Hyperbola Equation Properties Examples Hyperbola Formula
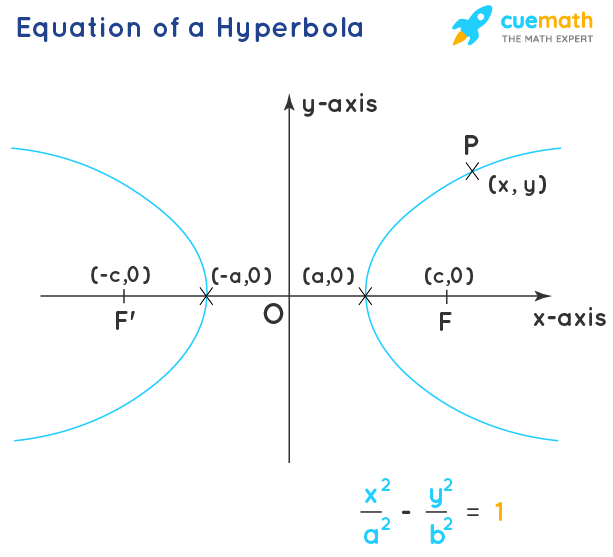
Hyperbola Equation Properties Examples Hyperbola Formula Example: the equation of the hyperbola is given as (x 5) 2 4 2 (y 2) 2 2 2 = 1. use the hyperbola formulas to find the length of the major axis and minor axis. solution: using the hyperbola formula for the length of the major and minor axis. length of major axis = 2a, and length of minor axis = 2b. The formula to calculate the eccentricity of a hyperbola is: equation. based on its center and the orientation of its branches, the equation of a hyperbola can be written in two forms: standard and parametric. standard form – centered at (0, 0) horizontal hyperbola.

Hyperbola Equation Foci Formula Parts Example Lesson Study Graph (x − 1)2 9 − (y − 2)2 16 = 1. solution: step 1: write the equation in standard form. the equation is in standard form. (x − 1)2 9 − (y − 2)2 16 = 1. step 2: determine whether the transverse axis is horizontal or vertical. since the x2 term is positive, the hyperbola opens left and right. In analytic geometry, a hyperbola is a conic section formed by intersecting a right circular cone with a plane at an angle such that both halves of the cone are intersected. this intersection produces two separate unbounded curves that are mirror images of each other (figure 10.2.2). figure 10.2.2: a hyperbola. Develop a formula for the equations of the asymptotes of a hyperbola. share it along with an example on the discussion board. make up your own equation of a hyperbola, write it in general form, and graph it. do all hyperbolas have intercepts? what are the possible numbers of intercepts for a hyperbola? explain. The equations of the asymptotes are y = ±b ax y = ± b a x. the standard form of the equation of a hyperbola with center (0,0) (0, 0) and transverse axis on the y axis is. y2 a2 − x2 b2 =1 y 2 a 2 − x 2 b 2 = 1. where. the length of the transverse axis is 2a 2 a. the coordinates of the vertices are (0,±a) (0, ± a).

Hyperbola Equation Properties Examples Hyperbola Formula Develop a formula for the equations of the asymptotes of a hyperbola. share it along with an example on the discussion board. make up your own equation of a hyperbola, write it in general form, and graph it. do all hyperbolas have intercepts? what are the possible numbers of intercepts for a hyperbola? explain. The equations of the asymptotes are y = ±b ax y = ± b a x. the standard form of the equation of a hyperbola with center (0,0) (0, 0) and transverse axis on the y axis is. y2 a2 − x2 b2 =1 y 2 a 2 − x 2 b 2 = 1. where. the length of the transverse axis is 2a 2 a. the coordinates of the vertices are (0,±a) (0, ± a). Example 3. show that the following equation is a hyperbola. graph it, and show its foci. 144x2 − 576x − 25y2 − 150y − 3249 = 0 144 x 2 − 576 x − 25 y 2 − 150 y − 3249 = 0. solution. the positive leading coefficient for the x2 x 2 term and the negative leading coefficient for the y2 y 2 term indicate that this is a hyperbola that. Definition. a hyperbola looks like two infinite bows, called "branches". looking at the left hand branch in this diagram: any point p is closer to f than to g by some constant amount. the other branch is a mirror image, where points are closer to g than to f by the same constant amount. as a formula:.

Comments are closed.