Global Wind And Pressure Patterns
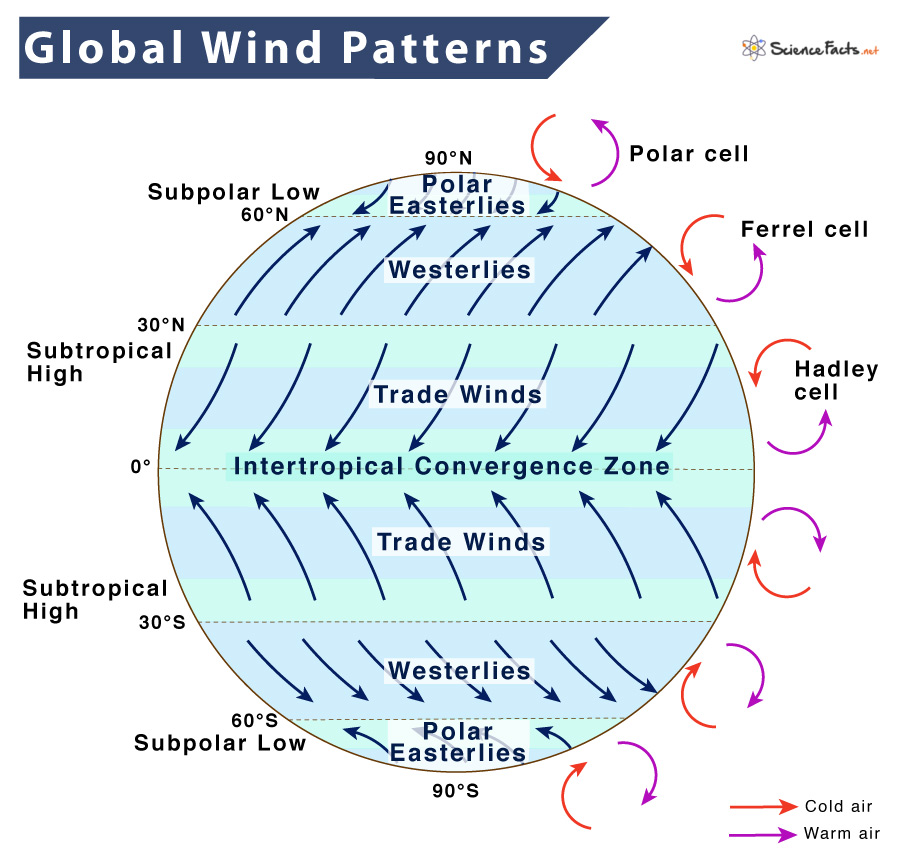
Global Winds Definition Patterns Belts And Causes This unique, permanent movement of winds across the surface of the earth due to permanent air pressure zones creates a distinct pattern known as global wind patterns or global wind systems. however, global winds do not move directly from north to south or south to north due to the rotation of the earth. Learn how the earth's rotation, insolation, and land sea distribution affect the surface wind and pressure patterns on an ideal and a real earth. explore the hadley cells, subtropical highs, itcz, monsoon, and polar regions.
Global Wind And Pressure Patterns See current wind, weather, ocean, and pollution conditions, as forecast by supercomputers, on an interactive animated map. updated every three hours. Learn how the earth's rotation, solar radiation, and pressure gradients create global wind and precipitation patterns. see diagrams, videos, and examples of the six hadley cells and their effects on weather and climate. Global atmospheric circulations. air flow on a planet with no rotation and no water. global atmospheric circulation is the movement of air around the planet. it explains how thermal energy and storm systems move over the earth's surface. without the earth’s rotation, tilt relative to the sun, and surface water, global circulation would be simple. The global wind belts are enormous and the winds are relatively steady. these winds are the result of air movement at the bottom of the major atmospheric circulation cells, where the air moves horizontally from high to low pressure. technology today allows anyone to see global wind patterns in real time, such as earth wind map.

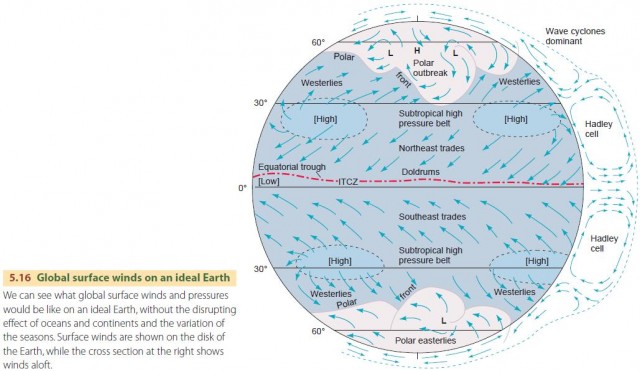
Global Wind Patterns Definition Global atmospheric circulations. air flow on a planet with no rotation and no water. global atmospheric circulation is the movement of air around the planet. it explains how thermal energy and storm systems move over the earth's surface. without the earth’s rotation, tilt relative to the sun, and surface water, global circulation would be simple. The global wind belts are enormous and the winds are relatively steady. these winds are the result of air movement at the bottom of the major atmospheric circulation cells, where the air moves horizontally from high to low pressure. technology today allows anyone to see global wind patterns in real time, such as earth wind map. Global wind patterns. large global wind systems are created by the uneven heating of the earth’s surface. these global wind systems, in turn, drive the oceans’ surface currents. to understand how global winds form and drive the major ocean currents, you need to know that wind is the basically the movement of air from an area of high. Especially the asian land mass causes significant deviations from the large scale pressure and wind belts (compare fig. 4.5 and in fig. 4.6). it can further be clearly observed that some tropical areas are dominated by trade winds (blowing in the same direction throughout the year), whereas other areas in the tropics and subtropics are.

Global Atmospheric Circulations Physical Geography Global wind patterns. large global wind systems are created by the uneven heating of the earth’s surface. these global wind systems, in turn, drive the oceans’ surface currents. to understand how global winds form and drive the major ocean currents, you need to know that wind is the basically the movement of air from an area of high. Especially the asian land mass causes significant deviations from the large scale pressure and wind belts (compare fig. 4.5 and in fig. 4.6). it can further be clearly observed that some tropical areas are dominated by trade winds (blowing in the same direction throughout the year), whereas other areas in the tropics and subtropics are.

Global Wind Patterns Environmental Impact Of Wind Energy Electrical A2z

Comments are closed.