Human Skin Layers And Functions

Structure And Function Of Skin Skin Layer And Diagram Skin. as the body’s largest organ, skin protects against germs, regulates body temperature and enables touch (tactile) sensations. the skin’s main layers include the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis and is prone to many problems, including skin cancer, acne, wrinkles and rashes. contents overview anatomy conditions and disorders care. The skin has three basic layers, each with a different role. the number of skin layers that exists depends on how you count them. you have three main layers of skin—the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue). within these layers are additional layers. if you count the layers within the layers, the skin has eight or even 10.

Human Skin Layers And Functions Skin that has four layers of cells is referred to as “thin skin.”. from deep to superficial, these layers are the stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, and stratum corneum. most of the skin can be classified as thin skin. “thick skin” is found only on the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. The epidermis is the thin outer layer of the skin. it consists of 2 primary types of cells: keratinocytes. keratinocytes comprise about 90% of the epidermis and are responsible for its structure and barrier functions. melanocytes. melanocytes are found at the base of the epidermis and make melanin. this gives the skin its color. dermis. The layers of your skin. your skin includes three layers known as epidermis, dermis, and fat. some health issues, such as dermatitis and infections, can affect how these different layers work to. Human skin, in human anatomy, the covering, or integument, of the body’s surface that both provides protection and receives sensory stimuli from the external environment. the skin consists of three layers of tissue: the epidermis, an outermost layer that contains the primary protective structure, the stratum corneum; the dermis, a fibrous.
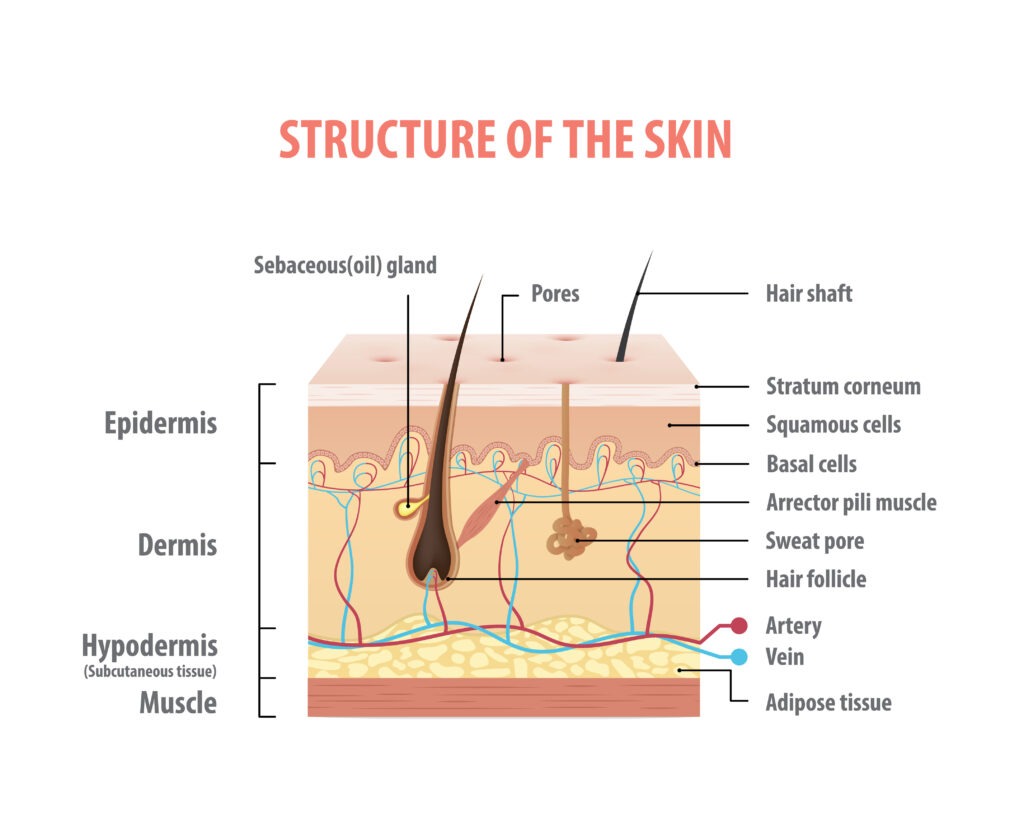
Skin Functions And Ageing The Skin Care Clinic The layers of your skin. your skin includes three layers known as epidermis, dermis, and fat. some health issues, such as dermatitis and infections, can affect how these different layers work to. Human skin, in human anatomy, the covering, or integument, of the body’s surface that both provides protection and receives sensory stimuli from the external environment. the skin consists of three layers of tissue: the epidermis, an outermost layer that contains the primary protective structure, the stratum corneum; the dermis, a fibrous. In addition, skin color, texture, and folds (see descriptions of skin marks, and growths, and color changes) help mark people as individuals. anything that interferes with skin function or causes changes in appearance (see effects of aging on the skin) can have major consequences for physical and mental health. The skin is the largest organ in the body, covering its entire external surface. the skin has 3 layers—the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis, which have different anatomical structures and functions (see image. cross section, layers of the skin). the skin's structure comprises an intricate network that serves as the body's initial barrier against pathogens, ultraviolet (uv) light, chemicals.
