How To Solve A Linear Programming Problem Using The Graphical Method
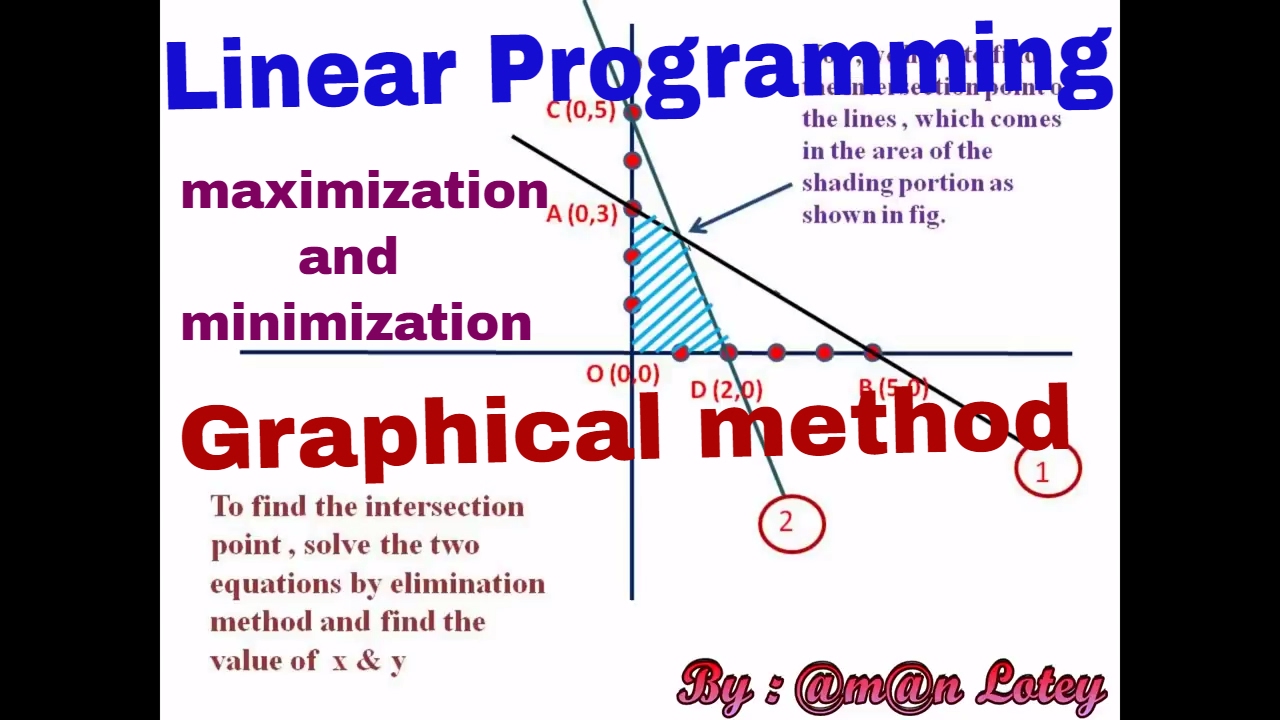
How To Solve Linear Programming Problem Class 12 Graphical Methodођ In this lesson we learn how to solve a linear programming problem using the graphical method with an example. we also see an example for an in feasible lp.th. Graphical solution of a linear programming problems. we can solve linear programming problems using two different methods are, corner point methods; iso cost methods; corner point methods. to solve the problem using the corner point method you need to follow the following steps: step 1: create mathematical formulation from the given problem. if.
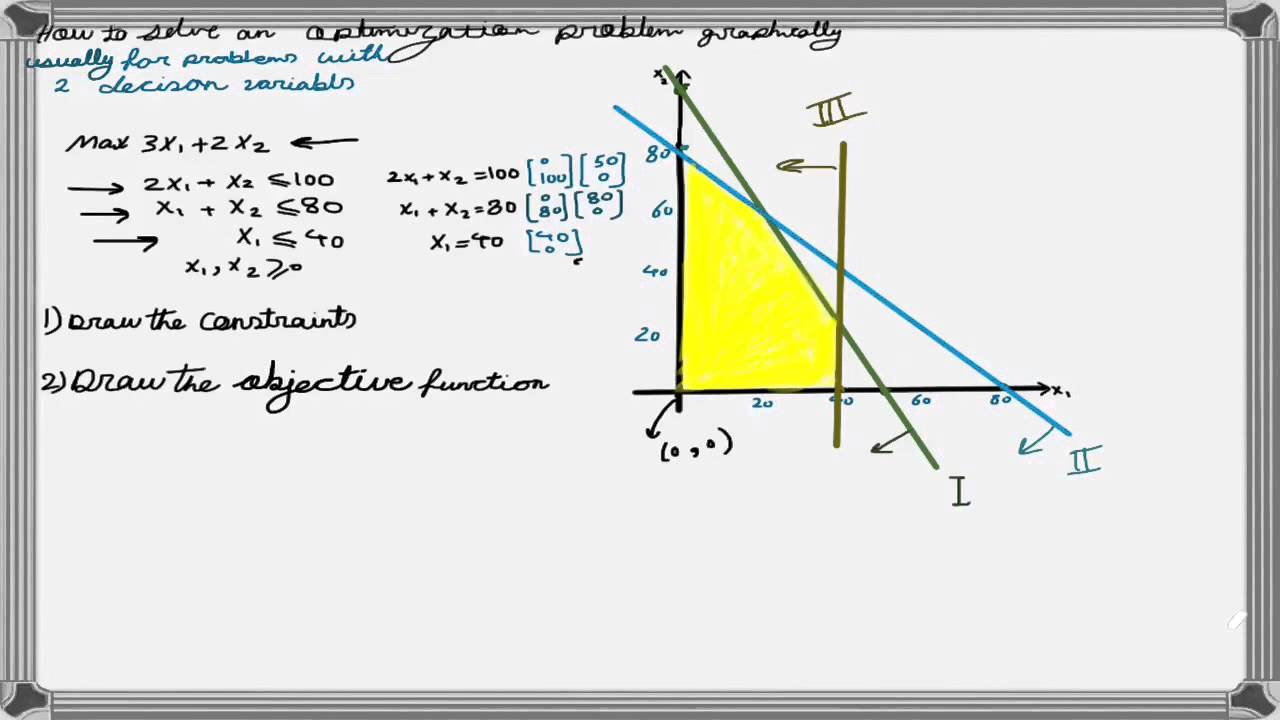
How To Solve A Linear Programming Problem Using The Graphical Method The use of our calculator is very simple and intuitive, however, we will explain its use step by step: before starting, you must have made the approach of the model to be optimized. remember that for the graphical method we normally work with 2 decision variables. you must enter the coefficients of the objective function and the constraints. A graphical method for solving linear programming problems is outlined below. solving linear programming problems – the graphical method 1. graph the system of constraints. this will give the feasible set. 2. find each vertex (corner point) of the feasible set. 3. substitute each vertex into the objective function to determine which vertex. Answer: we can solve the lpp with the graphical method by following these steps: 1st step: first of all, formulate the lp problem. 2nd step: then, make a graph and plot the constraint lines over there. 3rd step: determine the valid part of each constraint line. 4th step: recognize the possible solution area. If this is the case, then you have a bounded linear programming problem. if the dog could walk infinitely in any one direction, then the problem is unbounded. in the past example, you can see that the line of maximum profit will always touch the boundary of the feasible region. that observation inspires the fundamental theorem of linear.

Comments are closed.