How Do Tem And Sem Electron Microscopes Differ From Light Microscopes

How Do Tem And Sem Electron Microscopes Differ From Light Microscopes Scanning electron microscope (sem) imagine you are in a dark room with a weak flashlight. to explore your surroundings, you might sweep the light across the room, much like someone reading a book: left to right and top to bottom. sem functions similarly, sweeping the electron beam across the sample and recording the electrons that bounce back. The main difference between sem and tem is that sem creates an image by detecting reflected or knocked off electrons, while tem uses transmitted electrons (electrons that are passing through the sample) to create an image. as a result, tem offers valuable information on the inner structure of the sample, such as crystal structure, morphology.
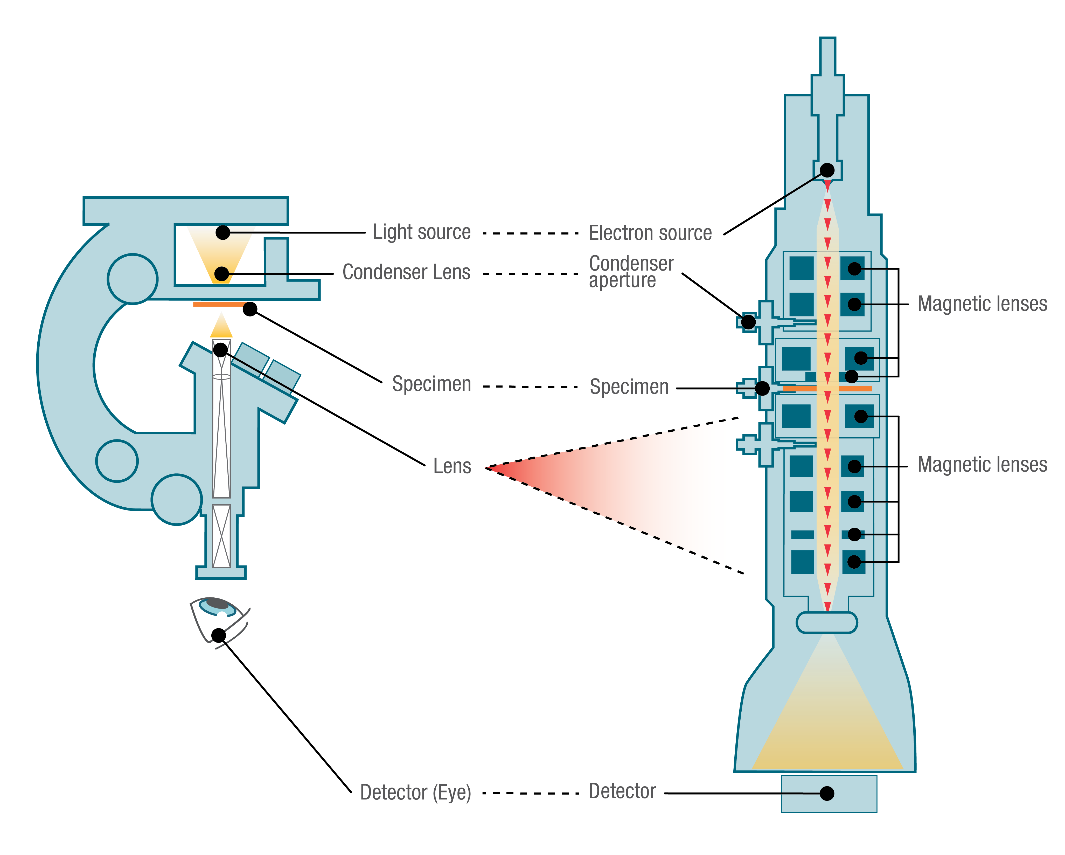
Light Microscope Vs Electron Microscope Life In Atomic Resolution Sem offers the best quality images of a sample's exterior, capturing its texture and composition with depth. it does this by directing a focused beam of electrons across the surface, collecting the emitted signals to form an image. in contrast, tem provides a window into the sample's interior, achieving higher resolution images that can display. In sem, the sample, located at the base of the electron column, is scanned and the resulting electron scattering is analyzed to produce an image. in tem, the sample is placed in the middle of the microscope and electrons pass through the sample before being collected. tem offers information on ultrathin samples' inner structure, while sem. The two mainstay techniques are transmission electron microscopy (tem) and scanning electron microscopy (sem). both methods use an electron source to create an image of a sample's surface or its. Sem and tem differ in the manner in which users operate their systems. sems usually use up to 30 kv of acceleration voltages, while tem users can configure it between 60 and 300 kv. tem magnifications are also much higher than the capacity of sems. tem users can magnify their samples more than 50 million times, while sem users can only magnify.
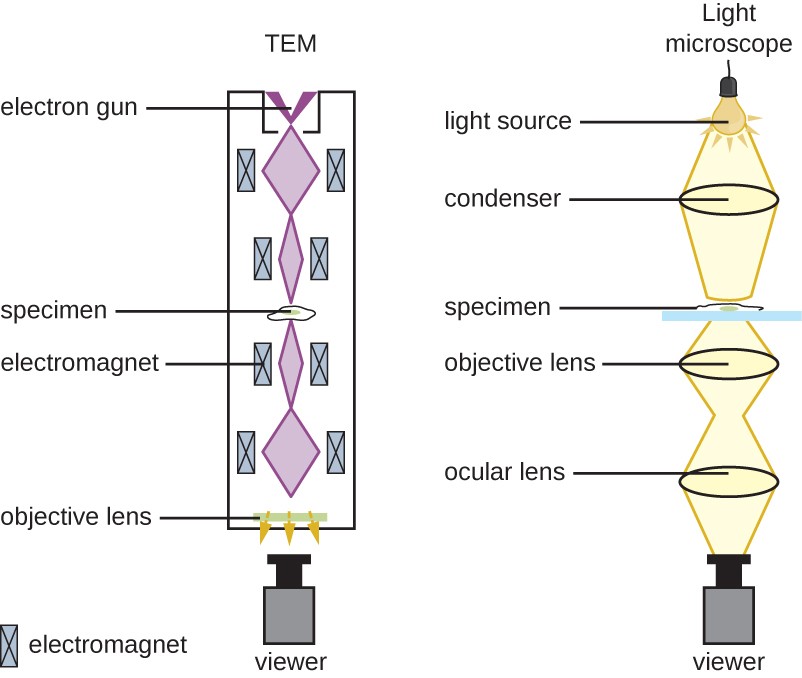
Instruments Of Microscopy Microbiology The two mainstay techniques are transmission electron microscopy (tem) and scanning electron microscopy (sem). both methods use an electron source to create an image of a sample's surface or its. Sem and tem differ in the manner in which users operate their systems. sems usually use up to 30 kv of acceleration voltages, while tem users can configure it between 60 and 300 kv. tem magnifications are also much higher than the capacity of sems. tem users can magnify their samples more than 50 million times, while sem users can only magnify. Technicians that are trained on the proper use of the microscope, electron emitters that need to be replaced much like light bulbs, and the electricity to run the machines all add to the cost. convenience and ease of use. transmission electron microscopes won’t fill a room, but they are wider and taller than a scanning electron microscope. How a scanning electron microscope (sem) works. a scanning electron microscope scans a beam of electrons over a specimen to produce a magnified image of an object. that's completely different from a tem, where the beam of electrons goes right through the specimen. electrons are fired into the machine.

Comments are closed.