Human Skin Cell Micrograph
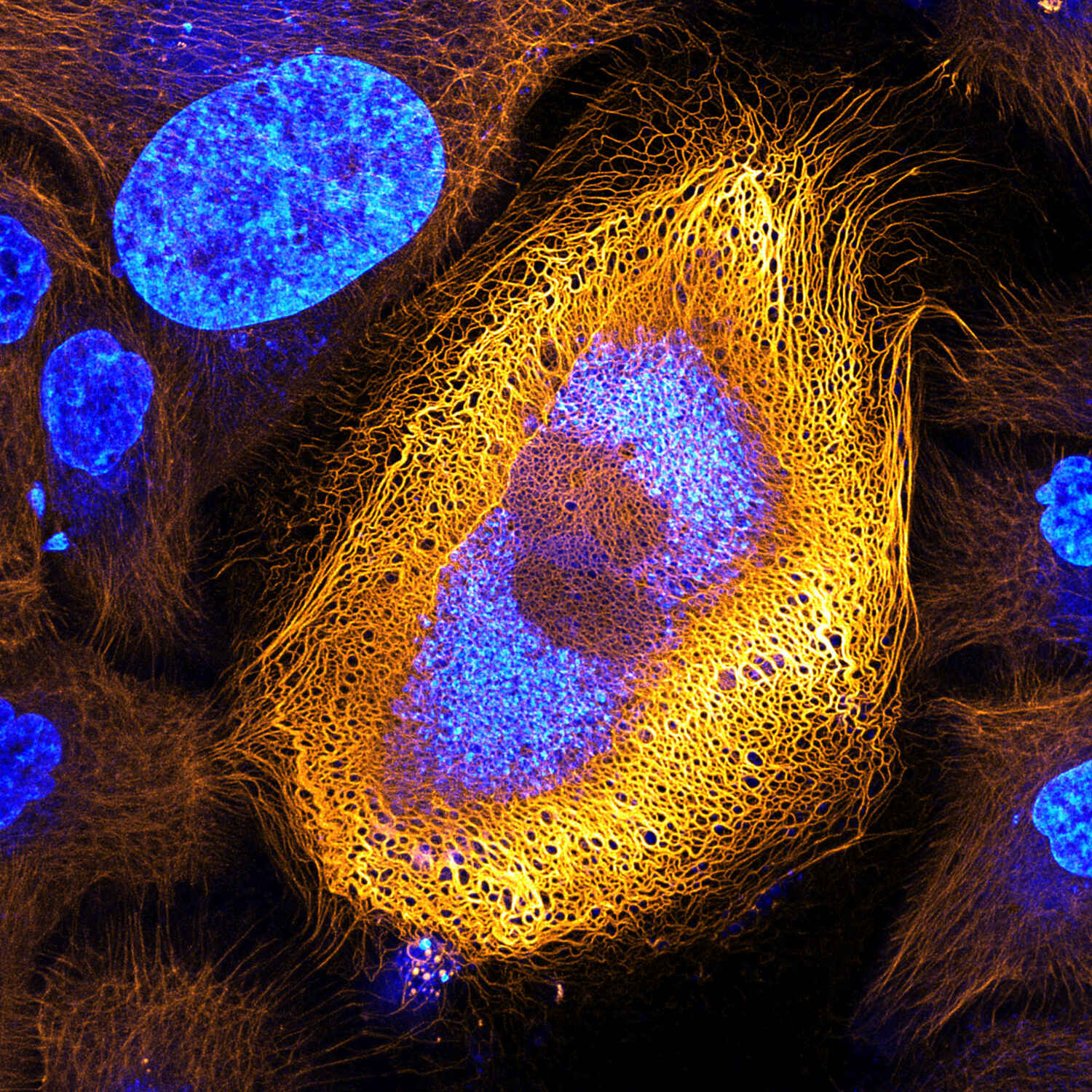
Stunning Microscopic View Of Human Skin Cells Wins 2017 Nikon Small This article will describe the anatomy and histology of the skin. undoubtedly, the skin is the largest organ in the human body; literally covering you from head to toe. the organ constitutes almost 8 20% of body mass and has a surface area of approximately 1.6 to 1.8 m2, in an adult. it is comprised of three major layers: epidermis, dermis and. Final thoughts. depending on the strength of the microscope you use, the skin can look like a landscape of layered scales or, with a weaker microscope, a surface that’s crisscrossed with lines and dotted with pores. hairs will appear large and thick, and if you’re lucky, you may even spot a few skin mites! but, as alien as our skin close.

Human Skin Cells Sem Stock Image C015 0762 Science Photo Library Human epidermal cells make up part of the largest organ in the body, the integumentary system. this vital organ is composed of skin, nails, hair, and its associated glands. the skin covers the entire body protecting the layers below from various threats such as pathogens, uv light, trauma, chemicals, and water loss. Slides with epithelial tissues usually have some of the underlying tissue found beneath the epithelial tissue with them. figure 3.1.1 3.1. 1: the different ways sheets of epithelial cells are categorized. (cc by, openstax, human anatomy) a layer of epithelial cells always serves as an outer layer for some structure, but, when looking at a. Caption. human skin cells. scanning electron micrograph (sem) of the surface layer of the human skin, the epidermis. the outer layer of the epidermis (stratum corneum) is a tough coating formed from overlapping layers of dead skin cells which are continuously sloughed off and replaced with cells from the living layers beneath. Skin is part of the integumentary system and considered to be the largest organ of the human body. there are three main layers of skin: the epidermis, the dermis, and the hypodermis (subcutaneous fat). the focus of this topic is on the epidermal and dermal layers of skin. skin appendages such as sweat glands, hair follicles, and sebaceous glands are reviewed in depth elsewhere.[1].

Human Skin Cells Under Microscope 400x Google Search Microscopic Caption. human skin cells. scanning electron micrograph (sem) of the surface layer of the human skin, the epidermis. the outer layer of the epidermis (stratum corneum) is a tough coating formed from overlapping layers of dead skin cells which are continuously sloughed off and replaced with cells from the living layers beneath. Skin is part of the integumentary system and considered to be the largest organ of the human body. there are three main layers of skin: the epidermis, the dermis, and the hypodermis (subcutaneous fat). the focus of this topic is on the epidermal and dermal layers of skin. skin appendages such as sweat glands, hair follicles, and sebaceous glands are reviewed in depth elsewhere.[1]. The skin is by far the largest organ of the human body, weighing about 10 pounds (4.5 kg) and measuring about 20 square feet (2 square meters) in surface area. it forms the outer covering for the entire body and protects the internal tissues from the external environment. the skin consists of two distinct layers: the epidermis and the dermis. A human anatomy article at microscopy uk: human skin. 10x microscope image creative commons license wiki the sebaceous glands lubricate the hair shaft and skin. {a} sebum is an oily mixture of fatty acids, waxes, and steroids which pass into the hair follicle {b} and find their way up the hair shaft on to the skin surface.

Light Micrograph Of Human Skin Cancer Cell High Res Stock Photo Getty The skin is by far the largest organ of the human body, weighing about 10 pounds (4.5 kg) and measuring about 20 square feet (2 square meters) in surface area. it forms the outer covering for the entire body and protects the internal tissues from the external environment. the skin consists of two distinct layers: the epidermis and the dermis. A human anatomy article at microscopy uk: human skin. 10x microscope image creative commons license wiki the sebaceous glands lubricate the hair shaft and skin. {a} sebum is an oily mixture of fatty acids, waxes, and steroids which pass into the hair follicle {b} and find their way up the hair shaft on to the skin surface.

Comments are closed.