Food Chain Food Web Tropical Grasslands Savannas
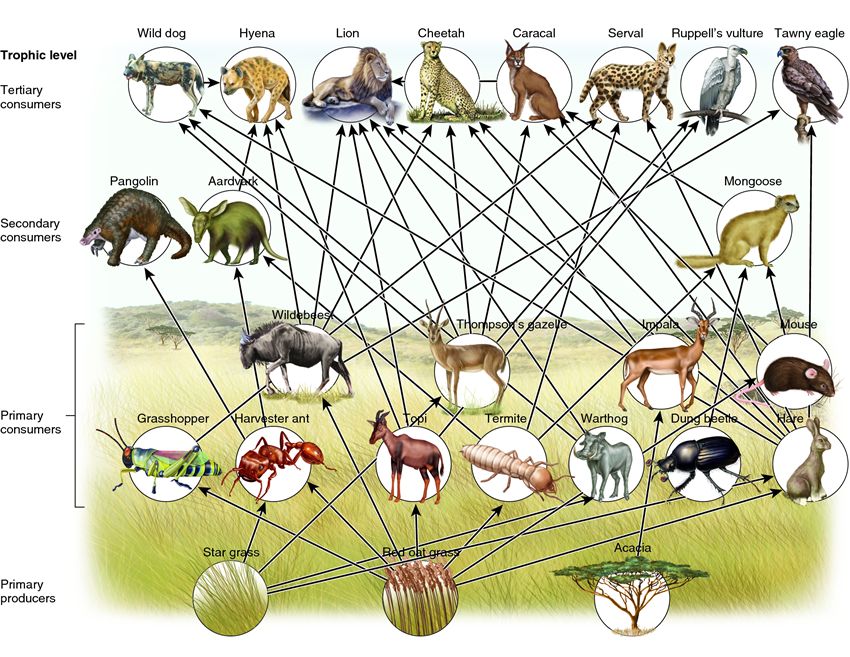
Food Chain Food Web The Tropical Grasslands Savannas Biome The producers the trees, shrubs and grass. the primary consumers – the zebras and elephants. the secondary consumers – the cheetah, hyena. the scavengers – the termites, vultures and hyena. the decomposers or detritivores – mushrooms, insects and microorganisms. * try the african savannah food web activity. to make black and white. Savanna food chain trophic levels and components explained. january 15, 2024 by ramzan asghar. the african savanna is a vast grassland ecosystem supporting diverse plant and animal life. the interactions between these organisms form complex food chains and webs that transfer energy within the biome. this article will discuss the different.
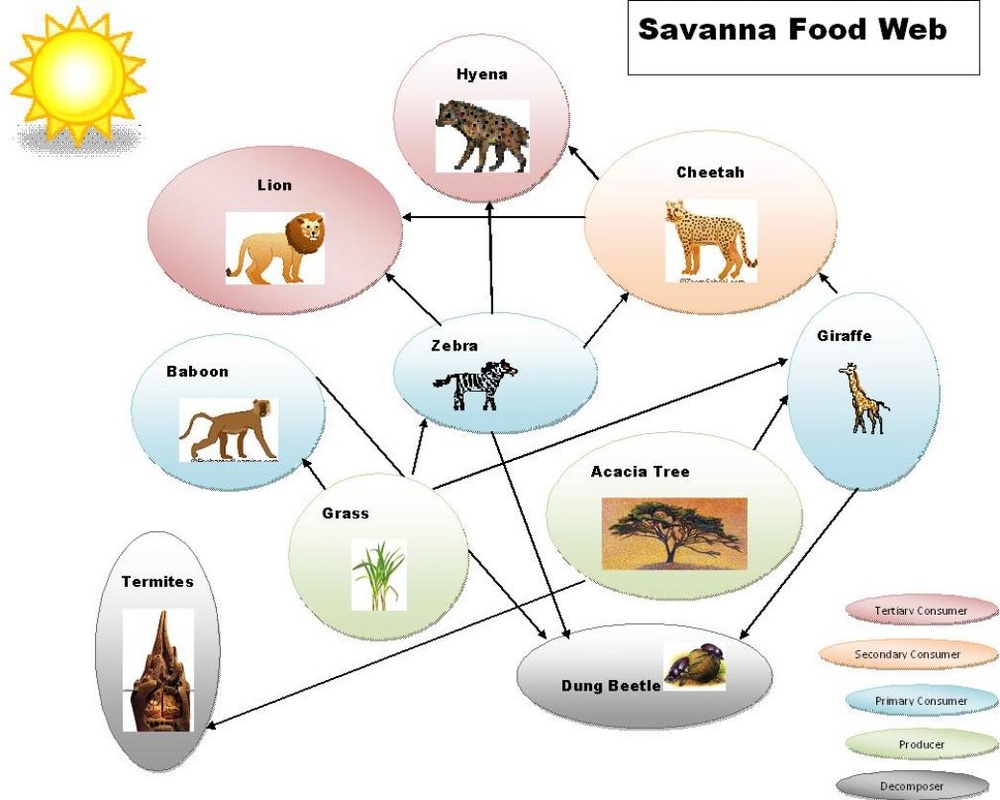
Food Chain Food Web The Tropical Grasslands Savannas Biome Savannas are also called tropical grasslands. this biome is characterized by flat land without many trees, and warm weather all year long. the temperature in the savanna rarely falls below 60. Overgrazing: excessive grazing by livestock can deplete grasses and shrubs, disrupting the savanna food web. poaching: illegal hunting of herbivores and predators disrupts the ecosystem’s natural balance. clearing of grassland: large parts of savanna grasslands, both the tough grasses and the trees, are cleared regularly. this results in the. These relationships, between the various species in an ecosystem, form food chains, and the collective interactions (links) form food webs. savanna ecosystems such as those that dominate angolan landscapes have two food chains—a grazing food chain and a detrital food chain, as illustrated in fig. 10.3. To understand the african savannah food web, first read about the african savannah biome using this link. then read about the different trophic levels of a typical food chain (below). the trophic level is the position that an organism (plant or animal) occupies in a food chain what it eats, and what eats it.
