Force Types
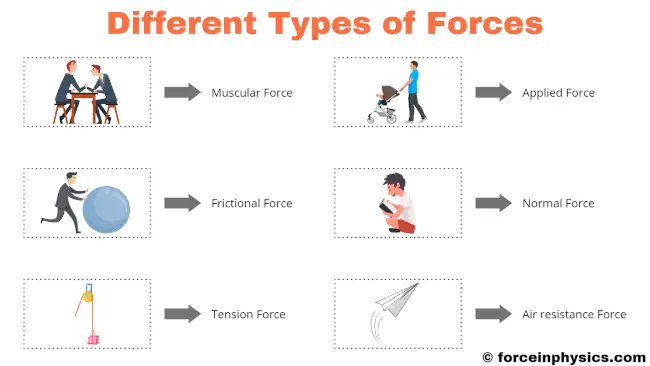
6 Types Of Forces Learn about the different types of forces, such as contact, action at a distance, frictional, gravitational, normal, and more. find definitions, examples, formulas, and diagrams for each force type. Learn about the different types of forces in physics and mechanics, such as contact forces, non contact forces, and fundamental forces. find out how to calculate force, its characteristics, and its effects on objects.
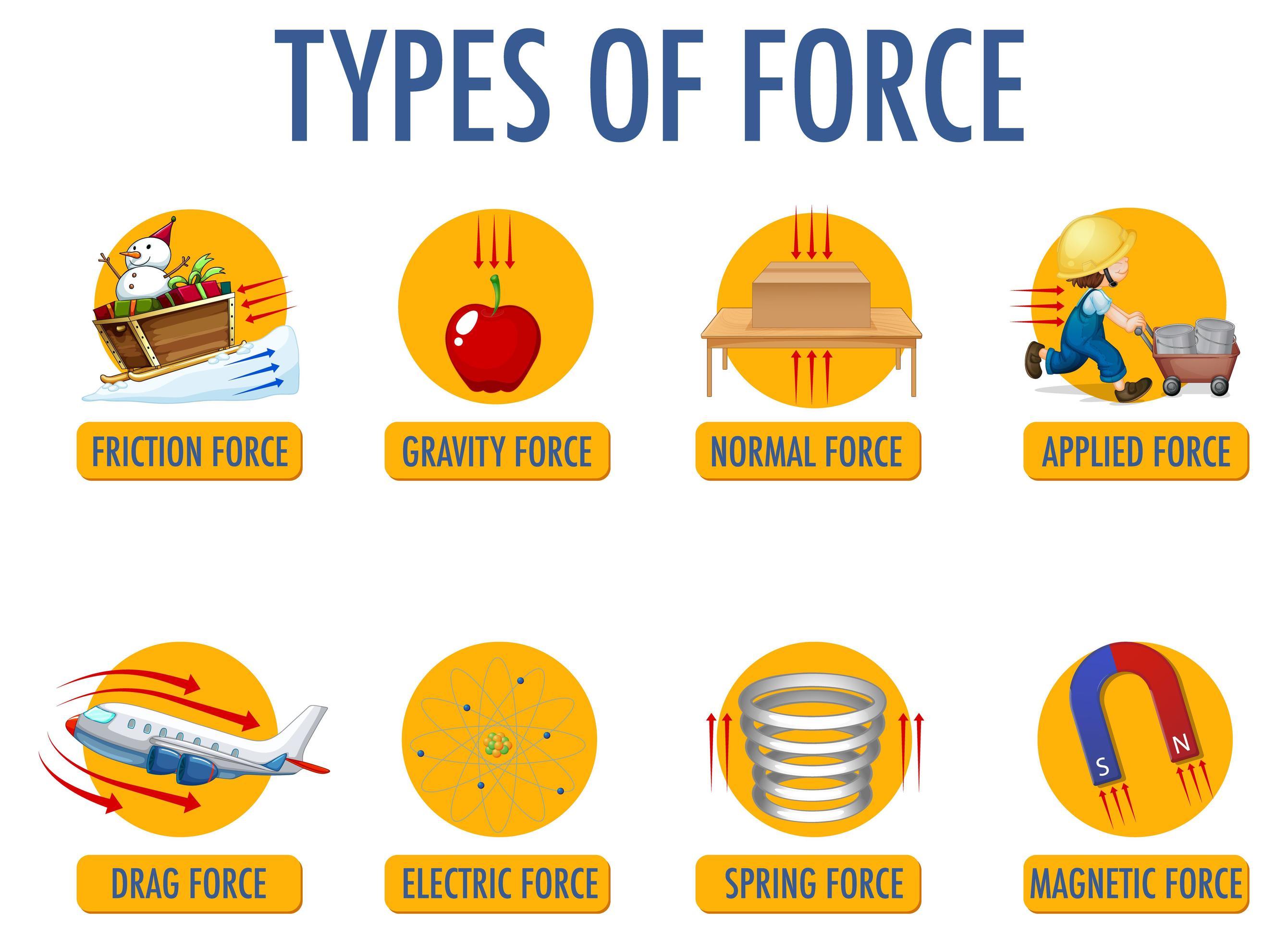
Types Of Force For Children Physics Educational 1784006 Vector Art At Learn what force is, how to measure it, and how it affects motion. explore the types of force, such as contact and non contact, with examples and solved problems. Force plays an important role in classical mechanics. the concept of force is central to all three of newton's laws of motion. types of forces often encountered in classical mechanics include elastic, frictional, contact or "normal" forces, and gravitational. Enrico fermi was the first to envision this type of force. while this force is appropriately labeled, it remains stronger than the gravitational force. however, its range is even smaller than that of the strong force, as can be seen in table 23.1. the weak nuclear force is more important than it may appear at this time, as will be addressed. One distinguishes between two types of frictional forces: kinetic and static, depending on whether the surfaces are sliding with respect to each other (kinetic) or not (static). because of newton’s third law, the objects associated with each surface will both experience a frictional force (same magnitude, opposite direction).

