Extraction Of Phytochemicals From Cannabis Sativa Plant Physiology

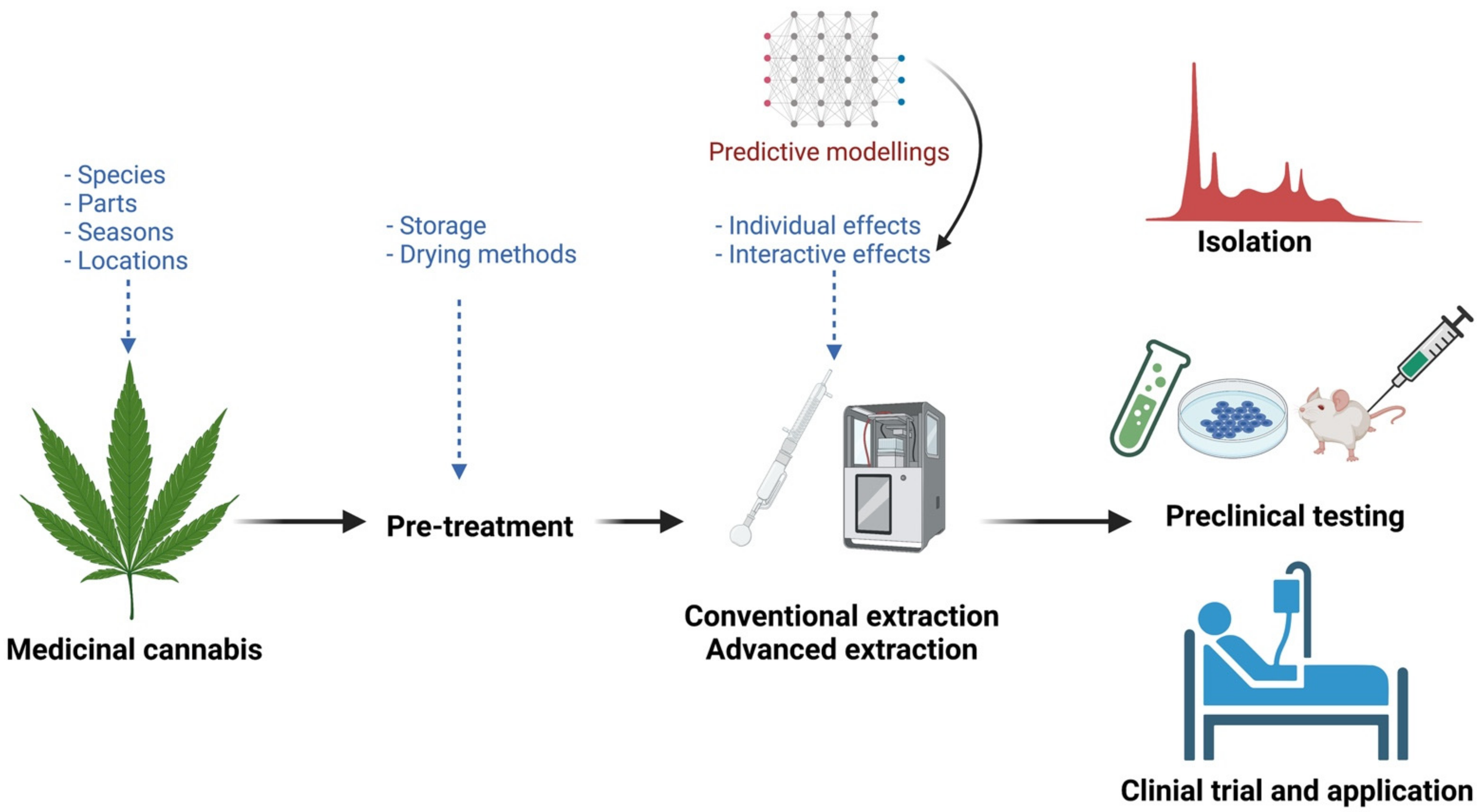
Extraction Of Phytochemicals From Cannabis Sativa Plant Physiology The focus of this narrative review was on cannabis sativa, initially where 93 papers were identified. papers on various drying and extraction methods specifically for cannabis sativa l. were included while those for using hemp as fiber and protein sources were excluded. overall, 12 papers about cannabis seed oil, hemp seed oil, or hemp plant. Secondly, using well preserved leaves, flowers, or fruits, the plant species is identified by a botanist at a herbarium. thirdly, plant parts of interest such as roots, stems, backs, leaves, or fruits are treated with an appropriate solvent to extract the phytochemicals. the extract is then concentrated by processes that aim to remove the solvent.

