Electron Configuration Basic Introduction

Electron Configuration Basic Introduction Youtube This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into electron configuration. it contains plenty of practice problems including the electron conf. Keep going! check out the next lesson and practice what you’re learning: khanacademy.org science ap chemistry beta x2eef969c74e0d802:atomic struct.

Electronic Configurations Intro Chemistry Libretexts In this case, 2 2 6 2 6 2 10 6 2 1= 39 and z=39, so the answer is correct. a slightly more complicated example is the electron configuration of bismuth (symbolized bi, with z = 83). the periodic table gives the following electron configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p65s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f14 5d10 6p3. The electron configurations of a few elements are provided with illustrations in this subsection. electron configuration of hydrogen. the atomic number of hydrogen is 1. therefore, a hydrogen atom contains 1 electron, which will be placed in the s subshell of the first shell orbit. the electron configuration of hydrogen is 1s 1, as illustrated. Electron configuration. in atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. [1] for example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6, meaning that the 1s, 2s, and 2p subshells are occupied by. The electron configuration for phosphorus is 1s 2 2s 2 2p6 3 s2 3p3 and the orbital diagram is drawn below. 1.4: electron configurations is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. the electron configuration of an atom indicates the number of valence electrons. valence electrons determine the unique.

Orbital Diagrams And Electron Configuration Basic Introduction Electron configuration. in atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. [1] for example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6, meaning that the 1s, 2s, and 2p subshells are occupied by. The electron configuration for phosphorus is 1s 2 2s 2 2p6 3 s2 3p3 and the orbital diagram is drawn below. 1.4: electron configurations is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. the electron configuration of an atom indicates the number of valence electrons. valence electrons determine the unique. Because lithium’s final electron goes into the 2s subshell, we write the electron configuration of a lithium atom as 1s 2 2s 1. the shell diagram for a lithium atom (figure \(\pageindex{1}\)). the shell closest to the nucleus (first shell) has 2 dots representing the 2 electrons in 1 s , while the outermost shell ( 2 s ) has 1 electron. The element sodium has the electron configuration 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1. the outer energy level is n = 3 and there is one valence electron. the attraction between this lone valence electron and the nucleus with 11 protons is shielded by the other 10 core electrons. the electron configuration for cesium is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6.
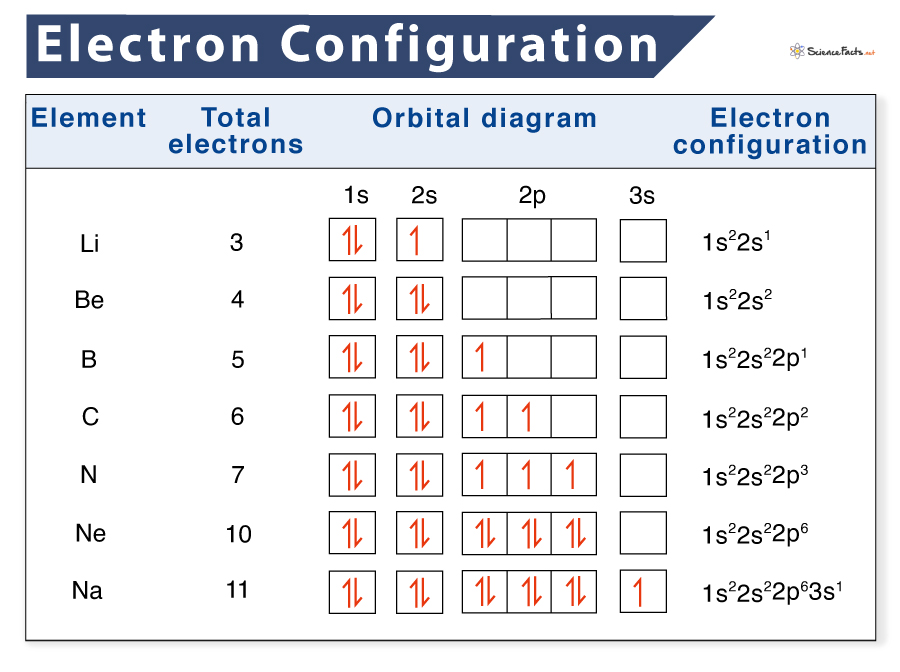
Electron Configuration Definition Examples Chart And Diagram Because lithium’s final electron goes into the 2s subshell, we write the electron configuration of a lithium atom as 1s 2 2s 1. the shell diagram for a lithium atom (figure \(\pageindex{1}\)). the shell closest to the nucleus (first shell) has 2 dots representing the 2 electrons in 1 s , while the outermost shell ( 2 s ) has 1 electron. The element sodium has the electron configuration 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1. the outer energy level is n = 3 and there is one valence electron. the attraction between this lone valence electron and the nucleus with 11 protons is shielded by the other 10 core electrons. the electron configuration for cesium is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6.

List Of Electron Configurations Of Elements

Comments are closed.