Energy Transfer In The Earths Atmosphere
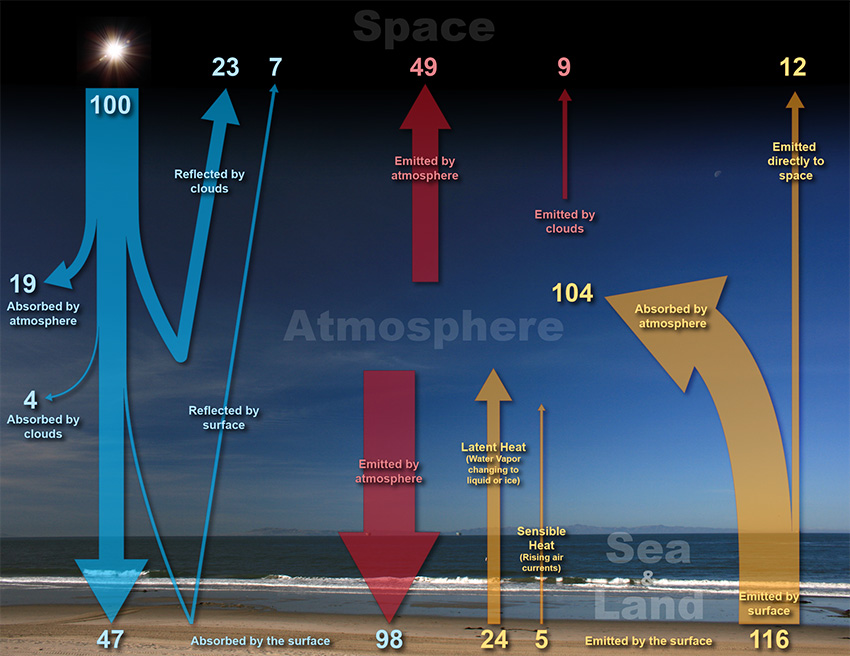
The Earth Atmosphere Energy Balance National Oceanic And Atmospheric Procedure. explain to students that these animations show how earth’s solar radiation is reflected or absorbed in earth’s atmosphere. clarify that the sun is earth’s heat source and energy from the sun travels to earth through electromagnetic waves to earth’s surface. that energy gives off heat that is then transferred into other forms. Convection. convection is the transfer of heat energy in a fluid. in the kitchen, this type of heating is most commonly seen as the circulation that develops in a boiling liquid. air in the atmosphere acts as a fluid. the sun's radiation strikes the earth's surface, thus warming it. as the surface's temperature rises due to conduction, heat.

