How To Describe The Inside Of A Typical Cell Quora
How To Describe The Inside Of A Typical Cell Quora We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. 1. a prokaryotic cell. there is only one membrane in prokaryotes, the cell membrane, and only one compartment in prokaryotic cells, the cytoplasm. that does not preclude a certain level of organization in prokaryotes, but it is not as complex as eukaryotes. the genomic dna is usually organized in a central nucleoid.

Biochemistry Lecture The genetic information within each cell acts as a sort of instruction manual, telling a cell how to function and replicate. why don’t we take a look at the inside of a typical cell? typical eukaryotic cell. image from a&p 6. the plasma membrane is exactly what it sounds like: a membrane made of plasma. Organelles are small structures within the cytoplasm that carry out functions necessary to maintain homeostasis in the cell. they are involved in many processes, for example energy production, building proteins and secretions, destroying toxins, and responding to external signals. organelles are considered either membranous or non membranous. The vacuole. the vacuole is a very large organelle that can occupy up to 90% of the interior space of plant cells. one of its key functions is storage. the vacuole is filled with cell sap, which consists mainly of water but also contains proteins, sugars, and other molecules. another function of the vacuole is to maintain turgor pressure, which. The plasma (cell) membrane separates the inner environment of a cell from the extracellular fluid. it is composed of a fluid phospholipid bilayer (two layers of phospholipids) as shown in figure 4.1.2 4.1. 2 below, and other molecules. not many substances can cross the phospholipid bilayer, so it serves to separate the inside of the cell from.
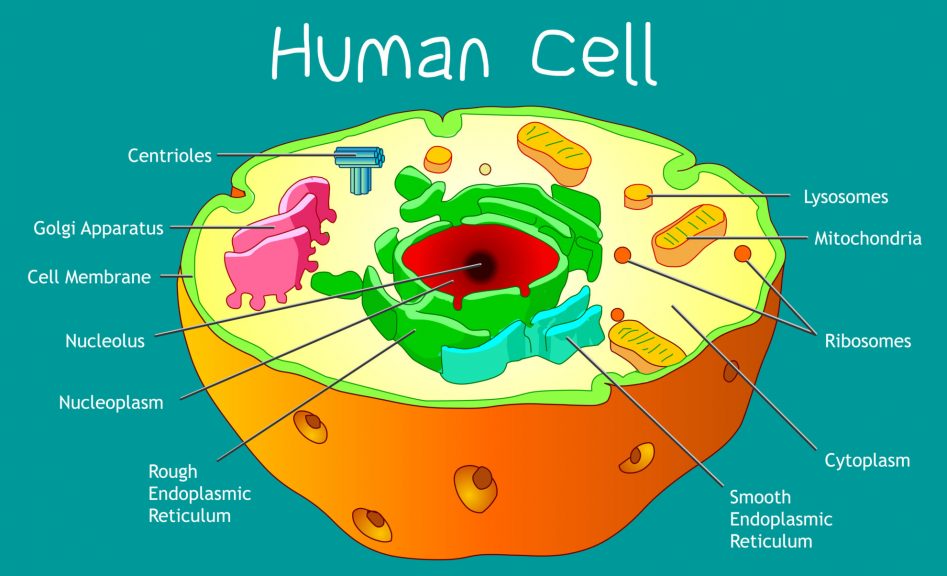
Human Cell Diagram To Label The vacuole. the vacuole is a very large organelle that can occupy up to 90% of the interior space of plant cells. one of its key functions is storage. the vacuole is filled with cell sap, which consists mainly of water but also contains proteins, sugars, and other molecules. another function of the vacuole is to maintain turgor pressure, which. The plasma (cell) membrane separates the inner environment of a cell from the extracellular fluid. it is composed of a fluid phospholipid bilayer (two layers of phospholipids) as shown in figure 4.1.2 4.1. 2 below, and other molecules. not many substances can cross the phospholipid bilayer, so it serves to separate the inside of the cell from. A cell is the smallest living organism and the basic unit of life on earth. together, trillions of cells make up the human body. cells have three parts: the membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm. When the central vacuole holds more water, the cell gets larger without having to invest a lot of energy in synthesizing new cytoplasm. 2.3: eukaryotic cell: structure and function is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. by definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane bound nucleus, a.

Eukaryotic Cells Biology I A cell is the smallest living organism and the basic unit of life on earth. together, trillions of cells make up the human body. cells have three parts: the membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm. When the central vacuole holds more water, the cell gets larger without having to invest a lot of energy in synthesizing new cytoplasm. 2.3: eukaryotic cell: structure and function is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. by definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane bound nucleus, a.

Comments are closed.