How To Use The Triangle Angle Bisector Theorem
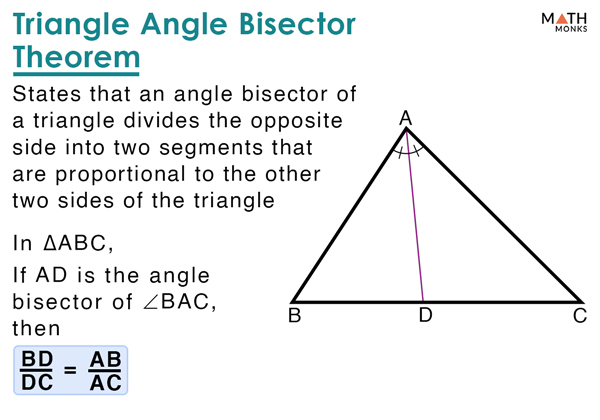
Angle Bisector Of A Triangle вђ Definition Theorem Examples Draw an angle say ∠abc, angled at b. using a compass, and taking b as centre and any radius, draw an arc intersecting ba at p and bc at q, respectively. now taking p and q as the centre and with the same radius, draw two arcs intersecting each other at r. join the vertex b to point r and draw the ray br. The converse of angle bisector theorem states that if the sides of a triangle satisfy the following condition "if a line drawn from a vertex of a triangle divides the opposite side into two parts such that they are proportional to the other two sides of the triangle", it implies that the point on the opposite side of that angle lies on its angle bisector.
Angle Bisector Of A Triangle вђ Definition Theorem Examples The angle bisector theorem is concerned with the relative lengths of the two segments that a triangle's side is divided into by a line that bisects the opposite angle. it equates their relative lengths to the relative lengths of the other two sides of the triangle. definition. proof of angle bisector theorem. using the angle bisector theorem. In geometry, the angle bisector theorem is concerned with the relative lengths of the two segments that a triangle 's side is divided into by a line that bisects the opposite angle. it equates their relative lengths to the relative lengths of the other two sides of the triangle. note that this theorem is not to be confused with the inscribed. Interior angle bisector theorem. the interior angle bisector theorem is simply referred to as angle bisector theorem. hence, an interior angle bisector of a triangle divides the opposite side in two parts such that the ratio of the two line segments is proportional to the ratio of the other two sides. Angle bisector theorem. an angle bisector cuts an angle exactly in half. one important property of angle bisectors is that if a point is on the bisector of an angle, then the point is equidistant from the sides of the angle. this is called the angle bisector theorem. in other words, if bd−→− b d → bisects ∠abc ∠ a b c, ba−→−.

Angle Bisector Of A Triangle Interior angle bisector theorem. the interior angle bisector theorem is simply referred to as angle bisector theorem. hence, an interior angle bisector of a triangle divides the opposite side in two parts such that the ratio of the two line segments is proportional to the ratio of the other two sides. Angle bisector theorem. an angle bisector cuts an angle exactly in half. one important property of angle bisectors is that if a point is on the bisector of an angle, then the point is equidistant from the sides of the angle. this is called the angle bisector theorem. in other words, if bd−→− b d → bisects ∠abc ∠ a b c, ba−→−. What the angle bisector theorem is and its proofwatch the next lesson: khanacademy.org math geometry triangle properties angle bisectors v angle. If a ray bisects an angle of a triangle, then it divides the opposite side of the triangle into segments that are proportional to the other two sides. the following figure gives an example of the angle bisector theorem. scroll down the page for more examples and solutions. using the triangle angle bisector theorem to solve a problem.

Comments are closed.