Electric Motor Windings Comparison
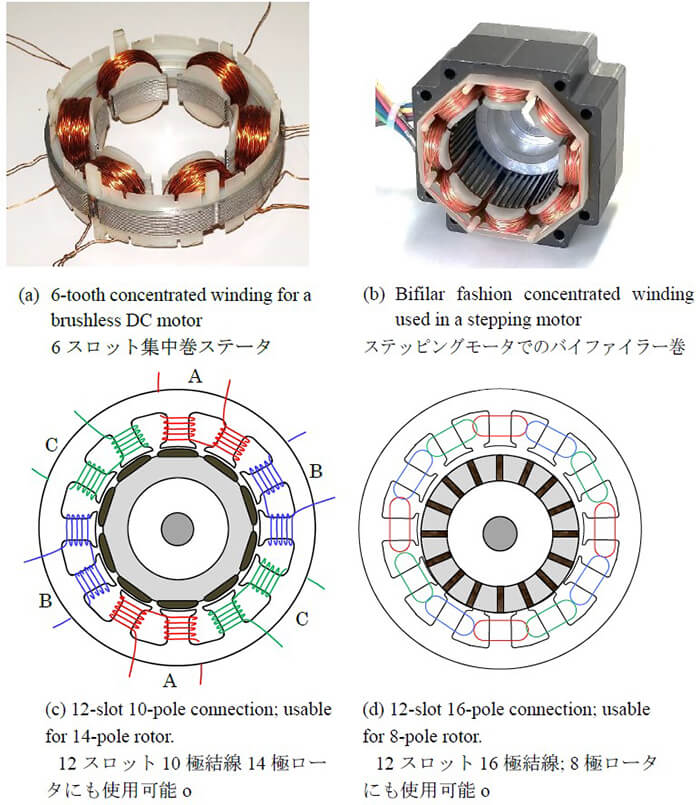
Electric Motor Windings Comparison 50 Off Windings for electric motors can be divided into concentrated winding and distributed winding. in the case of distributed winding, the winding is always wound over at least two stator teeth. in the case of concentrated winding, on the other hand, only one stator tooth is wound. both types of winding. Aluminium has more resistivity than copper (aluminium's resistivity is 1.6 times higher than that of copper). this means the aluminum winding size needs to be increased to accommodate and offer the same conductance. should any repairs need to be carried out on aluminium windings, it may prove more difficult as it can’t be soldered.
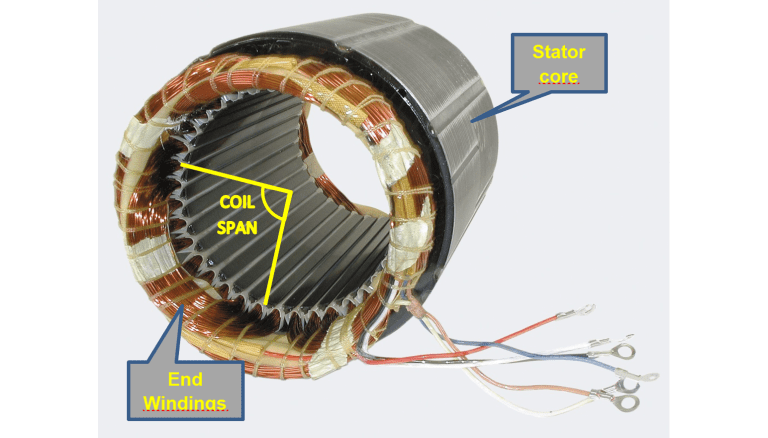
Motor Windings What Are The Differences Quantum Controls Rotor – a moving or rotating part. stator – a static or stationary part that cannot move or rotate. air gap – a small space between the stator and rotor of the electric motor. motor windings – coils of copper or aluminum wires act as electromagnets. an electric motor receives electrical energy from an external source of electricity and. There are two types of windings for electric motors. in this video i will show you the advantages and the disadvantages of the two types of windings. winding. The importance of motor winding in electric vehicles. hairpin motor winding. performance comparison. when it comes to performance, both round wire and hairpin motor winding have their. The connections required for high voltage wiring of a wye wound motor. in this wiring setup, there are 4 windings in series between any two line leads. compare this to the low voltage. from line 1 to line 2, the current only has one path through t1, t4, t7, t8, t5, and t2 back to line.

Comments are closed.