How The Sun S Path Can Inform Design Buildinggreen
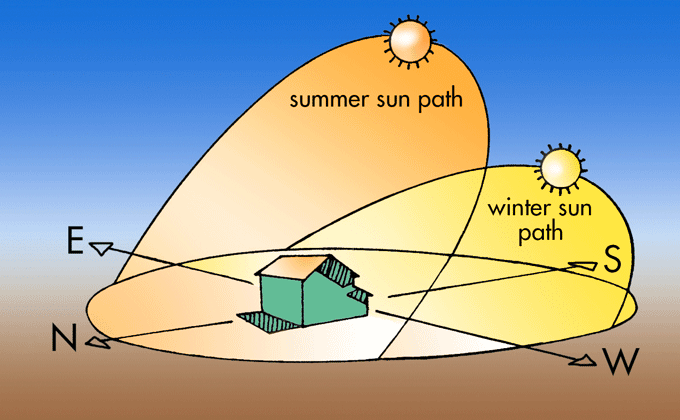
How The Sun S Path Can Inform Design Buildinggreen How the sun's path can inform design. designing a building with the sun in mind can help reduce both heating and cooling loads. sun shining into a building provides free heat and natural light. it can also create glare and, when the heat isn’t needed, discomfort and added demand for cooling. using sunlight when it’s needed and deflecting. Relative to building design, solar access generally refers to access to the sun’s apparent path across the southern sky (in the northern hemisphere). various devices were developed during the 1970s to simplify the task of determining solar access on a particular site, a few of which are still on the market.

Study Of Building Design Using Sun Path Download Scientific Diagram Sun analysis is the process of studying the sun's path across the sky and its variations throughout the year, and how this affects a specific location. while it is a fundamental aspect of permaculture design, it also extends its importance far beyond, touching various other fields. knowing when, where, and for how long the sun's rays will hit. Sun path diagrams play a crucial role in architecture by providing valuable information on the sun’s movement throughout the year. by analyzing these diagrams, architects can optimize solar heat gain and improve energy efficiency in their designs. one key aspect of optimizing solar heat gain is determining the orientation of a building. Sun, wind and light: architectural design strategies, 2nd edition. green building education. g. z. brown and mark dekay. john wiley & sons, 2001. paperback, 382 pages, $54.95. the building research establishment office building (in garston, uk) uses a stack ventilation strategy for cooling. A sun path diagram map is a graphical representation of the position of the sun in the sky at different times of the year. it is a useful tool for understanding solar positioning and can be used in various applications, such as architecture, urban planning, and solar energy system design. the sun’s position in the sky changes throughout the.

Sun Path Diagrams Architecture Sun, wind and light: architectural design strategies, 2nd edition. green building education. g. z. brown and mark dekay. john wiley & sons, 2001. paperback, 382 pages, $54.95. the building research establishment office building (in garston, uk) uses a stack ventilation strategy for cooling. A sun path diagram map is a graphical representation of the position of the sun in the sky at different times of the year. it is a useful tool for understanding solar positioning and can be used in various applications, such as architecture, urban planning, and solar energy system design. the sun’s position in the sky changes throughout the. The sun’s path, also known as its trajectory or arc, refers to the apparent movement of the sun as observed from the earth’s surface throughout the day. understanding the sun’s path is essential for architects and designers as it directly impacts building orientation, layout, and overall environmental performance. The sun stays in the sky for an average of 14 hours out of the 24 and travels at high altitude in the middle of the day, creating short shadows and barely penetrating through north facing windows – a blessing which can be further helped by a 450 600mm wide roof eave. in the morning and afternoon however, the sun is low enough on the horizon.

Sun Path Diagrams Architecture The sun’s path, also known as its trajectory or arc, refers to the apparent movement of the sun as observed from the earth’s surface throughout the day. understanding the sun’s path is essential for architects and designers as it directly impacts building orientation, layout, and overall environmental performance. The sun stays in the sky for an average of 14 hours out of the 24 and travels at high altitude in the middle of the day, creating short shadows and barely penetrating through north facing windows – a blessing which can be further helped by a 450 600mm wide roof eave. in the morning and afternoon however, the sun is low enough on the horizon.

Comments are closed.