How Multiple Sclerosis Ms Affects The Myelin Shealth

Multiple Sclerosis Nursing Tutorials Multiple sclerosis (ms) is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune cells attack and damage the myelin sheath in the central nervous system (cns), which includes the brain, spinal cord, and. Multiple sclerosis (ms) is the most common demyelinating and an autoimmune disease of the central nervous system characterized by immune mediated myelin and axonal damage, and chronic axonal loss attributable to the absence of myelin sheaths. t cell subsets (th1, th2, th17, cd8 , nkt, cd4 cd25 t regulatory cells) and b cells are involved.
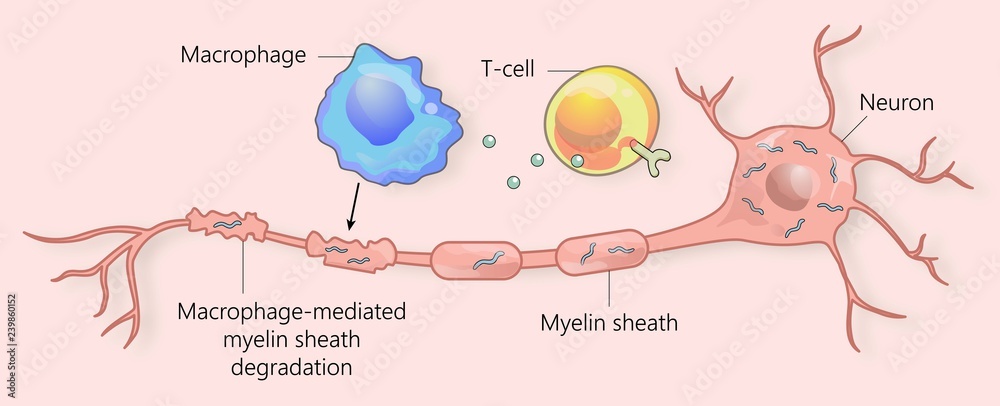
Multiple Sclerosis And Myelin Sheath Breakdown Stock Illustration In ms, the immune system launches an inflammatory attack in the central nervous system. this inflammation leads to demyelination — the deterioration and loss of the myelin sheath — and causes. Updated on may 29, 2024. multiple sclerosis (ms) is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the central nervous system (cns), damaging the protective myelin around nerves. damage to the myelin can impair the transmission of nerve signals, causing ms symptoms such as numbness and vision problems. Myelin sheath function. the myelin sheath serves three main purposes: it acts as insulation, similar to the plastic coating around electrical wires, keeping your nerve cells safe. it helps. The greatest unmet need in multiple sclerosis (ms) are treatments that delay, prevent or reverse progression. one of the most tractable strategies to achieve this is to therapeutically enhance endogenous remyelination; doing so restores nerve conduction and prevents neurodegeneration. the biology of remyelination—centred on the activation.

Comments are closed.