How Metamorphic Rock Is Formed
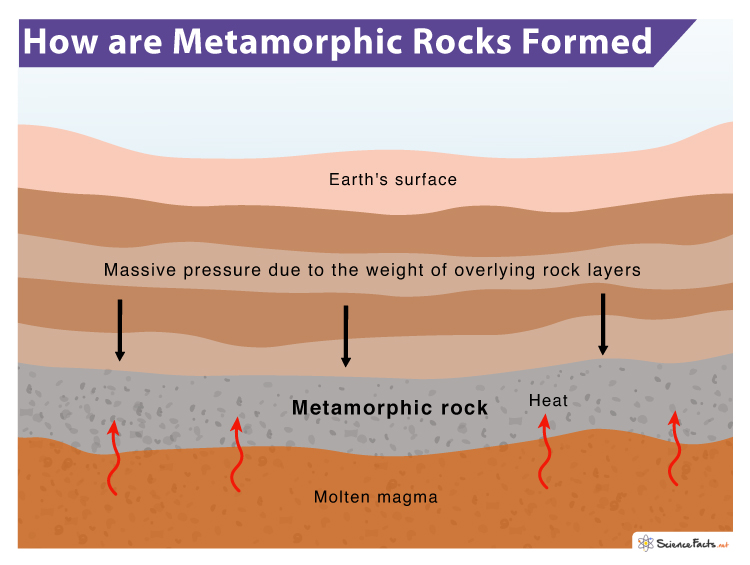
Metamorphic Rocks вђ Definition Formation Types Examples Schist: characterized by its sheet like structure and formed typically from mudstone or shale. its platy minerals are larger than those in slate. gneiss: has a banded or foliated appearance, usually formed from high grade metamorphism of igneous rocks like granite. marble: marble forms from limestone or dolomite. Sedimentary rock. noun. rock formed from fragments of other rocks or the remains of plants or animals. uplift. noun. elevation of the earth's surface due to tectonic or other natural activity. metamorphic rocks start as one type of rock and—with pressure, heat, and time—gradually change into a new type of rock.
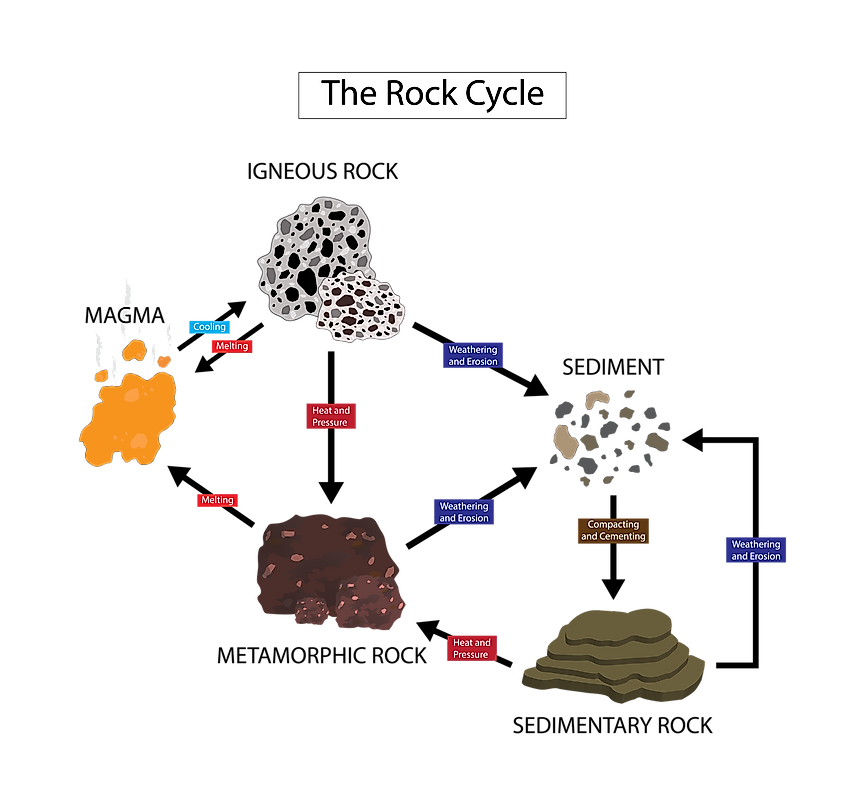
How Are Metamorphic Rocks Formed The Knowledge Library Metamorphic rock, any of a class of rocks that result from the alteration of preexisting rocks in response to changing environmental conditions, such as variations in temperature, pressure, and mechanical stress, and the addition or subtraction of chemical components. the preexisting rocks may be igneous, sedimentary, or other metamorphic rocks. Metamorphic rock is formed under extreme heat or pressure. unlike other types of rock, metamorphic rocks start as rocks which are then transformed into different rocks. metamorphic rocks are classified as either foliated or non foliated depending on their mineral structure and pattern. metamorphic rocks are rocks that have changed from one type. Metamorphic rock can be formed locally when rock is heated by the intrusion of hot molten rock called magma from the earth's interior. the study of metamorphic rocks (now exposed at the earth's surface following erosion and uplift) provides information about the temperatures and pressures that occur at great depths within the earth's crust. Metamorphic rocks form when rocks are subjected to high heat, high pressure, hot mineral rich fluids or, more commonly, some combination of these factors. conditions like these are found deep within the earth or where tectonic plates meet. the process of metamorphism does not melt the rocks, but instead transforms them into denser, more compact.

