Graphing Functions How To Graph Functions
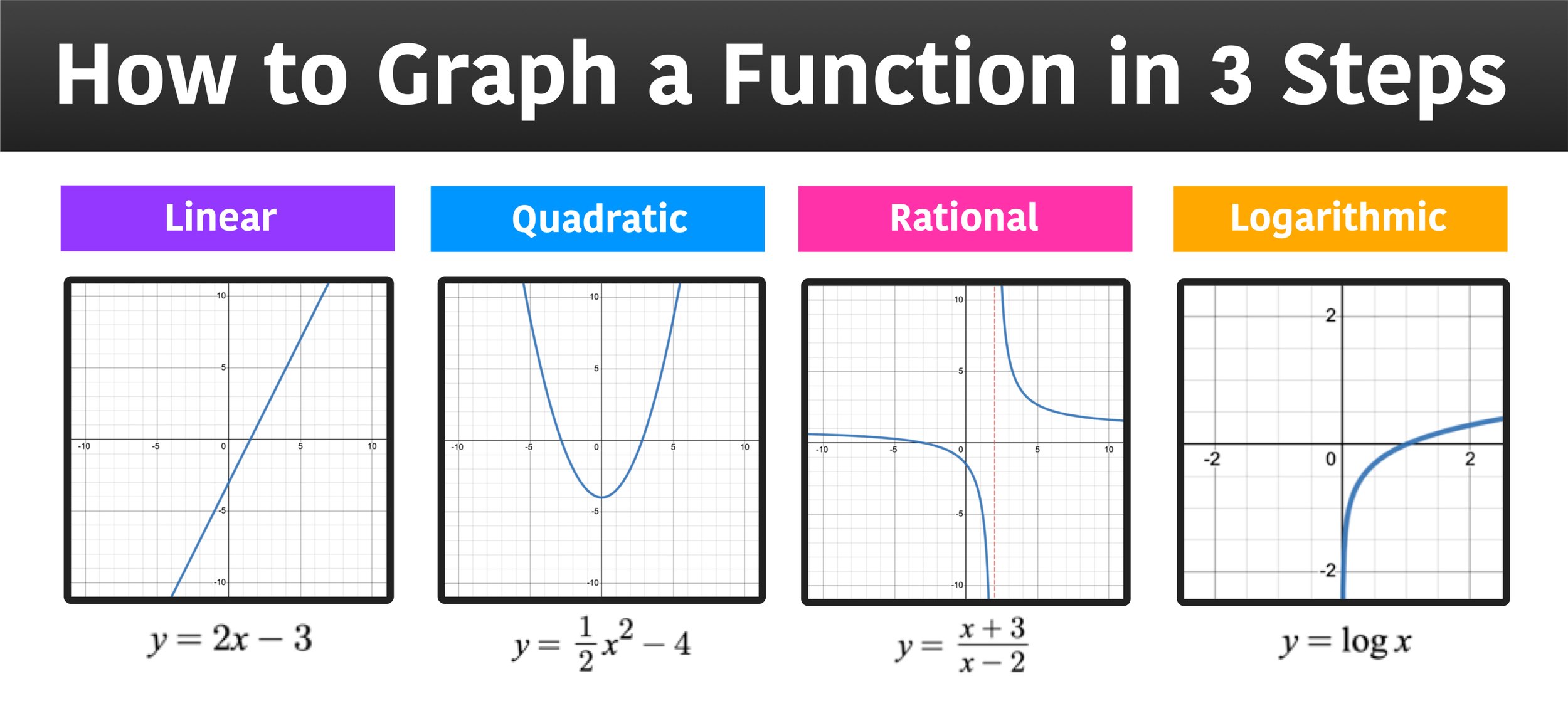
How To Graph A Function In 3 Easy Steps вђ Mashup Math To graph a function, i begin by determining the domain and range, which are the set of all possible inputs (x values) and outputs (y values) respectively. with this foundation, i plot points on the coordinate plane where each point represents an (x, y) pair that satisfies the function’s equation. for example, if i’m working with a simple. Graphing functions is drawing the curve that represents the function on the coordinate plane. if a curve (graph) represents a function, then every point on the curve satisfies the function equation. for example, the following graph represents the linear function f (x) = x 2. take any point on this line, say, ( 1, 3).

How To Graph A Function 6 Steps With Pictures Wikihow To graph a function ( f (x) ), i always begin by determining its domain and range. the domain of a function represents all the possible input values ( x ) can take, while the range is the set of all possible output values ( f (x) ) can produce. identifying these elements helps me understand the function’s behavior and where on the graph it. Graph : f (x) = 2x 3. to express this function on a graph (and all of the functions in this guide), we will be using the following 3 step method: step 1: identify the critical points and or any asymptotes. step 2: determine the points of the function. step 3: draw the line or curve and extend. Determining if a graph represents a function. the examples above were graphs of functions, but in the last section we talked about graphing relations and not just functions. however, functions are going to be the focus of what we work with in this course so this brings us to an important question: how do we know if a graph represents a function?. Draw two lines in a shape on a piece of paper. the horizontal line is your x axis. the vertical line is your y axis. 3. number your graph. mark both the x axis and the y axis with equally spaced numbers. for the x axis, the numbers are positive on the right side and negative on the left side.

Comments are closed.