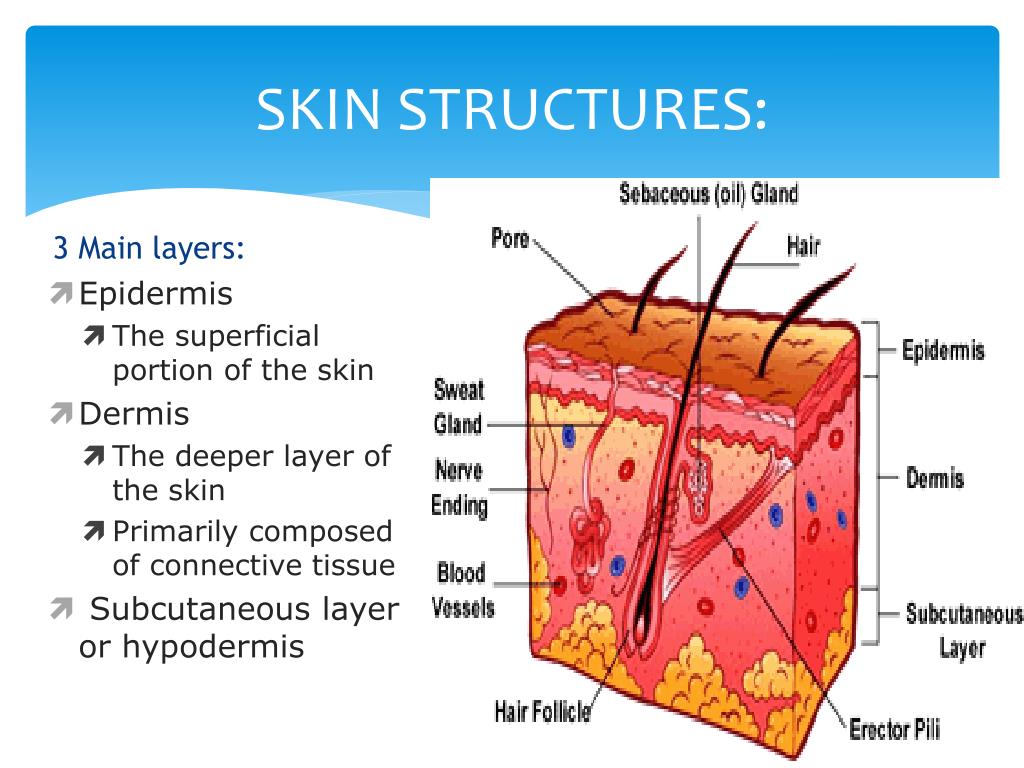
Skin Layers Diagram Labeled In addition, skin color, texture, and folds (see descriptions of skin marks, and growths, and color changes) help mark people as individuals. anything that interferes with skin function or causes changes in appearance (see effects of aging on the skin) can have major consequences for physical and mental health. The skin is the largest organ in the body, covering its entire external surface. the skin has 3 layers—the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis, which have different anatomical structures and functions (see image. cross section, layers of the skin). the skin's structure comprises an intricate network that serves as the body's initial barrier against pathogens, ultraviolet (uv) light, chemicals.