Types Of Force For Children Physics Educational Poster Illustration Enrico fermi was the first to envision this type of force. while this force is appropriately labeled, it remains stronger than the gravitational force. however, its range is even smaller than that of the strong force, as can be seen in table 23.1. the weak nuclear force is more important than it may appear at this time, as will be addressed. One distinguishes between two types of frictional forces: kinetic and static, depending on whether the surfaces are sliding with respect to each other (kinetic) or not (static). because of newton’s third law, the objects associated with each surface will both experience a frictional force (same magnitude, opposite direction). These ideas were developed in vectors. figure 5.2.2 5.2. 2: (a) an overhead view of two ice skaters pushing on a third skater. forces are vectors and add like other vectors, so the total force on the third skater is in the direction shown. (b) a free body diagram representing the forces acting on the third skater. Learn about the different types of forces in physics, such as contact forces and field forces, and how to describe them using vectors and units. see examples of common forces and how they affect objects in motion.
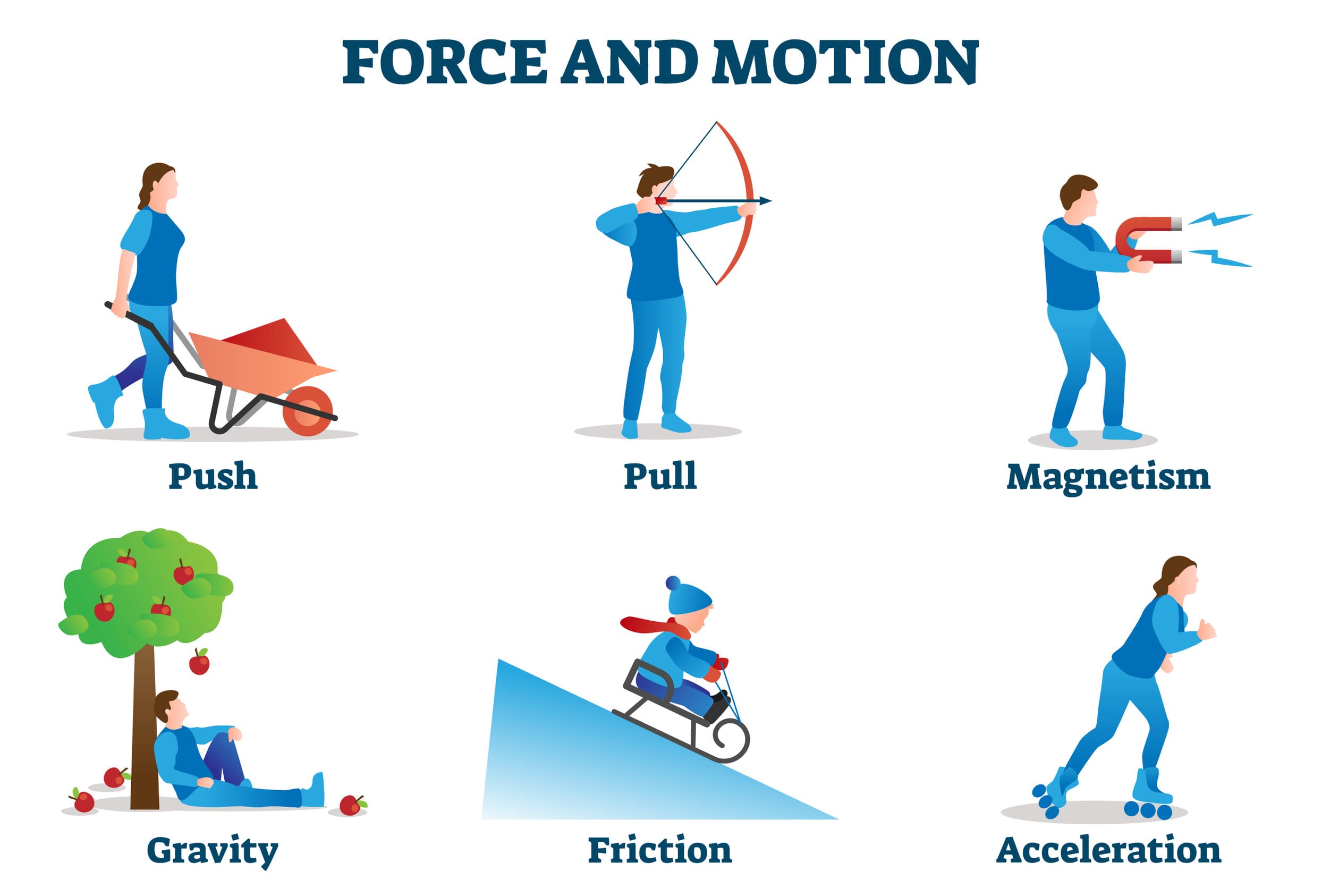
Forces And Shape Effects Of Forces Friction Springs Wires These ideas were developed in vectors. figure 5.2.2 5.2. 2: (a) an overhead view of two ice skaters pushing on a third skater. forces are vectors and add like other vectors, so the total force on the third skater is in the direction shown. (b) a free body diagram representing the forces acting on the third skater. Learn about the different types of forces in physics, such as contact forces and field forces, and how to describe them using vectors and units. see examples of common forces and how they affect objects in motion.

Comments are closed.