Geometry Properties Of Triangles Angle Bisectors Hard

Geometry Properties Of Triangles Angle Bisectors Hard Youtube Angle bisector theorem. an angle bisector cuts an angle exactly in half. one important property of angle bisectors is that if a point is on the bisector of an angle, then the point is equidistant from the sides of the angle. this is called the angle bisector theorem. in other words, if bd−→− b d → bisects ∠abc ∠ a b c, ba−→−. The angle bisector in geometry is the ray, line, or segment which divides a given angle into two equal parts. for example, an angle bisector of a 60 degree angle will divide it into two angles of 30 degrees each. in other words, it divides an angle into two smaller congruent angles. given below is an image of an angle bisector of ∠aob.

Properties Of Triangles Angle Bisectors Worksheets In this video we explain how to solve angle bisectors type of question.for more free math worksheets on the topic visit our website section: math w. Vocabulary. an angle bisector is a ray that splits an angle into two congruent, smaller angles. the angle bisector theorem states that if a point is on the bisector of an angle, then the point is equidistant from the sides of the angle. the angle bisector theorem converse states that if a point is in the interior of an angle and equidistant. Angle bisector definition. the definition of an angle bisector can be given as a ray or line segment that divides the given angle into two angles of equal measure. an angle bisector of a 60 ∘ angle will divide it into two angles of 30 ∘ each. it divides an angle into two congruent angles. Concurrency of angle bisectors theorem: the angle bisectors of a triangle intersect in a point that is equidistant from the three sides of the triangle. if a g ¯, b g ¯, and g c ¯ are the angle bisectors of the angles in the triangle, then e g = g f = g d. in other words, e g ¯, f g ¯, and d g ¯ are the radii of the inscribed circle.
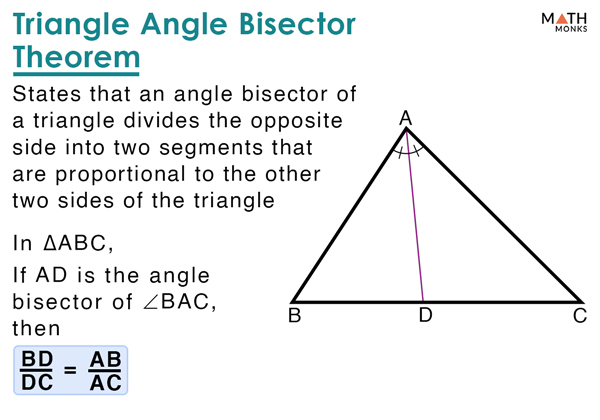
