Geosphere And The Rock Cycle Diagram Color Earth Science Lessons

The Rock Cycle Diagram And Explanation The rock cycle is the natural, continuous process that forms, breaks down, and reforms rock through geological, chemical, and physical processes. through the cycle, rocks convert between igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary forms. it is a dynamic system that recycles earth’s materials in different forms, from molten magma deep below the. Grade 5 5 ess2 earth’s systemsngss disciplinary core ideas. • earth’s major systems are the geosphere (solid and molten rock, soil, and sediments), the hydrosphere (water and ice), the atmosphere (air), and the biosphere (living things, including humans). these systems interact in multiple ways to affect earth’s surface materials and.

Rock Cycle Diagram Moomoomath And Science The life cycle of rocks. the life cycle of rocks refers to the continuous cycle of rock creation, alteration, and transformation. it illustrates how rocks can change from one type to another over geologic time. the rock cycle diagram showcases the dynamic nature of rocks and highlights the interconnectedness of the three rock types. The rock cycle. the rock cycle consists of a series of constant processes through which earth materials change from one form to another over time. as within the water cycle and the carbon cycle, some processes in the rock cycle occur over millions of years and others occur much more rapidly. there is no real beginning or end to the rock cycle. The geosphere. the geosphere includes the rocks and minerals on earth – from the molten rock and heavy metals in the deep interior of the planet to the sand on beaches and peaks of mountains. the geosphere also includes the abiotic (non living) parts of soils and the skeletons of animals that may become fossilized over geologic time. Rock is the most abundant thing on earth. rock is right under our feet! let’s look at what rock is, how it’s different from a mineral, the 3 types of rock, and the rock cycle. understanding the 3 types of rock helps us understand the natural process as the rock cycle is explained. in this post we also have a free printable.
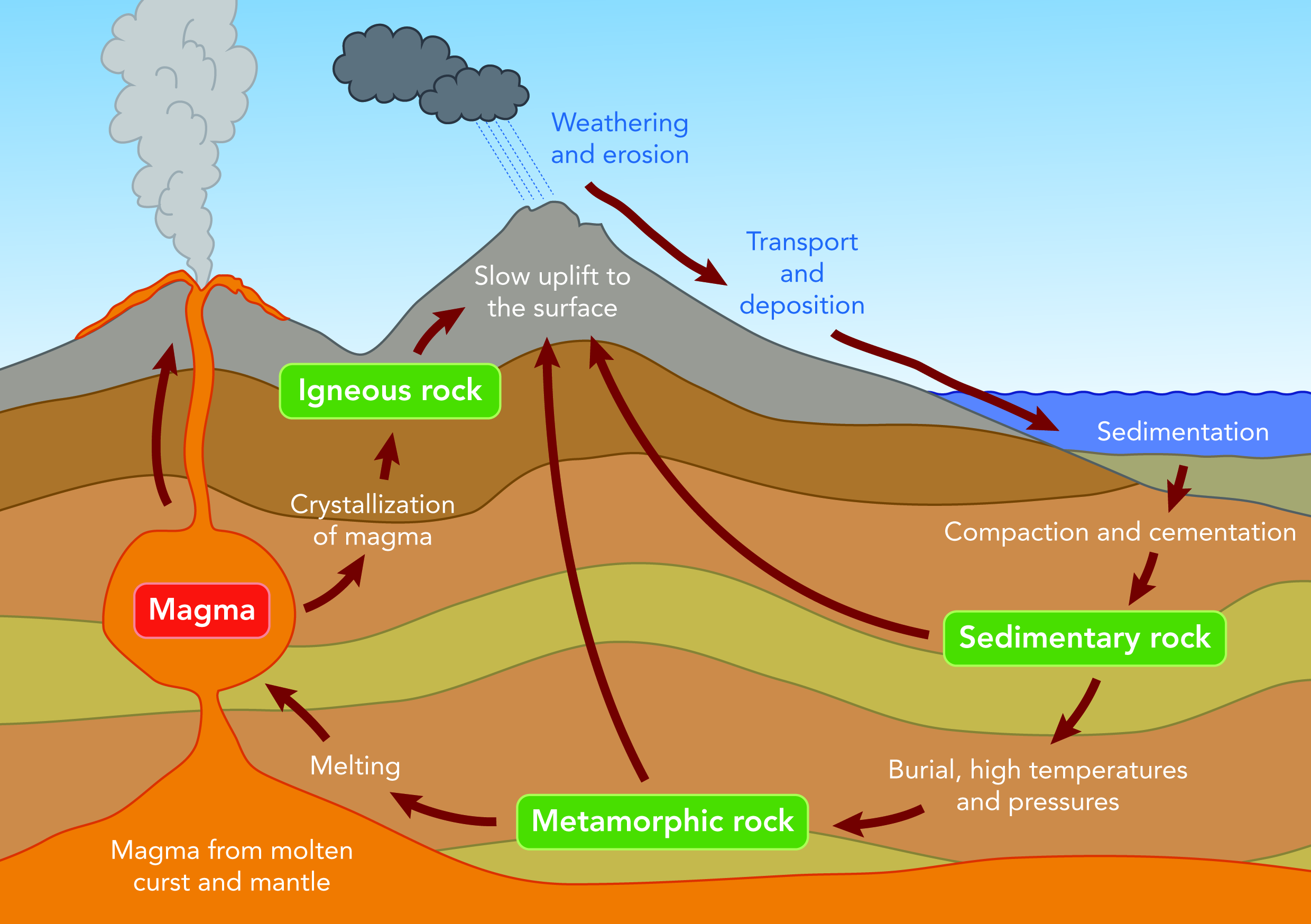
Easy Rock Cycle Diagram The geosphere. the geosphere includes the rocks and minerals on earth – from the molten rock and heavy metals in the deep interior of the planet to the sand on beaches and peaks of mountains. the geosphere also includes the abiotic (non living) parts of soils and the skeletons of animals that may become fossilized over geologic time. Rock is the most abundant thing on earth. rock is right under our feet! let’s look at what rock is, how it’s different from a mineral, the 3 types of rock, and the rock cycle. understanding the 3 types of rock helps us understand the natural process as the rock cycle is explained. in this post we also have a free printable. The rock cycle steps & science lesson. the rock cycle – a continuous process by which rocks are created, changed from one form to another, destroyed, and then formed again. a process taught in all earth science curricula, usually in the middle school or early high school years. and earth science is a fun science that can be super interactive!. The rock cycle is driven by two forces: earth’s internal heat, which causes material to move around in the core and mantle, driving plate tectonics. the hydrological cycle movement of water, ice, and air at the surface. the hydrological cycle is powered by the sun. figure 6.3 the rock cycle describes processes that form the three types of.

Geosphere And The Rock Cycle Diagram Color Earth Science Lessons The rock cycle steps & science lesson. the rock cycle – a continuous process by which rocks are created, changed from one form to another, destroyed, and then formed again. a process taught in all earth science curricula, usually in the middle school or early high school years. and earth science is a fun science that can be super interactive!. The rock cycle is driven by two forces: earth’s internal heat, which causes material to move around in the core and mantle, driving plate tectonics. the hydrological cycle movement of water, ice, and air at the surface. the hydrological cycle is powered by the sun. figure 6.3 the rock cycle describes processes that form the three types of.

Comments are closed.