Euler Equation Jacobian At Barbara Wilson Blog
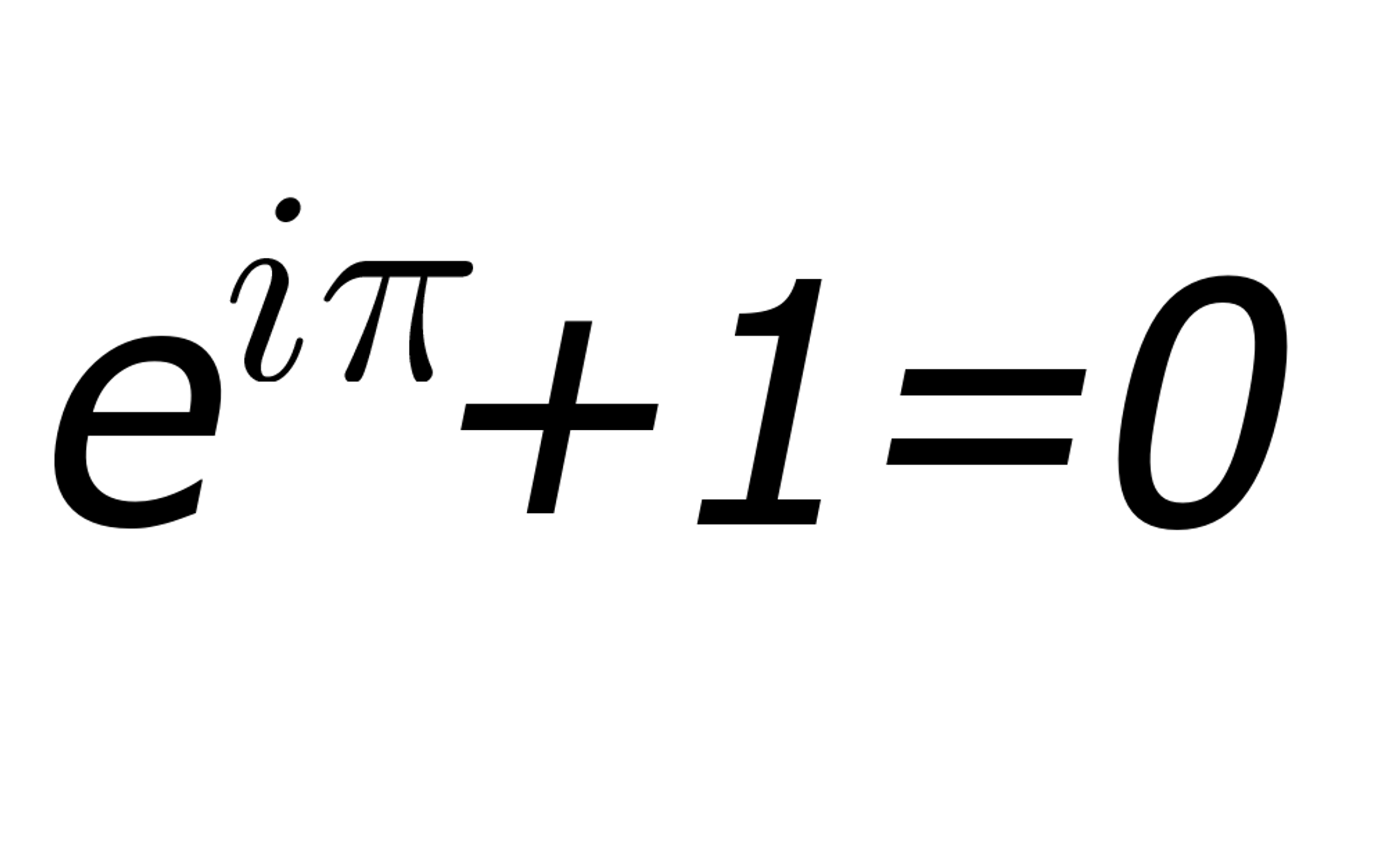
Euler Equation Jacobian At Barbara Wilson Blog Presumably you need the jacobian to solve a linearized approximation of the euler equations. the independent variables are q1 = ρ, q2 = ρu, and q3 = ρe. first, express pressure p and all of the components of f(q) in terms of the independent variables. rearranging the equation of state, the pressure is given by. Now we multiply the euler equations with proper combinations of these constants as follows: this is equal to: where: in particular, if , then. so the dimensionless euler equations look exactly the same as the original ones, we just need to rescale all the quantities using the relations above. 7.3.3.
