Human Ear Structure And Anatomy Online Biology Notes
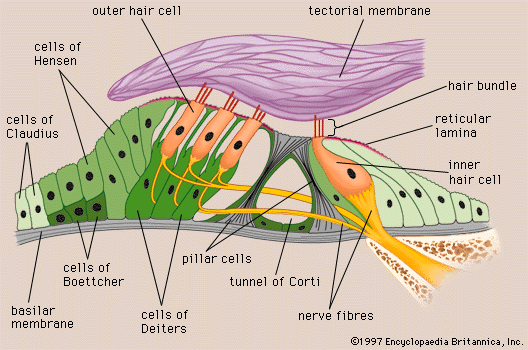
Human Ear Structure And Anatomy Online Biology Notes Organ of corti is an organized structure consisting of hair cells and supporting cells. hair cells are arranged in rows along the length. the outer hair cells are arranged in three rows and inner hair cells are arranged in single row. each outer and inner hair cell have sensory hair which are specialized microvilli. human ear: structure and anatomy. Ear definition. the ear is the organ found in animals which is designed to perceive sounds. most animals have some sort of ear to perceive sounds, which are actually high frequency vibrations caused by the movement of objects in the environment. the human ear picks up and interprets high frequency vibrations of air, while the sound sensing.

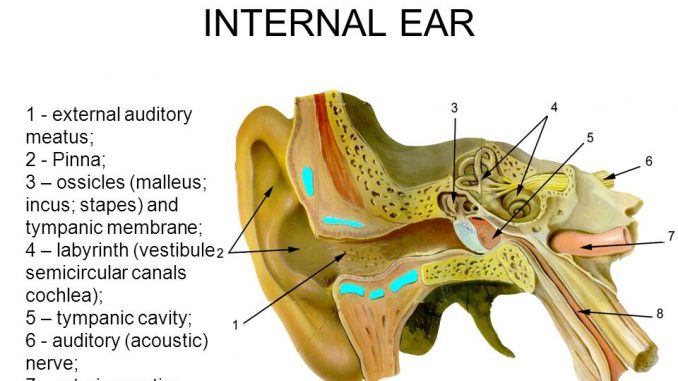
Structure And Function Of Human Ear With Diagram Teachoo Human ear, organ of hearing and equilibrium that detects and analyzes sound by transduction and maintains the sense of balance. anatomically, the ear has three distinguishable parts: the outer, middle, and inner ear. learn about the anatomy and physiology of the human ear in this article. Human ear. 32,77,062. the ear is a sensitive organ of the human body. it is mainly concerned with detecting, transmitting and transducing sound. maintaining a sense of balance is another important function performed by the human ear. let us have an overview of the structure and functions of the human ear. 3. internal ear: there is a body cavity on each side enclosed in the hard periotic bone which contains the perilymph. the later corresponds to the cerebrospinal fluid. a structure, the membranous labyrinth floats in the perilymph. the membranous labyrinth consists of three semicircular ducts, utricle, saccule, endolymphaticus and cochlea. The pinna is made of cartilage. • the outer ear is concerned with the transmission of sound. • the outer ear consists of the pinna, the ear canal and the outer layer of the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane. • the ear canal is filled with air and is about 2.5cm long. • ear wax is part of the ears protection mechanism.

Human Ear Anatomy Parts Of Ear Structure Diagram And Ear Problem 3. internal ear: there is a body cavity on each side enclosed in the hard periotic bone which contains the perilymph. the later corresponds to the cerebrospinal fluid. a structure, the membranous labyrinth floats in the perilymph. the membranous labyrinth consists of three semicircular ducts, utricle, saccule, endolymphaticus and cochlea. The pinna is made of cartilage. • the outer ear is concerned with the transmission of sound. • the outer ear consists of the pinna, the ear canal and the outer layer of the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane. • the ear canal is filled with air and is about 2.5cm long. • ear wax is part of the ears protection mechanism. The ear is a complex part of an even more complex sensory system. it is situated bilaterally on the human skull, at the same level as the nose. the main functions of the ear are, of course, hearing, as well as constantly maintaining balance. the ear is anatomically divided into three portions: external ear. middle ear. The ear canal, or the external acoustic meatus, is a short, curved tube that burrows through the temporal bone for about 1 inch or 2 and a half centimeters and ends at the tympanic membrane. on the inside, the ear canal is covered by skin, along with hair follicles and ceruminous glands which secrete cerumen, or the sticky, yellow ish.
Human Ear Structure And Anatomy Online Biology Notes The ear is a complex part of an even more complex sensory system. it is situated bilaterally on the human skull, at the same level as the nose. the main functions of the ear are, of course, hearing, as well as constantly maintaining balance. the ear is anatomically divided into three portions: external ear. middle ear. The ear canal, or the external acoustic meatus, is a short, curved tube that burrows through the temporal bone for about 1 inch or 2 and a half centimeters and ends at the tympanic membrane. on the inside, the ear canal is covered by skin, along with hair follicles and ceruminous glands which secrete cerumen, or the sticky, yellow ish.

Human Ear Structure Function Parts Britannica

Comments are closed.