Evolution And Changes
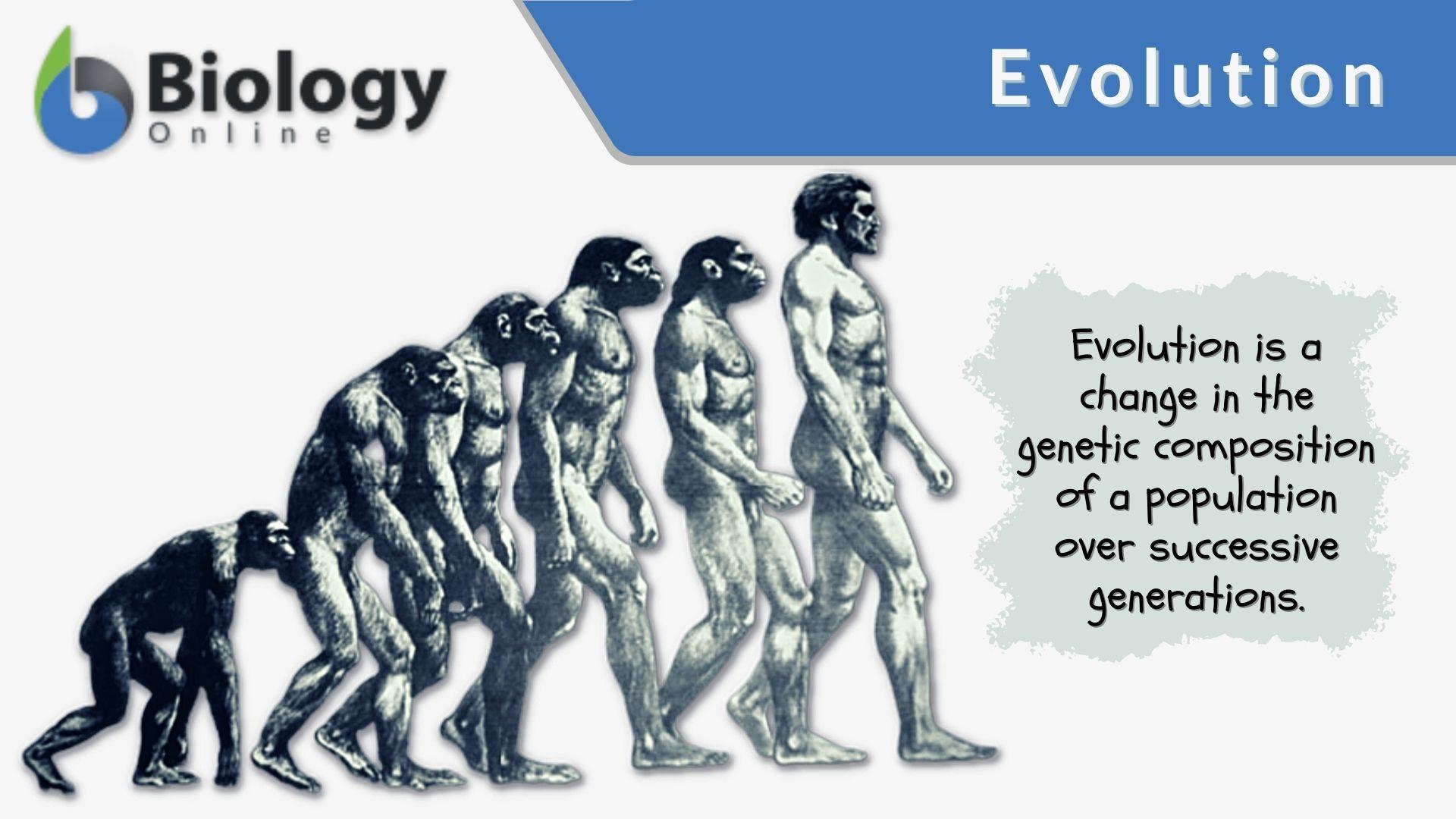
Evolution Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary Evolution is the change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. [1] [2] it occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more or less common within a population over successive generations. [3]. Evolution, theory in biology postulating that the various types of plants, animals, and other living things on earth have their origin in other preexisting types and that the distinguishable differences are due to modifications in successive generations. the theory of evolution is one of the fundamental keystones of modern biological theory.