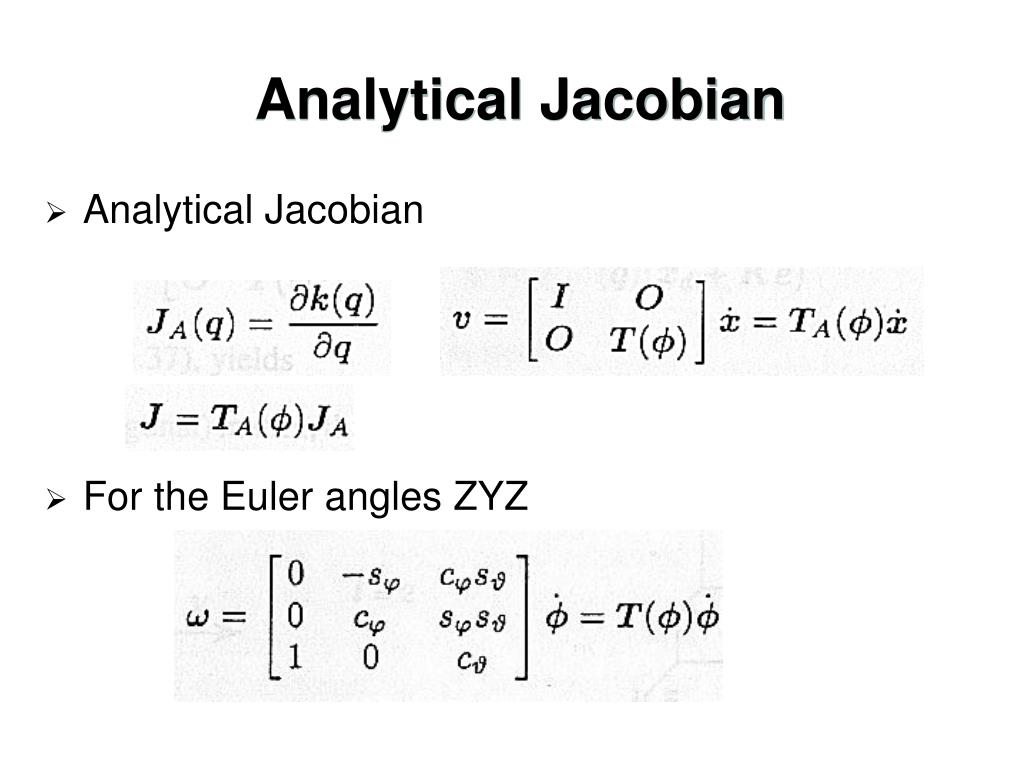
Euler Equation Jacobian At Barbara Wilson Blog 1.2 analysis of the equations of gas dynamics: the jacobian ma trices the euler equations for the three dimensional ow of an inviscid gas can be written in integral form, using the summation convention, as d dt z wdv z d f inds= 0 where is the domain, d its boundary, !n the normal to the boundary, and dv and ds are the volume and area elements. Simply replaced scalar u with vector \(\mathbf{f}\). in all our schemes, similarly replace the scalar derivative:. Now if you let , the last equation reduces to a newton iteration for the steady state euler equations: because of this connection, you see that the jacobian matrix should be theoretically exact to reach the steady state in a minimum amount of iterations (hopefully quadratically). however, this last system is hard to solve numerically. For smooth solutions, the entropy equation implies that p = const along. a particle path. for 1 d problems, if the in ow is uniform in time then the entropy is constant everywhere. we can put the euler equations in the form. we have or. @x @t @x @t a) (u a a) (u @u @u @p @p = 0. which implies that.
