Foci Of Hyperbola Equation Given An Equation Find The Vertices

Conic Sections Hyperbola Find Equation Given Foci And Vertices Y This calculator will find either the equation of the hyperbola from the given parameters or the center, foci, vertices, co vertices, (semi)major axis length, (semi)minor axis length, latera recta, length of the latera recta (focal width), focal parameter, eccentricity, linear eccentricity (focal distance), directrices, asymptotes, x intercepts, y intercepts, domain, and range of the entered. When given the coordinates of the foci and vertices of a hyperbola, we can write the equation of the hyperbola in standard form. see example \(\pageindex{2}\) and example \(\pageindex{3}\). when given an equation for a hyperbola, we can identify its vertices, co vertices, foci, asymptotes, and lengths and positions of the transverse and.

Hyperbola Equation Foci Formula Parts Example Lesson Study Learn how to write the equation of hyperbolas given the characteristics of the hyperbolas. the standard form of the equation of a hyperbola is of the form: (. Also, this hyperbola's foci and vertices are to the left and right of the center, on a horizontal line paralleling the x axis. from the equation, clearly the center is at (h, k) = (−3, 2). since the vertices are a = 4 units to either side, then they are at the points (−7, 2) and at (1, 2). the equation a2 b2 = c2 gives me:. The standard form of the equation of a hyperbola with center (0,0) (0, 0) and transverse axis on the x axis is. x2 a2 − y2 b2 =1 x 2 a 2 − y 2 b 2 = 1. where. the length of the transverse axis is 2a 2 a. the coordinates of the vertices are (±a,0) (± a, 0) the length of the conjugate axis is 2b 2 b. Calculate hyperbola center, axis, foci, vertices, eccentricity and asymptotes step by step hyperbola equation calculator. en. related symbolab blog posts.
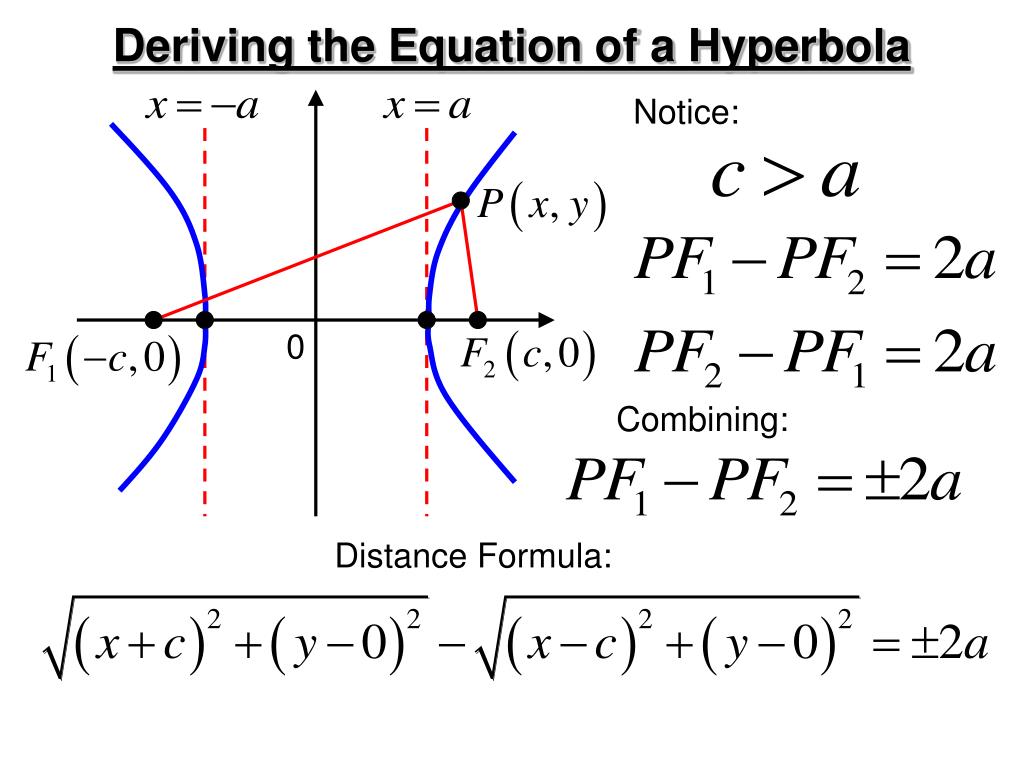
Foci Of Hyperbola Equation Given An Equation Find The Vertices The standard form of the equation of a hyperbola with center (0,0) (0, 0) and transverse axis on the x axis is. x2 a2 − y2 b2 =1 x 2 a 2 − y 2 b 2 = 1. where. the length of the transverse axis is 2a 2 a. the coordinates of the vertices are (±a,0) (± a, 0) the length of the conjugate axis is 2b 2 b. Calculate hyperbola center, axis, foci, vertices, eccentricity and asymptotes step by step hyperbola equation calculator. en. related symbolab blog posts. Just as with ellipses, writing the equation for a hyperbola in standard form allows us to calculate the key features: its center, vertices, co vertices, foci, asymptotes, and the lengths and positions of the transverse and conjugate axes. conversely, an equation for a hyperbola can be found given its key features. The foci are side by side, so this hyperbola's branches are side by side, and the center, foci, and vertices lie on a line paralleling the x axis. so the y part of the equation will be subtracted and the a2 will go with the x part of the equation. the center is midway between the two foci, so the center must be at (h, k) = (−1, 0).

Conic Sections Find Equation Of A Hyperbola Given Vertices And Foci Just as with ellipses, writing the equation for a hyperbola in standard form allows us to calculate the key features: its center, vertices, co vertices, foci, asymptotes, and the lengths and positions of the transverse and conjugate axes. conversely, an equation for a hyperbola can be found given its key features. The foci are side by side, so this hyperbola's branches are side by side, and the center, foci, and vertices lie on a line paralleling the x axis. so the y part of the equation will be subtracted and the a2 will go with the x part of the equation. the center is midway between the two foci, so the center must be at (h, k) = (−1, 0).

Comments are closed.