Ppt Rock Cycle Sec 2 1 Powerpoint Presentation Id 2020031 Metamorphic rock can be formed locally when rock is heated by the intrusion of hot molten rock called magma from the earth's interior. the study of metamorphic rocks (now exposed at the earth's surface following erosion and uplift) provides information about the temperatures and pressures that occur at great depths within the earth's crust. Metamorphic rocks form when rocks are subjected to high heat, high pressure, hot mineral rich fluids or, more commonly, some combination of these factors. conditions like these are found deep within the earth or where tectonic plates meet. the process of metamorphism does not melt the rocks, but instead transforms them into denser, more compact. Skarn: also known as tactite, it is a non foliated metamorphic rock. it forms when carbonate rocks near a magma body are altered by contact metamorphism and metasomatism. slate: a foliated metamorphic rock formed through the metamorphism of shale. it is a low grade metamorphic rock that breaks into thin and fragile pieces. Metamorphism is the changing of rocks by heat and pressure. during this process, rocks change either physically and or chemically. they change so much that they become an entirely new rock. figure 4.13: the platy layers in this large outcrop of metamorphic rock show the effects of pressure on rocks during metamorphism.
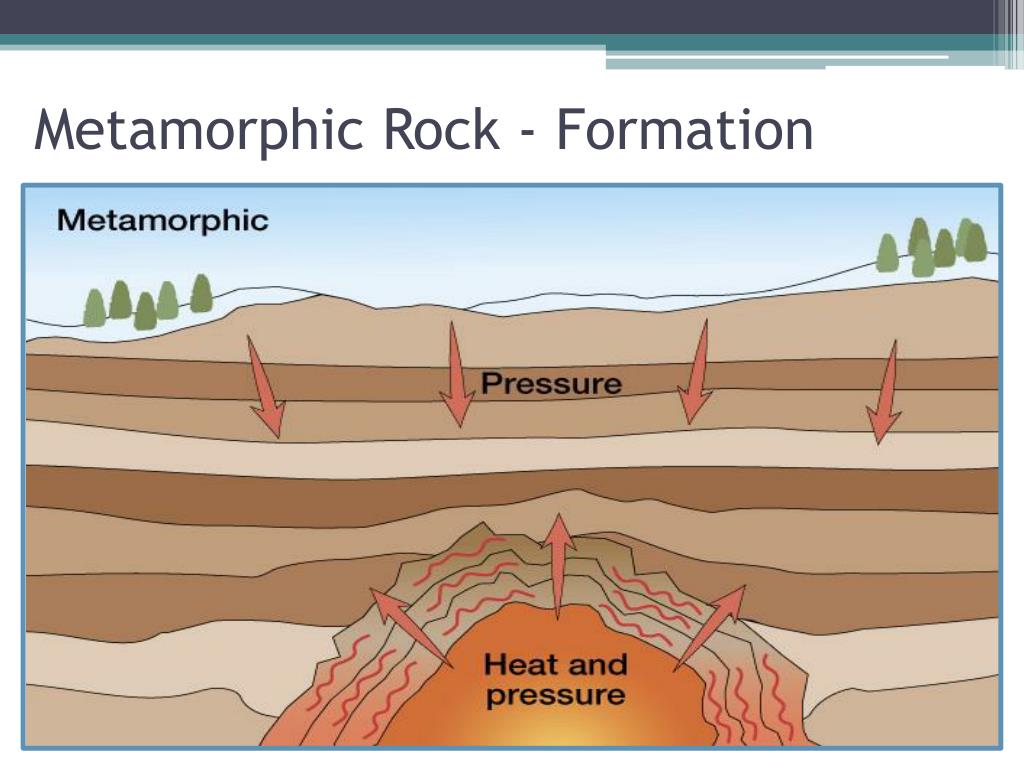
Metamorphic Rock Formation Skarn: also known as tactite, it is a non foliated metamorphic rock. it forms when carbonate rocks near a magma body are altered by contact metamorphism and metasomatism. slate: a foliated metamorphic rock formed through the metamorphism of shale. it is a low grade metamorphic rock that breaks into thin and fragile pieces. Metamorphism is the changing of rocks by heat and pressure. during this process, rocks change either physically and or chemically. they change so much that they become an entirely new rock. figure 4.13: the platy layers in this large outcrop of metamorphic rock show the effects of pressure on rocks during metamorphism.

Comments are closed.