Heat Transfer In The Atmosphere Physical Geography Heat transfer by movement of heated materials is called convection. heat that radiates from the ground warms the air, which rises and initiates convection cells in the atmosphere. figure 16.4.1 16.4. 1: the transfer of heat energy through earth's atmosphere by radiation, conduction and convection. (noaa) image is in the public domain. The earth atmosphere energy balance is achieved as the energy received from the sun balances the energy lost by the earth back into space. in this way, the earth maintains a stable average temperature and therefore a stable climate. using 100 units of energy from the sun as a baseline the energy balance is as follows: at the top of the. Conduction in the atmosphere. conduction, radiation, and convection all play a role in moving heat between earth's surface and the atmosphere. since air is a poor conductor, most energy transfer by conduction occurs right near earth's surface. conduction directly affects air temperature only a few centimeters into the atmosphere. Motions in the atmosphere. the global energy budget has been studied in two basic ways: by examining the energy flux through the earth atmosphere system (see above—examples of pioneering efforts are houghton, 1954; budyko and kondratyev. 1964) and by efforts to determine the use of this energy and its transformation between potential and kinetic forms (early efforts include margules, 1903.
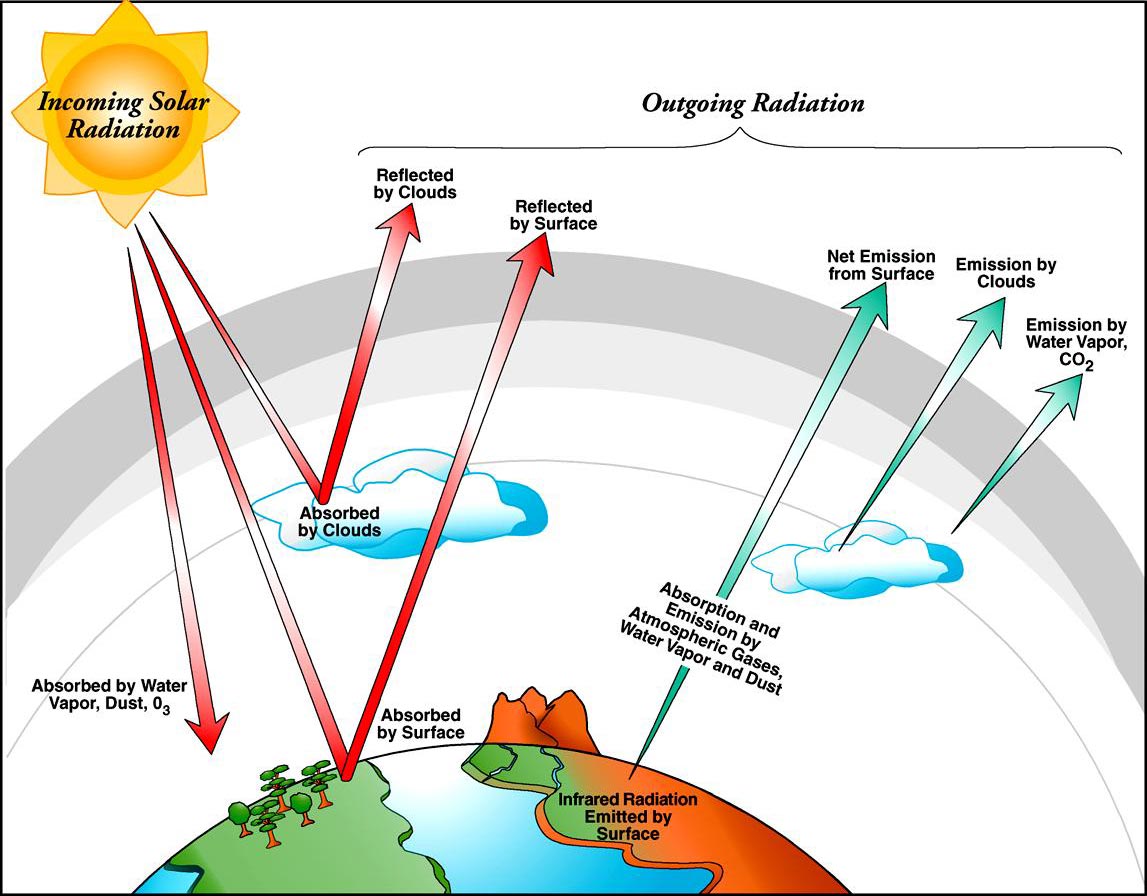
Science Made Simple What Is Atmospheric Radiation Conduction in the atmosphere. conduction, radiation, and convection all play a role in moving heat between earth's surface and the atmosphere. since air is a poor conductor, most energy transfer by conduction occurs right near earth's surface. conduction directly affects air temperature only a few centimeters into the atmosphere. Motions in the atmosphere. the global energy budget has been studied in two basic ways: by examining the energy flux through the earth atmosphere system (see above—examples of pioneering efforts are houghton, 1954; budyko and kondratyev. 1964) and by efforts to determine the use of this energy and its transformation between potential and kinetic forms (early efforts include margules, 1903. The earth atmosphere system 1.1 introduction the earth’s atmosphere is the gaseous envelope surrounding the planet. like other planetary atmospheres, it figures centrally in transfers of energy between the sun, the earth, and deep space. it also figures in transfers of energy from one region of the globe to another. The greenhouse effect. heat moves in the atmosphere the same way it moves through the solid earth (plate tectonics chapter) or another medium. what follows is a review of the way heat flows and is transferred, but applied to the atmosphere. radiation is the transfer of energy between two objects by electromagnetic waves.

Conduction Ucar Center For Science Education The earth atmosphere system 1.1 introduction the earth’s atmosphere is the gaseous envelope surrounding the planet. like other planetary atmospheres, it figures centrally in transfers of energy between the sun, the earth, and deep space. it also figures in transfers of energy from one region of the globe to another. The greenhouse effect. heat moves in the atmosphere the same way it moves through the solid earth (plate tectonics chapter) or another medium. what follows is a review of the way heat flows and is transferred, but applied to the atmosphere. radiation is the transfer of energy between two objects by electromagnetic waves.

Comments are closed.