House Electrical Voltage

House Electrical Voltage The standard voltage in different parts of the house can vary. while most outlets dish out the standard 110 120v or 220 240v, specialized outlets, like those for ovens or dryers, might have different requirements. consistent voltage isn’t just a fancy term; it’s crucial for the longevity of your appliances. So, the voltage delivered to homes with single phase service today is 120 240, and some are rated at 125 250, except for an occasional large house or apartment building with 3 phase service (3 hot wires). this type of system provides 120 volts to the neutral or ground, and 208 volts between the hot conductors.

What Is The Standard House Outlet Voltage The nec does not specify maximum voltage, but plus 5% is the accepted standard. this puts the acceptable voltage range of a nominal 120 volt receptacle at between 114 and 126 volts. you will rarely get a reading of exactly 120.0 volts. voltage is typically set a little higher at the tap at the electric utility’s transformer to allow for. Voltage differences: 110v, 115v, 120v, 220v, 230v, 240v. you'll often hear voltages in your home referred to as 110v, 115v, or 120v. this can be confusing but the bottom line is they are referring to the exact same thing. 120v is the ac voltage on a single hot wire in your home with respect to neutral (or ground). Electricity in homes is measured in several ways. current, measured in amperes (amps), represents the flow of electricity. voltage, measured in volts, is the electrical pressure driving the current. wattage, the product of amps and volts, measures the electrical power used. most u. s. homes receive 120 240 volt alternating current (ac) power. Residential voltage in the usa and canada is 120 240 volts ac. power enters the dwelling’s main electrical panel from a power company transformer as two 120 volt lines with phases that are 180 degrees apart. 120 and 240 volts (along with neutral and ground) is then distributed to outlet boxes (switch, outlet, light fixture, etc) throughout the dwelling.
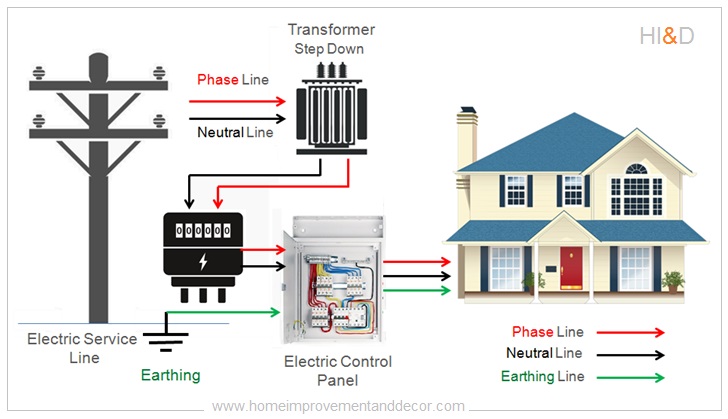
How Does House Electricity Work Wiring Diagram And Schematics Electricity in homes is measured in several ways. current, measured in amperes (amps), represents the flow of electricity. voltage, measured in volts, is the electrical pressure driving the current. wattage, the product of amps and volts, measures the electrical power used. most u. s. homes receive 120 240 volt alternating current (ac) power. Residential voltage in the usa and canada is 120 240 volts ac. power enters the dwelling’s main electrical panel from a power company transformer as two 120 volt lines with phases that are 180 degrees apart. 120 and 240 volts (along with neutral and ground) is then distributed to outlet boxes (switch, outlet, light fixture, etc) throughout the dwelling. Step 6. touch one tester probe to one of the silver lugs above the main breaker and the other tester probe to the remaining silver lug above the breaker. the multimeter tester should register a voltage between 210 and 250 volts. contact your service provider and an electrician for any voltage reading lower or higher than normal fluctuation. At the user end of the grid, the difference between 100 volts and 120 volts is so minute that they are unnoticeable by the end user. eventually, a national standard for electrical service delivery was adopted. today, across the us, it is accepted that you receive electrical service of 120 volts plus or minus ten percent.
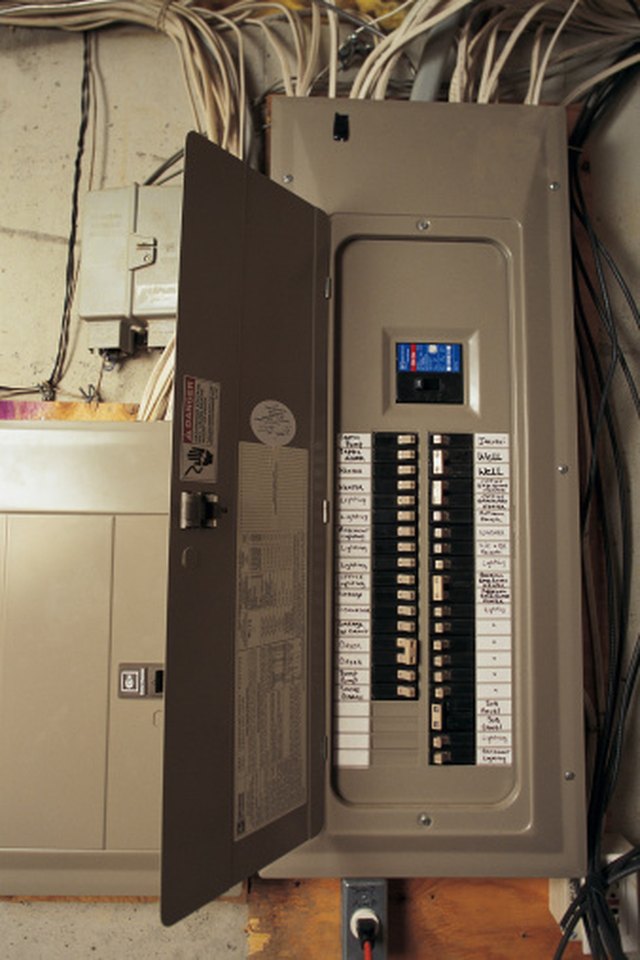

How To Check The Current Voltage In A House Hunker Step 6. touch one tester probe to one of the silver lugs above the main breaker and the other tester probe to the remaining silver lug above the breaker. the multimeter tester should register a voltage between 210 and 250 volts. contact your service provider and an electrician for any voltage reading lower or higher than normal fluctuation. At the user end of the grid, the difference between 100 volts and 120 volts is so minute that they are unnoticeable by the end user. eventually, a national standard for electrical service delivery was adopted. today, across the us, it is accepted that you receive electrical service of 120 volts plus or minus ten percent.

Comments are closed.