Separations Free Full Text Comparison Of The Efficiency Of Deep 4.1. conventional extraction of phytochemicals from cannabis. cannabis is chemically diverse, with cannabinoids, phenolic compounds, and terpenes being the most important phytochemicals . several conventional extraction techniques have been applied to extract phytochemicals from cannabis using various solvents [75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83]. This is a narrative review paper which focuses on critiquing drying and extraction methods of cannabis sativa l. plant. relevant keywords such as medicinal cannabis, extraction, solvent, cannabinoids, and terpenes have been searched in pubmed, embase, medline, google scholar, and cochrane library (wiley) databases. 1. introduction. cannabinoids and terpenoids are widely recognized as the primary therapeutic agents of hemp (cannabis sativa l.) inflorescence and extracts [1,2].these phytochemical families can be found in copious amounts in the trichrome structures of female hemp inflorescence, and in smaller quantities within the leaves []. Overall, multi faced extraction technologies have been used to extract phytochemicals in the whole c. sativa plant, underutilized plant parts, or residues. especially, the hempseed cake is a good resource for extracting flavonoids and polyphenols, and c. sativa inflorescences are a good resource for extracting cannabinoids, essential oils, and.
Molecules Free Full Text A Comprehensive Review On The Techniques 1. introduction. cannabinoids and terpenoids are widely recognized as the primary therapeutic agents of hemp (cannabis sativa l.) inflorescence and extracts [1,2].these phytochemical families can be found in copious amounts in the trichrome structures of female hemp inflorescence, and in smaller quantities within the leaves []. Overall, multi faced extraction technologies have been used to extract phytochemicals in the whole c. sativa plant, underutilized plant parts, or residues. especially, the hempseed cake is a good resource for extracting flavonoids and polyphenols, and c. sativa inflorescences are a good resource for extracting cannabinoids, essential oils, and. Biosynthetic pathway leading to phytocannabinoids. the biosynthesis of cannabinoids from c. sativa has only been recently elucidated. the precursors of cannabinoids actually originate from two distinct biosynthetic pathways: the polyketide pathway, giving rise to olivetolic acid (ola) and the plastidal 2 c methyl d erythritol 4 phosphate (mep) pathway, leading to the synthesis of geranyl. Cannabis (cannabis sativa, or hemp) and its constituents in particular the cannabinoids have been the focus of extensive chemical and biological research for almost half a century since the discovery of the chemical structure of its major active constituent, Δ 9 tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ 9 thc). the plant's behavioral and psychotropic effects.

A Extraction Of Plants B Chemistry Of Phytochemical Extraction Biosynthetic pathway leading to phytocannabinoids. the biosynthesis of cannabinoids from c. sativa has only been recently elucidated. the precursors of cannabinoids actually originate from two distinct biosynthetic pathways: the polyketide pathway, giving rise to olivetolic acid (ola) and the plastidal 2 c methyl d erythritol 4 phosphate (mep) pathway, leading to the synthesis of geranyl. Cannabis (cannabis sativa, or hemp) and its constituents in particular the cannabinoids have been the focus of extensive chemical and biological research for almost half a century since the discovery of the chemical structure of its major active constituent, Δ 9 tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ 9 thc). the plant's behavioral and psychotropic effects.

Pdf Comparison Of The Efficiency Of Deep Eutectic And Organic

Comments are closed.