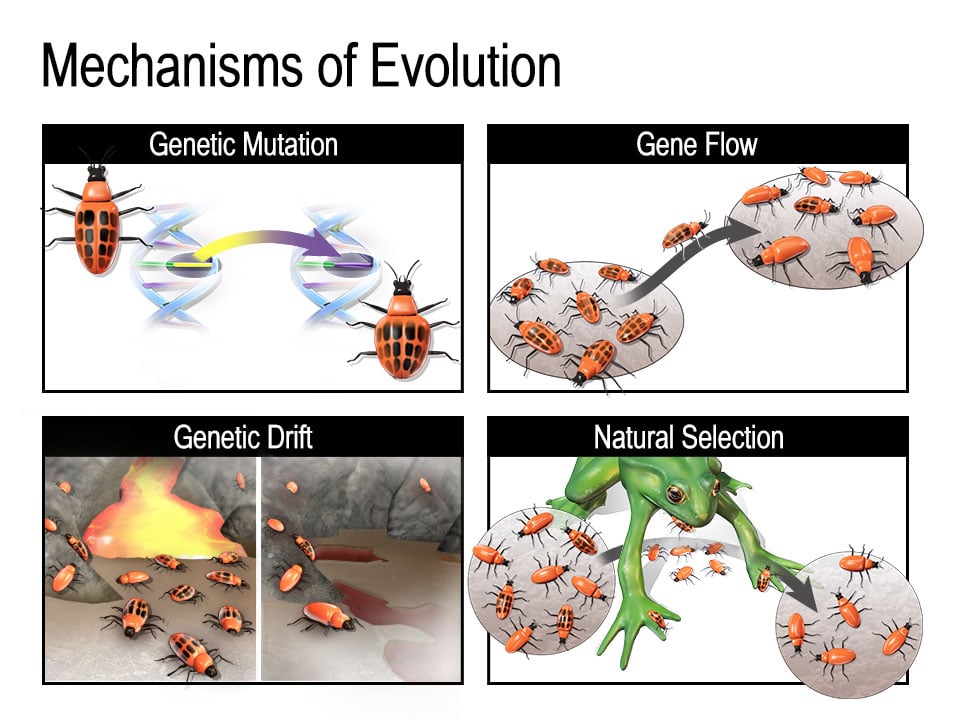
Mechanisms Of Evolution A theory is an idea about how something in nature works that has gone through rigorous testing through observations and experiments designed to prove the idea right or wrong. when it comes to the evolution of life, various philosophers and scientists, including an eighteenth century english doctor named erasmus darwin, proposed different. Evolution 101. an introduction to evolution: what is evolution and how does it work? the history of life: looking at the patterns – change over time and shared ancestors; mechanisms: the processes of evolution – selection, mutation, migration, and more; microevolution – evolution within a population; speciation – how new species arise. Through the process of descent with modification, this common ancestor gave rise to the diverse species that we see documented in the fossil record and around us today. evolution means that we’re all distant cousins: humans and oak trees, hummingbirds and whales. four seasons photo credit joisey showaa, illustration ucmp. you can learn lots. Evolution. evolution is a process that results in changes in the genetic material of a population over time. evolution reflects the adaptations of organisms to their changing environments and can.
Biology Human Evolution Stages Evolutionary Vector Image Through the process of descent with modification, this common ancestor gave rise to the diverse species that we see documented in the fossil record and around us today. evolution means that we’re all distant cousins: humans and oak trees, hummingbirds and whales. four seasons photo credit joisey showaa, illustration ucmp. you can learn lots. Evolution. evolution is a process that results in changes in the genetic material of a population over time. evolution reflects the adaptations of organisms to their changing environments and can. Human evolution, the process by which human beings developed on earth from now extinct primates. viewed zoologically, we humans are homo sapiens, a culture bearing upright walking species that lives on the ground and very likely first evolved in africa about 315,000 years ago. we are now the only living members of what many zoologists refer to. Evolution is a process that results in changes in the genetic content of a population over time. there are two general classes of evolutionary change: microevolution and macroevolution.

Comments are closed.