Fearing For His Life A Paralyzed Dog With Its Legs Groaned In Pain For

Fearing For His Life A Paralyzed Dog With Its Legs Groaned In Pain For Systemic causes of paralysis in dogs. paralysis in dogs from general illness is more common than most people think. diseases caused by toxins, bacteria, viruses, fungi, or immune reactions can. The lumbosacral plexus is a complex network of nerves between the hind leg and spinal cord. a dog’s hind leg’s femoral, sciatic, peroneal, and tibial nerves are susceptible to damage and injury. the dog loses the ability to flex its joint, bear weight on the affected leg, and feel pain or exhibit reflexes based on the nerve damage location.

Fearing For His Life A Paralyzed Dog With Its Legs Groaned In Pain For To help with this, use a long towel or sheet and put it under your dog's belly. hold the ends as you walk (think of a stork holding a baby). this way, your dog can propel himself with the front. The paralyzed pet will probably have some ability to drag himself or change positions somewhat, but be aware of sores developing on pressure points. especially vulnerable areas include: elbows, ankles, and hips. if sores develop, see your veterinarian for care. padding or bandages for these areas may be needed. Adopting a paralyzed dog . fortunately, many paralyzed dogs can still live happy lives with proper care and attention. before adopting a disabled dog of any kind, make sure you understand the type of care the dog needs so you can allow time in your life for the dog's needs. educate yourself about proper techniques before you take the paralyzed. Place one hand under your dog’s abdomen just in front of their back legs between the hips and wrap your fingers up one side of the abdomen, while keeping your thumb on the other side of the abdomen. gently begin to squeeze your fingers and thumb together and press your whole hand toward the tail. once urine starts to flow, apply steady.
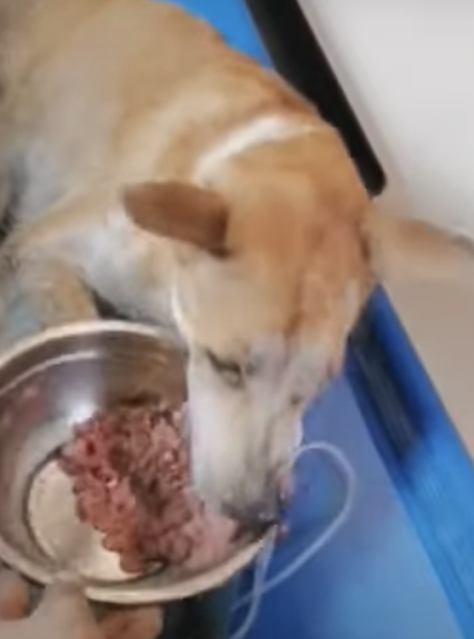

Fearing For His Life A Paralyzed Dog With Its Legs Groaned In Pain For Adopting a paralyzed dog . fortunately, many paralyzed dogs can still live happy lives with proper care and attention. before adopting a disabled dog of any kind, make sure you understand the type of care the dog needs so you can allow time in your life for the dog's needs. educate yourself about proper techniques before you take the paralyzed. Place one hand under your dog’s abdomen just in front of their back legs between the hips and wrap your fingers up one side of the abdomen, while keeping your thumb on the other side of the abdomen. gently begin to squeeze your fingers and thumb together and press your whole hand toward the tail. once urine starts to flow, apply steady. Spinal injury. paralysis in dogs is usually caused by a problem in the spine or brain. spinal compression, herniated discs, and nerve problems can all disrupt the communication between a dog’s spine and brain. when the nerves are unable to function normally, dogs will lose the ability to walk, stand, and control their legs. Pain. lameness. weakness. abnormal gait. shift in weight. limb dragging. horner’s syndrome, or issues with the eye on the same side as affected limb. types. front leg paralysis is often caused by damage to the neck and shoulder nerve roots, or in the radial, median or ulnar nerves in the affected leg.
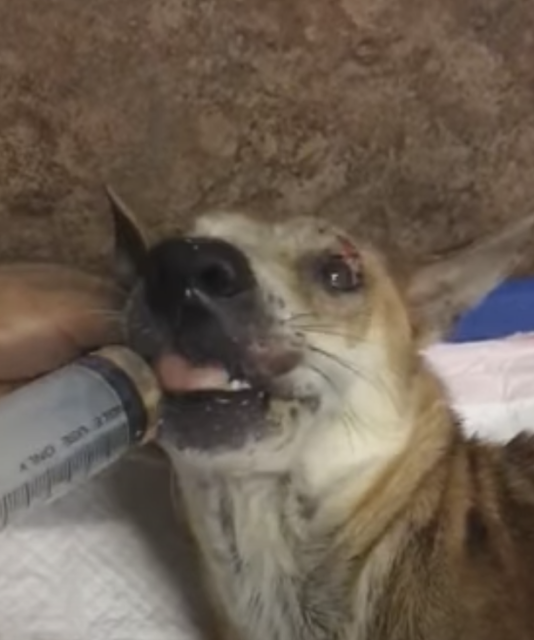
Fearing For His Life A Paralyzed Dog With Its Legs Groaned In Pain For Spinal injury. paralysis in dogs is usually caused by a problem in the spine or brain. spinal compression, herniated discs, and nerve problems can all disrupt the communication between a dog’s spine and brain. when the nerves are unable to function normally, dogs will lose the ability to walk, stand, and control their legs. Pain. lameness. weakness. abnormal gait. shift in weight. limb dragging. horner’s syndrome, or issues with the eye on the same side as affected limb. types. front leg paralysis is often caused by damage to the neck and shoulder nerve roots, or in the radial, median or ulnar nerves in the affected leg.
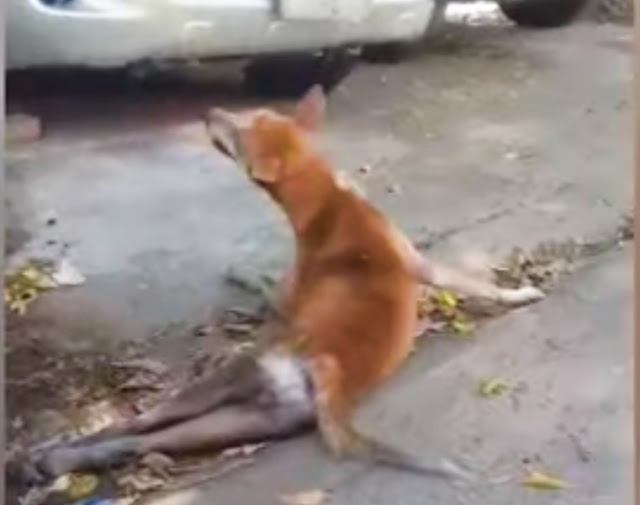

Fearing For His Life A Paralyzed Dog With Its Legs Groaned In Pain For

Comments are closed.