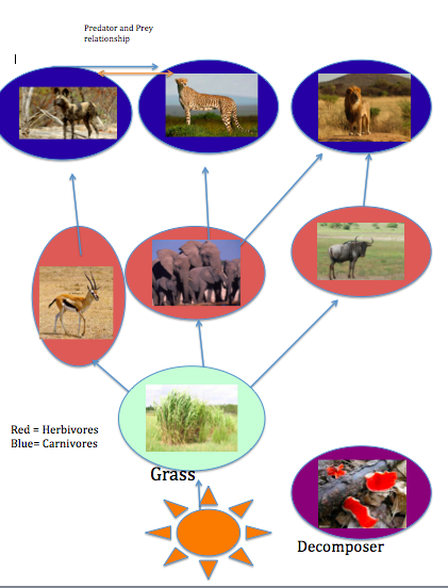
Food Chain Food Web The Tropical Grasslands Savannas Biome These relationships, between the various species in an ecosystem, form food chains, and the collective interactions (links) form food webs. savanna ecosystems such as those that dominate angolan landscapes have two food chains—a grazing food chain and a detrital food chain, as illustrated in fig. 10.3. To understand the african savannah food web, first read about the african savannah biome using this link. then read about the different trophic levels of a typical food chain (below). the trophic level is the position that an organism (plant or animal) occupies in a food chain what it eats, and what eats it. Primary producers. savannas are dominated by tall grasses, which are the primary producers that convert energy from the sun and minerals and nutrients from the soil into the biomass that forms the basis of the food web. in the savanna, the lowest trophic level often includes shrubs and sparse trees, including palms, pines and acacias. Food web. sources of energy are the bermudagrass and the senegal gum acacia. they absorb the heat and rays of the sun and start making food through photosynthesis. the herbivores (plant eating animals) eat them. carnivores (meat eating animals) then eat the herbivores. fluctuations, or variation, of either herbivores and carnivores can affect.
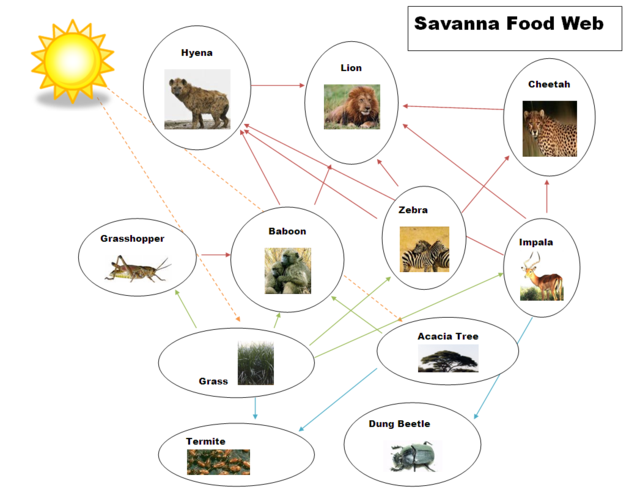
Food Chain Food Web The Tropical Grasslands Savannas Biome Primary producers. savannas are dominated by tall grasses, which are the primary producers that convert energy from the sun and minerals and nutrients from the soil into the biomass that forms the basis of the food web. in the savanna, the lowest trophic level often includes shrubs and sparse trees, including palms, pines and acacias. Food web. sources of energy are the bermudagrass and the senegal gum acacia. they absorb the heat and rays of the sun and start making food through photosynthesis. the herbivores (plant eating animals) eat them. carnivores (meat eating animals) then eat the herbivores. fluctuations, or variation, of either herbivores and carnivores can affect.

Food Chain Food Web Tropical Grasslands And Savannas

Comments are closed.