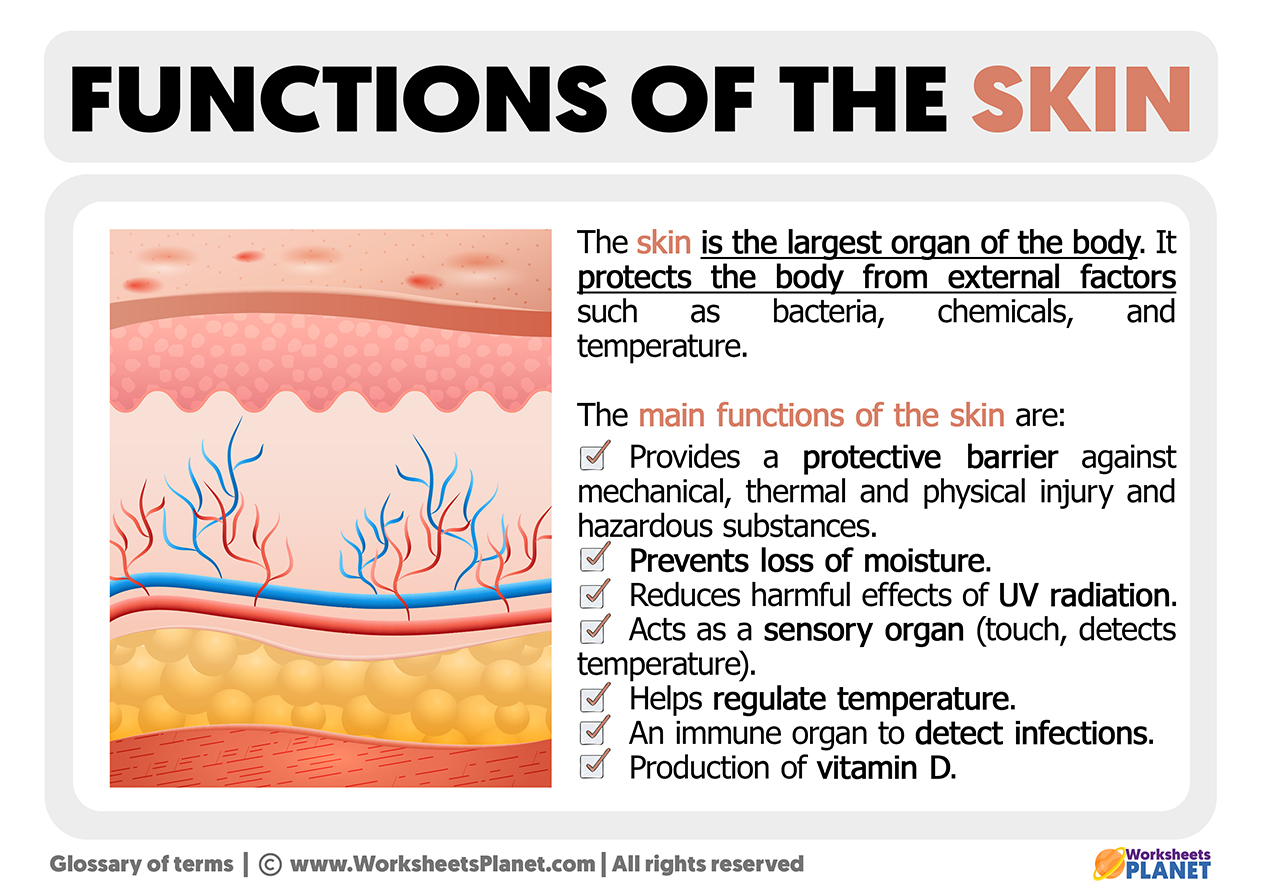
Functions Of The Skin

Comments are closed.