparable to gas guzzling and energy inefficient. Warm blooded. warm blooded is an informal term referring to animal species whose bodies maintain a temperature higher than that of their environment. in particular, homeothermic species (including birds and mammals) maintain a stable body temperature by regulating metabolic processes. other species have various degrees of thermoregulation.

Difference Between Cold Blooded And Warm Blooded Animals в The downside is that warm blooded organisms have to use a large amount of energy obtained from food for heat. warm blooded animals, therefore, consume a relatively large amount of food (usually up to five to ten times larger) than cold blooded animals. in that respect, warm blooded animals are comparable to gas guzzling and energy inefficient. Warm blooded. warm blooded is an informal term referring to animal species whose bodies maintain a temperature higher than that of their environment. in particular, homeothermic species (including birds and mammals) maintain a stable body temperature by regulating metabolic processes. other species have various degrees of thermoregulation. Ectotherms, also known as "cold blooded" animals, rely on external sources of heat to warm their bodies, while endotherms, or "warm blooded" animals, generate their own body heat internally. this fundamental difference in thermoregulation has significant implications for various aspects of an animal's physiology, behavior, and ecological niche. Glossary. endotherm: an organism that can control its own body temperature (also called warm blooded) ectotherm: an organism that depends on its surroundings to control its body temperature (also called cold blooded) metabolism: all the chemical reactions that take place in an organism’s body.
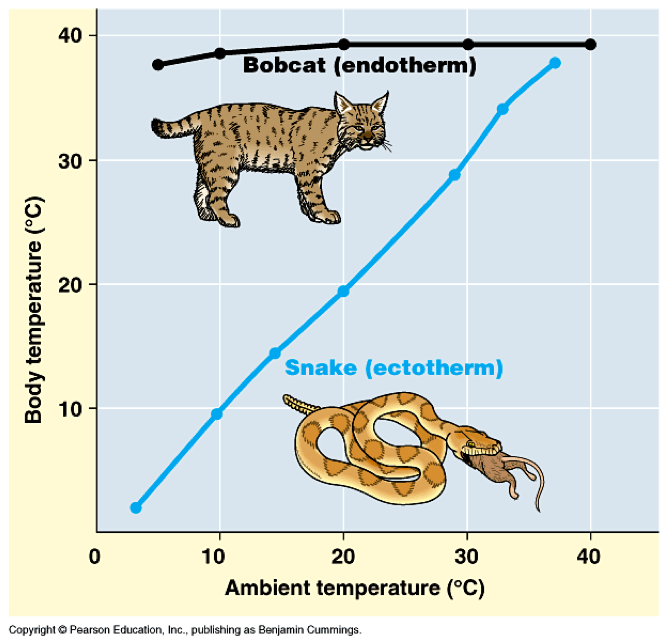
Class Reptilia The Biology Classroom Ectotherms, also known as "cold blooded" animals, rely on external sources of heat to warm their bodies, while endotherms, or "warm blooded" animals, generate their own body heat internally. this fundamental difference in thermoregulation has significant implications for various aspects of an animal's physiology, behavior, and ecological niche. Glossary. endotherm: an organism that can control its own body temperature (also called warm blooded) ectotherm: an organism that depends on its surroundings to control its body temperature (also called cold blooded) metabolism: all the chemical reactions that take place in an organism’s body.
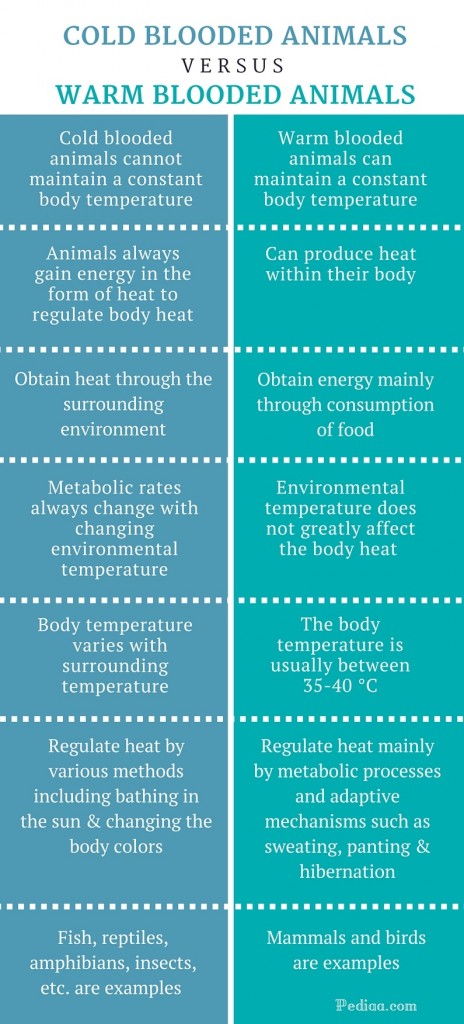
Difference Between Cold Blooded And Warm Blooded Animals C

Comments are closed.