Angle Bisector Of A Triangle вђ Definition Theorem Examples Angle bisector definition. the definition of an angle bisector can be given as a ray or line segment that divides the given angle into two angles of equal measure. an angle bisector of a 60 ∘ angle will divide it into two angles of 30 ∘ each. it divides an angle into two congruent angles. Concurrency of angle bisectors theorem: the angle bisectors of a triangle intersect in a point that is equidistant from the three sides of the triangle. if a g ¯, b g ¯, and g c ¯ are the angle bisectors of the angles in the triangle, then e g = g f = g d. in other words, e g ¯, f g ¯, and d g ¯ are the radii of the inscribed circle. Every triangle has three angle bisectors, one for each interior angle. 2. properties of angle bisectors: the angle bisector divides the opposite side into two segments that are proportional to the other two sides of the triangle. the three angle bisectors of a triangle are concurrent; they meet at a single point called the “incenter” of the. The angle bisector theorem is concerned with the relative lengths of the two segments that a triangle's side is divided into by a line that bisects the opposite angle. it equates their relative lengths to the relative lengths of the other two sides of the triangle. to bisect an angle means to cut it into two equal parts or angles. say that we wanted to bisect a 50 degree angle, then we.
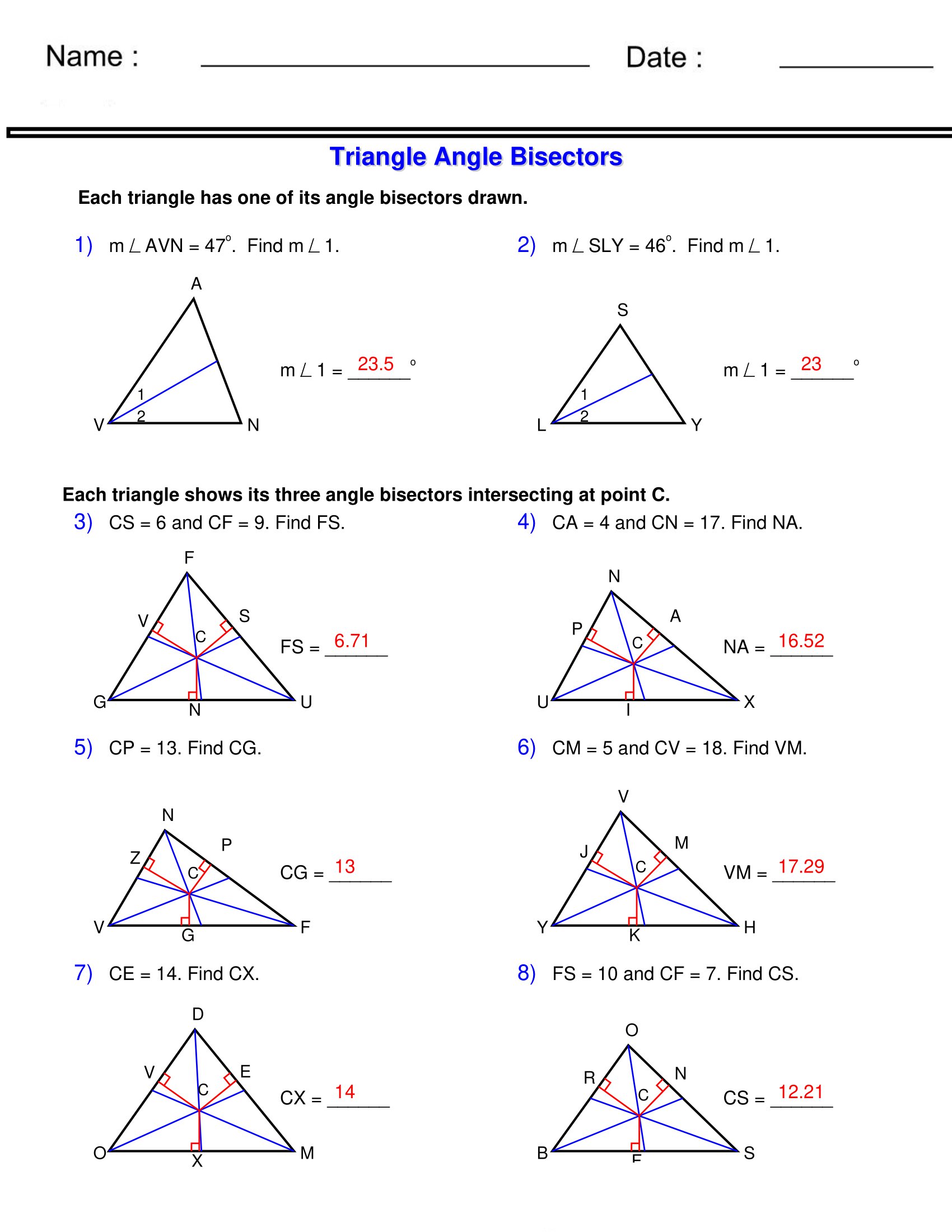
Angle Bisectors Triangle Worksheets Made By Teachers Every triangle has three angle bisectors, one for each interior angle. 2. properties of angle bisectors: the angle bisector divides the opposite side into two segments that are proportional to the other two sides of the triangle. the three angle bisectors of a triangle are concurrent; they meet at a single point called the “incenter” of the. The angle bisector theorem is concerned with the relative lengths of the two segments that a triangle's side is divided into by a line that bisects the opposite angle. it equates their relative lengths to the relative lengths of the other two sides of the triangle. to bisect an angle means to cut it into two equal parts or angles. say that we wanted to bisect a 50 degree angle, then we.
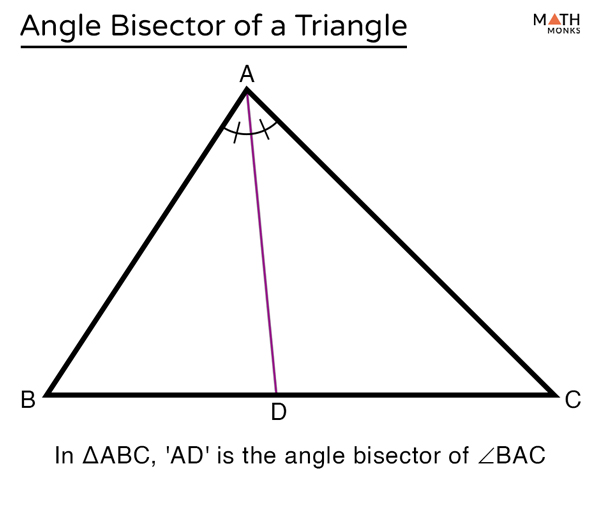
Angle Bisector Of A Triangle вђ Definition Theorem Examples

Comments are closed.