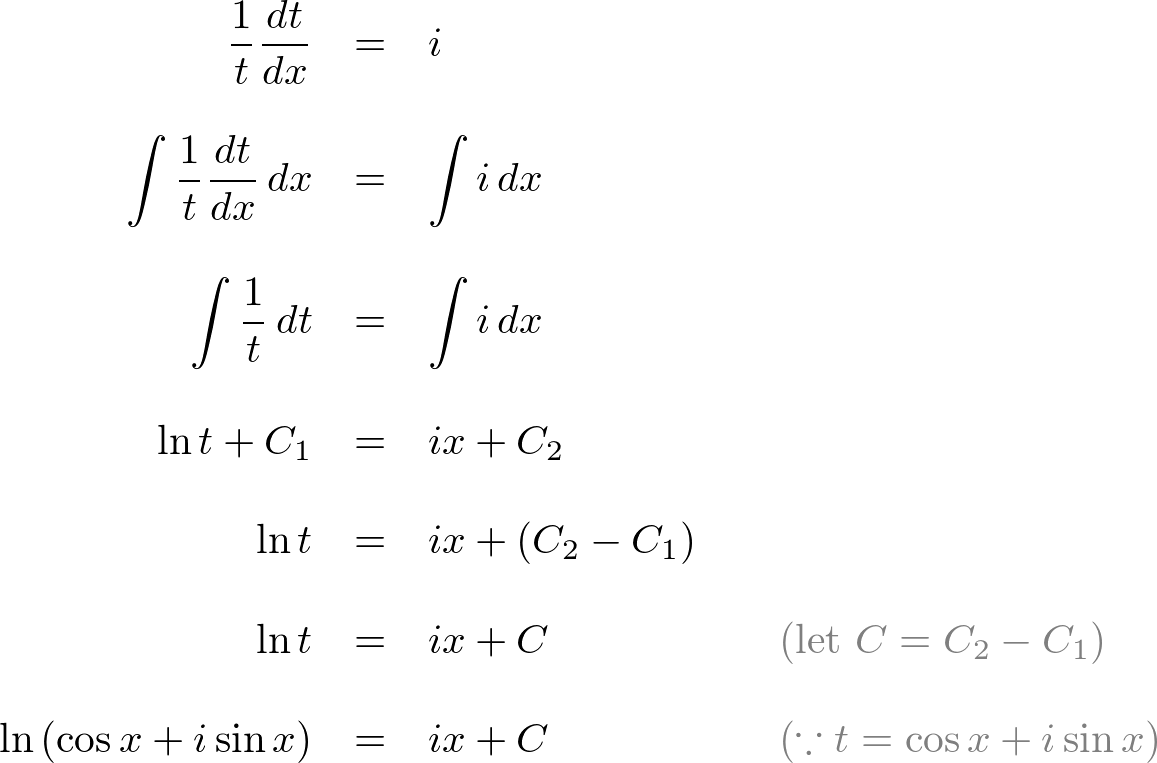
Euler Equation Jacobian At Barbara Wilson Blog Now if you let , the last equation reduces to a newton iteration for the steady state euler equations: because of this connection, you see that the jacobian matrix should be theoretically exact to reach the steady state in a minimum amount of iterations (hopefully quadratically). however, this last system is hard to solve numerically. For smooth solutions, the entropy equation implies that p = const along. a particle path. for 1 d problems, if the in ow is uniform in time then the entropy is constant everywhere. we can put the euler equations in the form. we have or. @x @t @x @t a) (u a a) (u @u @u @p @p = 0. which implies that. An attempt is made to remove, at least partially, the non local nature associated with the pressure term of the incompressible euler equations. we consider the dynamics of the jacobian matrix j ( t ) relating spatial and material coordinates in incompressible three dimensional euler equations. You can then plug this into the euler equations: ∂w ∂t → ∂w ∂q ∂q ∂t ∂f(w) ∂x = 0 ∂f(w) ∂x = 0 ∂ w ∂ t ∂ f (w) ∂ x = 0 → ∂ w ∂ q ∂ q ∂ t ∂ f (w) ∂ x = 0. where the fluxes are still expressed in terms of the conservative variables. if you wanted to derive governing equations for the primitives.
