General Features Classification Of Fungi Mycology Notes

General Features Classification Of Fungi Mycology Notes Fungi are eukaryotic microorganisms. they can occur as yeasts, molds, or as a combination of both forms. some fungi are capable of causing superficial, cutaneous, subcutaneous, systemic or allergic diseases. yeasts are microscopic fungi consisting of solitary cells that reproduce by budding. molds, in contrast, occur in long filaments known as. Fungi are eukaryotic microorganisms. fungi can occur as yeasts, molds, or as a combination of both forms. some fungi are capable of causing superficial, cutaneous, subcutaneous, systemic or allergic diseases. yeasts are microscopic fungi consisting of solitary cells that reproduce by budding. molds, in contrast, occur in long filaments known as hyphae, which grow by apical extension. hyphae.
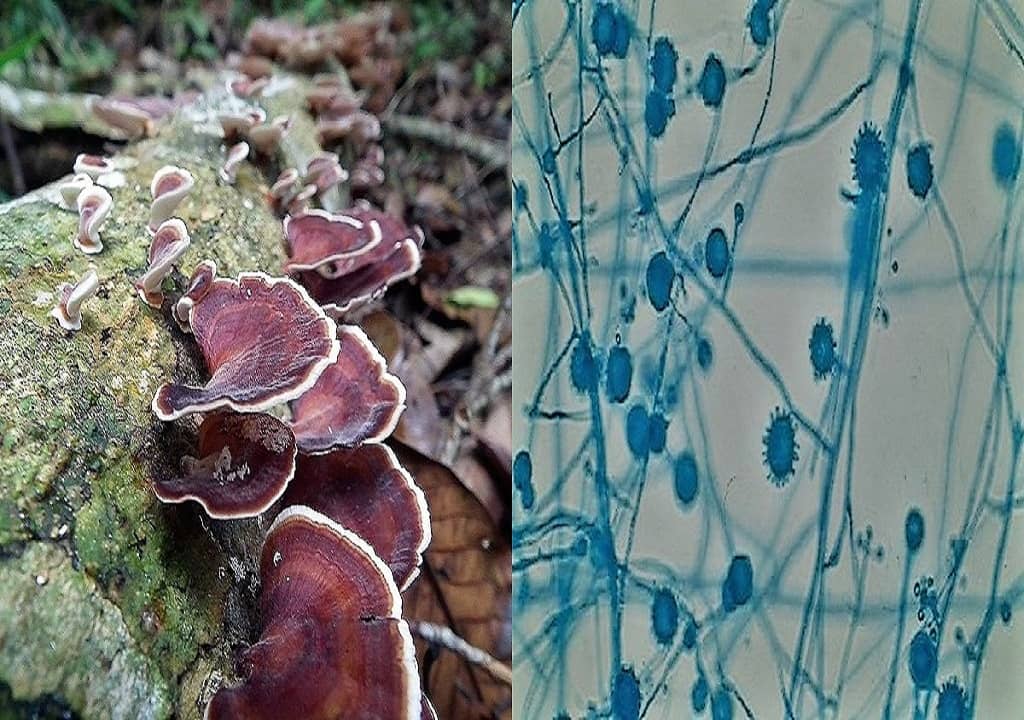

