Hydrological Cycle Water Cycle вђ Geography Notes Blog
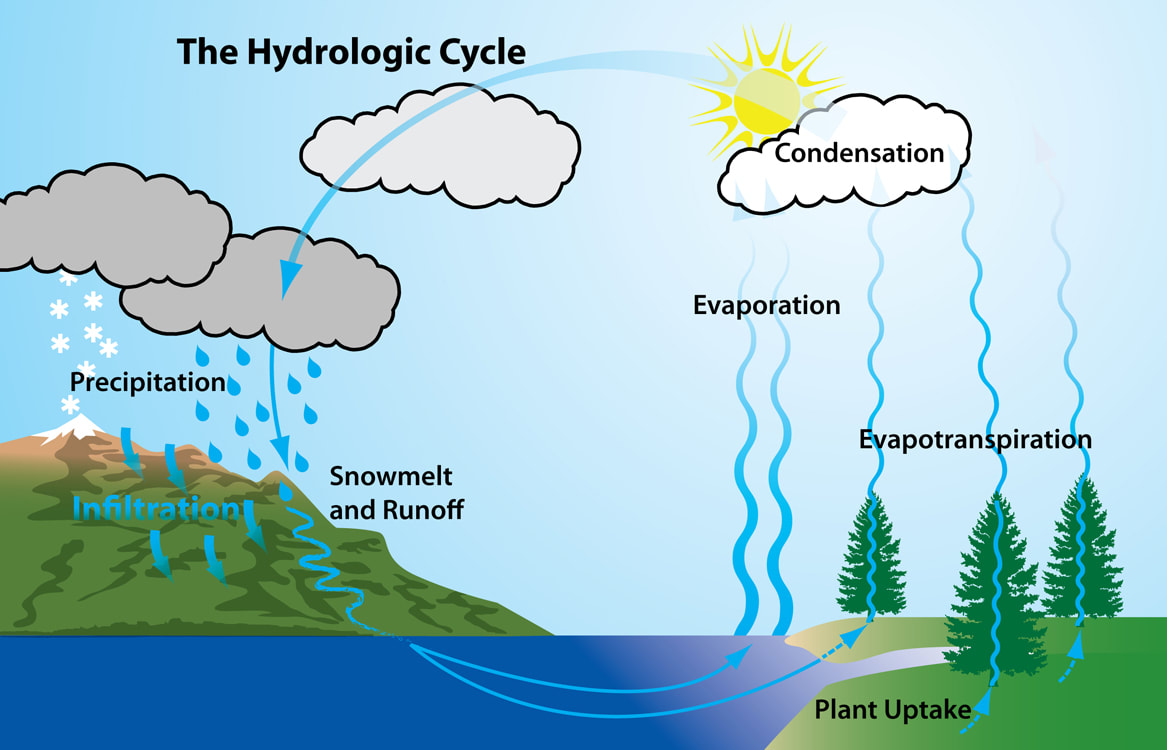
The Hydrological Cycle Notesychs The hydrological cycle, commonly known as the water cycle, is a natural process that describes the continuous movement and circulation of water on, above, and below the earth’s surface. it involves the transformation of water between its various states—liquid, solid (ice), and gas (water vapor)—as it moves through the atmosphere, land. This article provides a diagram of hydrological cycle. the rain water that falls on the ground surface is divided into three parts: they are: (i) one part directly returns to the air as water vapour by evaporation and transpiration from plants. (ii) another part flows over the surface in rivers and ultimately reaches sea or ocean.

Labelled Diagram Of The Water Cycle The water cycle or hydrologic cycle is a continuous biogeochemical process by which water circulates through the earth’s atmosphere, surface, and underground environments. this cycle is essential for maintaining life on earth, regulating climate, and shaping the planet’s ecosystems. water moves through various states—liquid, solid, and. Water reaches in the atmosphere through evaporation from seas, lakes, rivers, soil moisture and transpiration from plants etc. and according to changing climatic conditions condenses in the form of clouds and again reaches the hydrosphere and lithosphere. this cyclical movement of water in different forms is called hydrological cycle. The hydrological cycle, also known as the water cycle, refers to the continuous movement and circulation of water on earth. it involves various processes that ensure the constant exchange of water between the earth’s surface, the atmosphere, and back to the surface again. the hydrological cycle is a closed system, as the system has no inputs. The hydrological cycle is otherwise called the “water cycle”; it is the typical water reusing framework on earth. because of sun based radiation, water dissipates, by and large from the ocean, lakes, and so forth. water likewise dissipates from plant leaves through the component of transpiration.

Comments are closed.