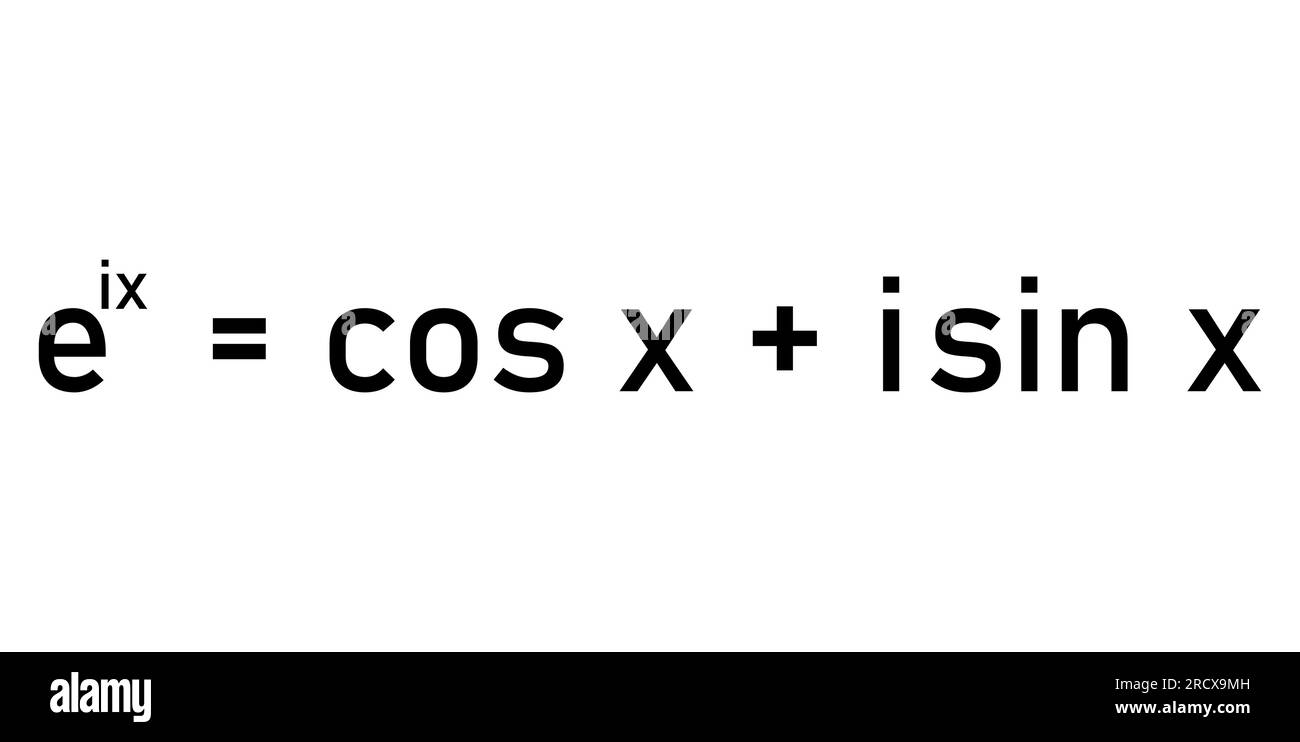
Euler Equation Jacobian At Barbara Wilson Blog An attempt is made to remove, at least partially, the non local nature associated with the pressure term of the incompressible euler equations. we consider the dynamics of the jacobian matrix j ( t ) relating spatial and material coordinates in incompressible three dimensional euler equations. You can then plug this into the euler equations: ∂w ∂t → ∂w ∂q ∂q ∂t ∂f(w) ∂x = 0 ∂f(w) ∂x = 0 ∂ w ∂ t ∂ f (w) ∂ x = 0 → ∂ w ∂ q ∂ q ∂ t ∂ f (w) ∂ x = 0. where the fluxes are still expressed in terms of the conservative variables. if you wanted to derive governing equations for the primitives.

Solved The I D Euler Equations Are Given By Partial Partial Chegg

Comments are closed.