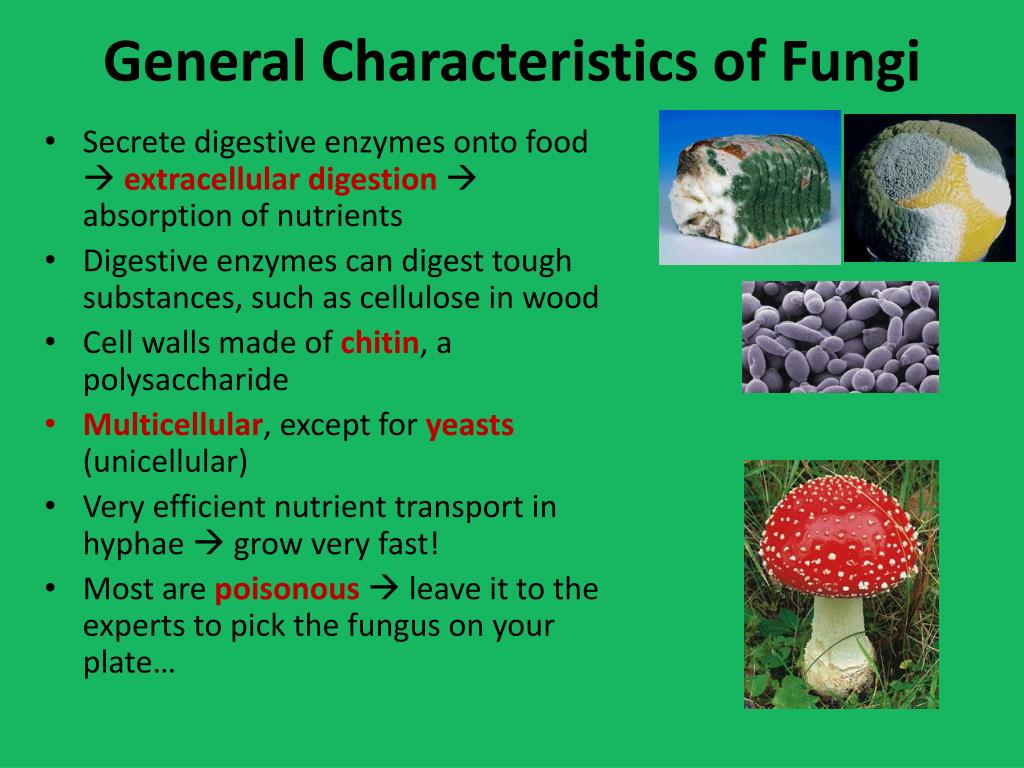
General Features Classification Of Fungi Mycology Notes Introduction to mycology. mycology is the branch of microbiology that deals with the study of fungi and fungal diseases. general characteristics of fungi. ⇒ all fungi are eukaryotic protists. ⇒ they may be multicellular (moulds) or unicellular (yeasts). ⇒ they are chemotropic organisms i.e. obtaining their nutrients from chemicals in nature. Mycology is a branch of natural science involved in studies related to fungi, their structure, genetic composition, biochemical properties, taxonomy, and their applications. fungi are eukaryotic microorganisms that occur as yeasts, molds, or as a combination of both forms. the characteristic features of fungi include the chitinous cell walls. The term "mycology" is derived from greek word "mykes" meaning mushroom. therefore mycology is the study of fungi. the ability of fungi to invade plant and animal tissue was observed in early 19thcentury but the first documented animal infection by any fungus was made by bassi, who in 1835 studied the muscardine disease of silkworm and proved. Fungi (singular: fungus) are one of the kingdoms of life in biology, along with animals, plants, protists, bacteria, and archaebacteria. examples of fungi include yeast, mushrooms, toadstools (poisonous mushrooms), and molds. the scientific study of fungi is called mycology. around 150,000 species of fungi are known, but there may be between 2.

Mycology Classification Of Fungi Structure Advantages Disadvantages The term "mycology" is derived from greek word "mykes" meaning mushroom. therefore mycology is the study of fungi. the ability of fungi to invade plant and animal tissue was observed in early 19thcentury but the first documented animal infection by any fungus was made by bassi, who in 1835 studied the muscardine disease of silkworm and proved. Fungi (singular: fungus) are one of the kingdoms of life in biology, along with animals, plants, protists, bacteria, and archaebacteria. examples of fungi include yeast, mushrooms, toadstools (poisonous mushrooms), and molds. the scientific study of fungi is called mycology. around 150,000 species of fungi are known, but there may be between 2. Prevention and control of fungal infection. treatment. keynotes. mycology is the science that deals with the study of fungi whereas medical mycology is the science that deals with the study of fungi that causes disease is called medical mycology. general features . fungi are a group of eukaryotic organisms. they are found in soil, water, air. Fungi are eukaryotic microorganisms which are heterotrophic and essentially aerobic with limited anaerobic capabilities. fungi synthesize lysine by the l αadipic acid biosynthetic pathway. they possess chitinous cell walls, plasma membranes containing ergosterol, 80srrna and microtubules composed of tubulin. fungi grow as yeasts, molds or a combination of both (i.e. dimorphism).
Mycology Classification Of Fungi Structure Advantages Disadvantages Prevention and control of fungal infection. treatment. keynotes. mycology is the science that deals with the study of fungi whereas medical mycology is the science that deals with the study of fungi that causes disease is called medical mycology. general features . fungi are a group of eukaryotic organisms. they are found in soil, water, air. Fungi are eukaryotic microorganisms which are heterotrophic and essentially aerobic with limited anaerobic capabilities. fungi synthesize lysine by the l αadipic acid biosynthetic pathway. they possess chitinous cell walls, plasma membranes containing ergosterol, 80srrna and microtubules composed of tubulin. fungi grow as yeasts, molds or a combination of both (i.e. dimorphism).
General Features Classification Of Fungi Mycology Not Vrogue Co

Comments are closed.