Genetics In 60 Seconds Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Snp
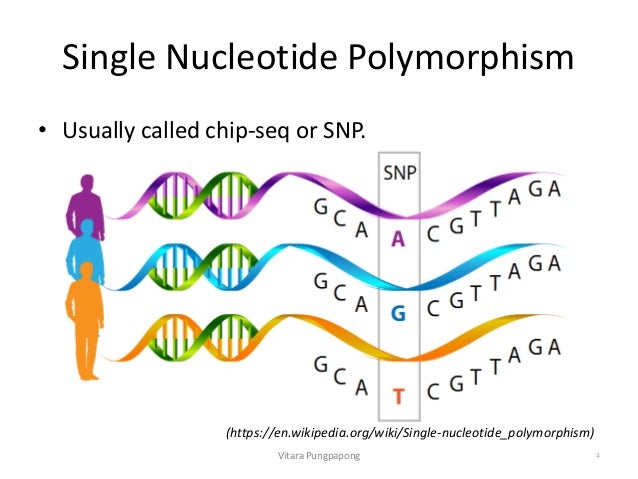
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Analysis Snps Single nucleotide polymorphisms, frequently called snps (pronounced “snips”), are the most common type of genetic variation among people. each snp represents a difference in a single dna building block, called a nucleotide. for example, a snp may replace the nucleotide cytosine (c) with the nucleotide thymine (t) in a certain stretch of dna. Single nucleotide polymorphism, or snp. if you are reading a news story where it says, for example, scientists find the genetic contributors to diabetes or some other condition or trait, you're probably reading about snps. a snp is a one letter place where your genome varies from another genome sequence.

Polymorphism Single Nucleotide Single Nucleotide Polymorphism ођ Recent news. single nucleotide polymorphism (snp), variation in a genetic sequence that affects only one of the basic building blocks— adenine (a), guanine (g), thymine (t), or cytosine (c)—in a segment of a dna molecule and that occurs in more than 1 percent of a population. an example of an snp is the substitution of a c for a g in the. Snp quick reference. snp (pronounced "snip") stands for single nucleotide polymorphism. snps are single nucleotide substitutions of one base for another. each snp location in the genome can have up to four versions: one for each nucleotide, a, c, g, and t. a snp and its distribution in a population might look like the images below and to the left. Author summary our study explores why viral load (copies measured by rt qpcr) varies during sars cov 2 infections by analyzing viral mutations and measuring viral copies in 9,902 individuals over two years. we aimed to understand how genetic differences in sars cov 2 influence viral copies, considering host age and vaccination status. using a genome wide association study (gwas), we identified. In genetics and bioinformatics, a single nucleotide polymorphism (snp s n ɪ p ; plural snps s n ɪ p s ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), [ 1 ] many publications [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] do not apply.

Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Snps Are Genetic Mutations That Alter Author summary our study explores why viral load (copies measured by rt qpcr) varies during sars cov 2 infections by analyzing viral mutations and measuring viral copies in 9,902 individuals over two years. we aimed to understand how genetic differences in sars cov 2 influence viral copies, considering host age and vaccination status. using a genome wide association study (gwas), we identified. In genetics and bioinformatics, a single nucleotide polymorphism (snp s n ɪ p ; plural snps s n ɪ p s ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), [ 1 ] many publications [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] do not apply. A single nucleotide polymorphism, or snp, is a single base pair difference in the dna sequence of individual members of a species; not necessarily a pathological mutation, but commonly studied as. Introduction. single nucleotide polymorphisms (snps), pronounced as “snips,” is the common type of variation found in dna between genes (genetics home reference). each snp differs by a single dna block represented as nucleotide. for example, a snp may be replaced by adenine (a) in place of guanine (g) in a stretch of dna.
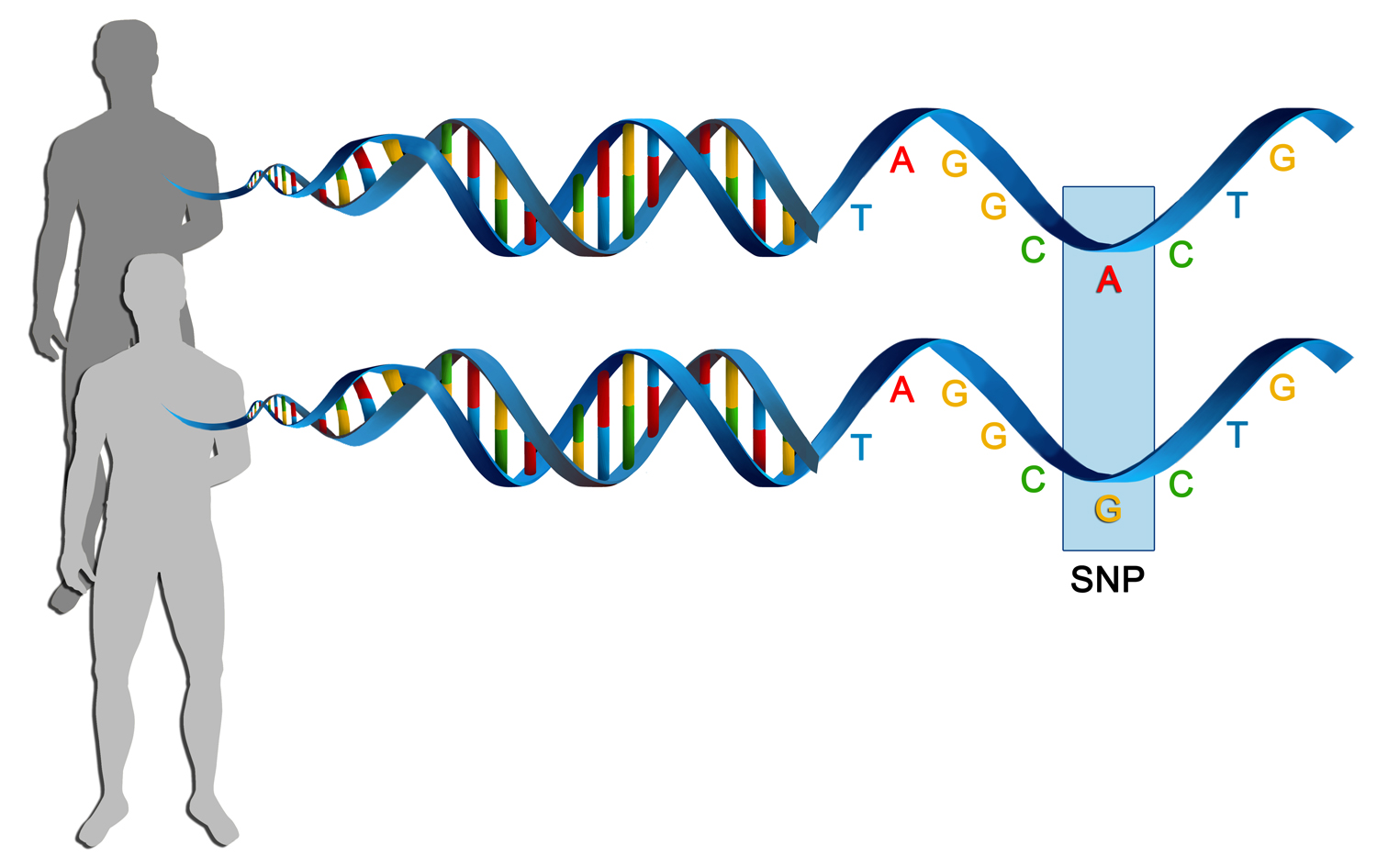
What Are Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Example A single nucleotide polymorphism, or snp, is a single base pair difference in the dna sequence of individual members of a species; not necessarily a pathological mutation, but commonly studied as. Introduction. single nucleotide polymorphisms (snps), pronounced as “snips,” is the common type of variation found in dna between genes (genetics home reference). each snp differs by a single dna block represented as nucleotide. for example, a snp may be replaced by adenine (a) in place of guanine (g) in a stretch of dna.

An Introduction To Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Snp

Comments are closed.