Figure 1 From Combined Endoscopic Laparoscopic T Tube Insertion For The
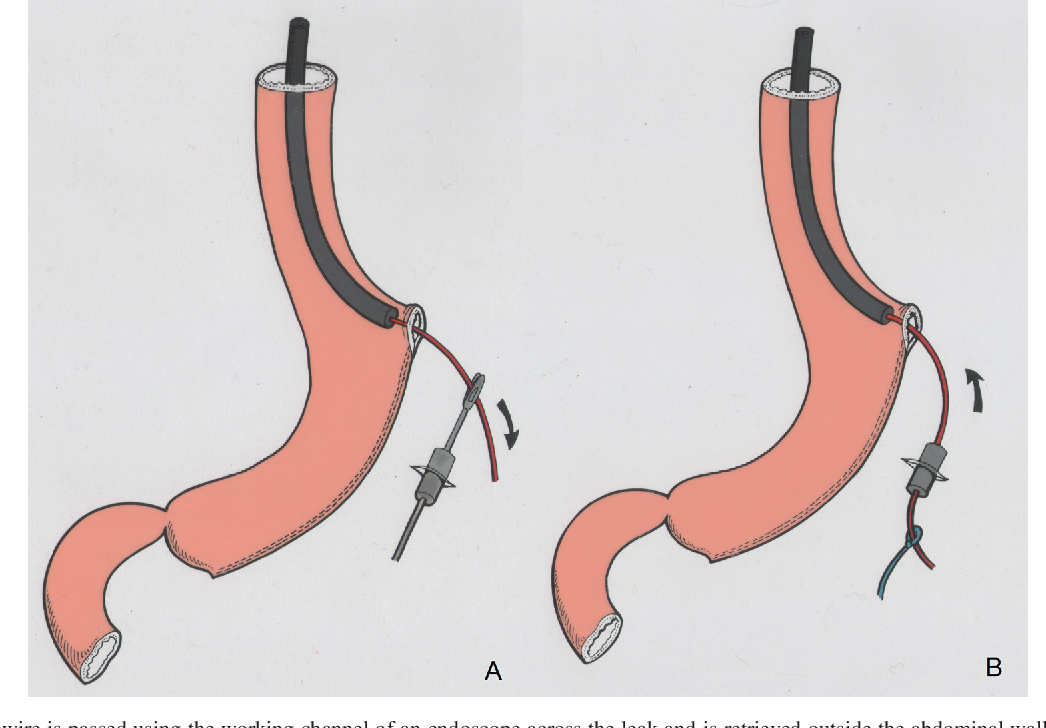
Figure 1 From Combined Endoscopic Laparoscopic T Tube Insertion For The The t tube is then inserted via a choledochostomy and the common bile duct is closed with interrupted sutures.5 laparoscopic t tube placement differs from the above technique in that vigorous retraction of the gallbladder is required in order to expose the common bile duct and facilitate t tube placement. this lap. Laparoscopic t tube placement differs from the above technique in that vigorous retraction of the gallbladder is required in order to expose the common bile duct and facilitate t tube placement. this laparoscopic retraction of the gallbladder creates a knuckle in the common bile duct ( figure 4 ), which makes t tube placement more difficult.

Pdf Combined Endoscopic Laparoscopic T Tube Insertion An Altern Background and objectives: laparoscopic common bile duct exploration (lcbde) has been verified to be an effective technique in treating choledocholithiasis, and t tube insertion has been widely performed after lcbde. with growing doubts regarding the effectiveness and safety of t tube drainage (ttd), it has been suggested to replace such with. Some studies proposed that choledochotomy with primary laparoscopic closure of the cbd is safe, eliminates the need for t tube placement, and reduces operating time and postoperative morbidity [109, 110]. yamazaki et al. reported significant differences in hospital stay between primary closure and t tube insertion (18.3 days versus 31.5 days. 1 introduction. choledocholithiasis, the presence of gallstones in the common bile duct (cbd), is common in 10% to 20% of patients with symptomatic gallstones (wil‐liams et al., 2017). choledocholithiasis is linked to a number of health problems including biliary colic, jaundice, cholangitis, pancreatitis, and liver abscess (caddy and tham. Laparoscopic transcystic common bile duct exploration during laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the treatment of choice for patients with coexisting gallbladder and bile duct stones. failure of this usually indicates laparoscopic choledocotomy, after which most patients are managed with primary duct closure and less frequently with t tube placement or bilioenteric anastomosis. the objective of.
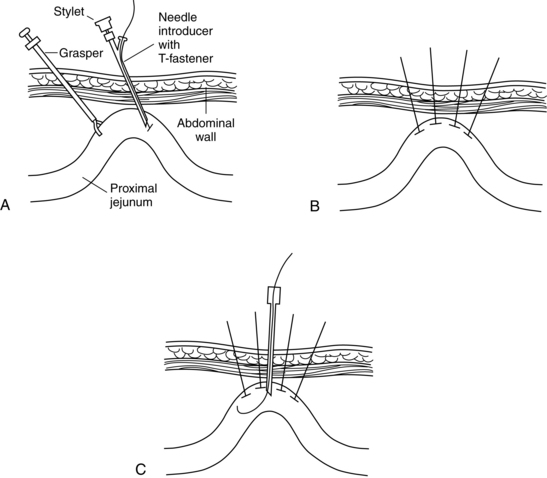
Percutaneous Tube Management Musculoskeletal Key 1 introduction. choledocholithiasis, the presence of gallstones in the common bile duct (cbd), is common in 10% to 20% of patients with symptomatic gallstones (wil‐liams et al., 2017). choledocholithiasis is linked to a number of health problems including biliary colic, jaundice, cholangitis, pancreatitis, and liver abscess (caddy and tham. Laparoscopic transcystic common bile duct exploration during laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the treatment of choice for patients with coexisting gallbladder and bile duct stones. failure of this usually indicates laparoscopic choledocotomy, after which most patients are managed with primary duct closure and less frequently with t tube placement or bilioenteric anastomosis. the objective of. Fig. 1. operative technique. (a) anchoring stitches placed through the abdominal wall securing the stomach up to the abdominal wall during the procedure. (b) the esophagogastroduodenoscope grasper grabs the silk tie on the end of the gastrojejunal tube. (c) the esophagogastroduodenoscope advances into the jejunum. (d) anchoring stitches are fastened subcutaneously. "combined laparoscopic. The objective of this paper is to describe the indications and complications of t tube placement after laparoscopic choledocotomy in a consecutive series of single stage management of 554 patients. case series analysis of a prospectively collected historical database of all patients treated with t tube drainage at cosme argerich hospital from july 2008 and december 2020.

Comments are closed.