Goods Utility

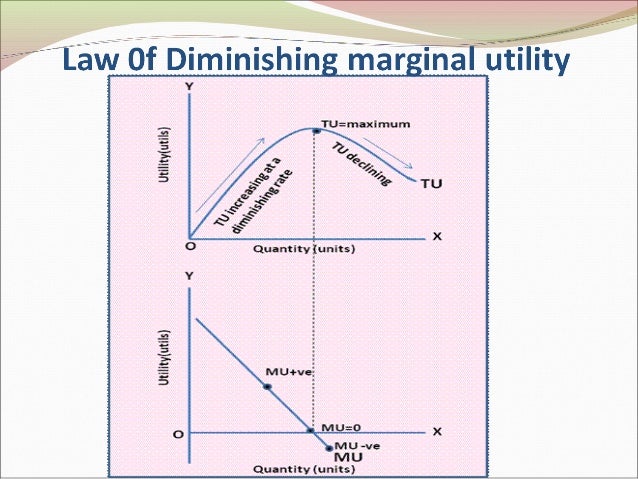
Goods Utility Utility can be used to measure the usefulness of goods and services to consumers. while there are limitations when more variables and differences appear in the market, various types of economic. The total utility curve in figure 7.1 “total utility and marginal utility curves” shows that mr. higgins achieves the maximum total utility possible from movies when he sees six of them each month. it is likely that his total utility curves for other goods and services will have much the same shape, reaching a maximum at some level of.

Goods Utility There are four main types of economic utility. the first is form utility or the amount of value that someone receives from goods or services they need. time utility has to do with the amount of. A utility function that describes a preference for one bundle of goods (x a) vs another bundle of goods (x b) is expressed as u (x a, x b). where there are perfect complements, the utility. In economics, utility refers to the satisfaction levels consumers receive from buying and using a product or service. according to utility theory, people make purchase decisions based on the degree of satisfaction they get from an item or service. that is why goods with higher utility are prioritized higher in a person’s budget. Utility and value, in economics, the determination of the prices of goods and services. the modern industrial economy is characterized by a high degree of interdependence of its parts. the supplier of components or raw materials, for example, must deliver the desired quantities of his products at the right moment and in the desired.

Solution Unit 1c Goods Utility Studypool In economics, utility refers to the satisfaction levels consumers receive from buying and using a product or service. according to utility theory, people make purchase decisions based on the degree of satisfaction they get from an item or service. that is why goods with higher utility are prioritized higher in a person’s budget. Utility and value, in economics, the determination of the prices of goods and services. the modern industrial economy is characterized by a high degree of interdependence of its parts. the supplier of components or raw materials, for example, must deliver the desired quantities of his products at the right moment and in the desired. At a price of $2 per pound, ms. andrews maximizes utility by purchasing 5 pounds of apples per month. when the price of apples falls to $1 per pound, the quantity of apples at which she maximizes utility increases to 12 pounds per month. it is through a consumer’s reaction to different prices that we trace the consumer’s demand curve for a. Utility functions, expressing utility as a function of the amounts of the various goods consumed, are treated as either cardinal or ordinal, depending on whether they are or are not interpreted as providing more information than simply the rank ordering of preferences among bundles of goods, such as information concerning the strength of.
Goods Utility At a price of $2 per pound, ms. andrews maximizes utility by purchasing 5 pounds of apples per month. when the price of apples falls to $1 per pound, the quantity of apples at which she maximizes utility increases to 12 pounds per month. it is through a consumer’s reaction to different prices that we trace the consumer’s demand curve for a. Utility functions, expressing utility as a function of the amounts of the various goods consumed, are treated as either cardinal or ordinal, depending on whether they are or are not interpreted as providing more information than simply the rank ordering of preferences among bundles of goods, such as information concerning the strength of.

Comments are closed.