Eye Color Description Heredity Variations Britannica

Eye Color Description Heredity Variations Britannica The iris, the coloured part of the eye, is the ring of muscle and collagen fibres around the central black opening of the eye known as the pupil, through which light passes. the colour of the iris is commonly described by simple terms, such as blue, gray, green, hazel, or brown. however, eye colour varies across a continuous spectrum, such that. Heredity, the sum of all biological processes by which particular characteristics are transmitted from parents to their offspring. the concept of heredity encompasses two seemingly paradoxical observations about organisms: the constancy of a species from generation to generation and the variation among individuals within a species. constancy.

Heredity Traits Eye Color Scientists have identified several specific genes that are associated with eye color, such as oca2, herc2, and slc24a4. these genes play a role in the production and distribution of melanin, the pigment that gives color to our hair, skin, and eyes. variations in these genes can result in different eye colors. Eye color. eye color is a polygenic phenotypic trait determined by two factors: the pigmentation of the eye 's iris [1][2] and the frequency dependence of the scattering of light by the turbid medium in the stroma of the iris. [3]: 9. in humans, the pigmentation of the iris varies from light brown to black, depending on the concentration of. Human eye, specialized sense organ in humans that is capable of receiving visual images, which are relayed to the brain. the anatomy of the eye includes auxiliary structures, such as the bony eye socket and extraocular muscles, as well as the structures of the eye itself, such as the lens and the retina. Genes are the basic unit of heredity. this means that genes determine what traits are passed down from a mother and father to their child. eye color, height, and hair color are some examples of the traits that are controlled by genes. genes exist inside the cells that make up living things.

77 Eye Color Heredity Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock Human eye, specialized sense organ in humans that is capable of receiving visual images, which are relayed to the brain. the anatomy of the eye includes auxiliary structures, such as the bony eye socket and extraocular muscles, as well as the structures of the eye itself, such as the lens and the retina. Genes are the basic unit of heredity. this means that genes determine what traits are passed down from a mother and father to their child. eye color, height, and hair color are some examples of the traits that are controlled by genes. genes exist inside the cells that make up living things. Eye color is a physical trait that describes the color of an individual’s eyes. it is determined by a combination of genetic factors, including the presence of specific alleles, as well as other environmental factors. in terms of genetics, eye color is a polygenic trait, meaning that it is influenced by multiple genes. In addition to confirming the association of snps in 11 previously known eye color genes (11, 13, 14, 17, 28), the identification of 50 novel eye color–associated genetic loci helps explain previously missing heritability of eye color variability in european populations. moreover, because of the multiethnic design of our study, we demonstrate.
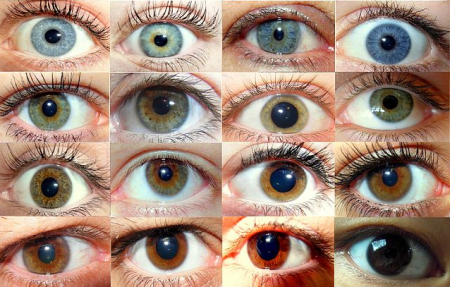
Heredity Definition Types Examples Study Eye color is a physical trait that describes the color of an individual’s eyes. it is determined by a combination of genetic factors, including the presence of specific alleles, as well as other environmental factors. in terms of genetics, eye color is a polygenic trait, meaning that it is influenced by multiple genes. In addition to confirming the association of snps in 11 previously known eye color genes (11, 13, 14, 17, 28), the identification of 50 novel eye color–associated genetic loci helps explain previously missing heritability of eye color variability in european populations. moreover, because of the multiethnic design of our study, we demonstrate.

Heredity Traits Eye Color

Comments are closed.