Hyperbolas All About Hyperbolas Hw
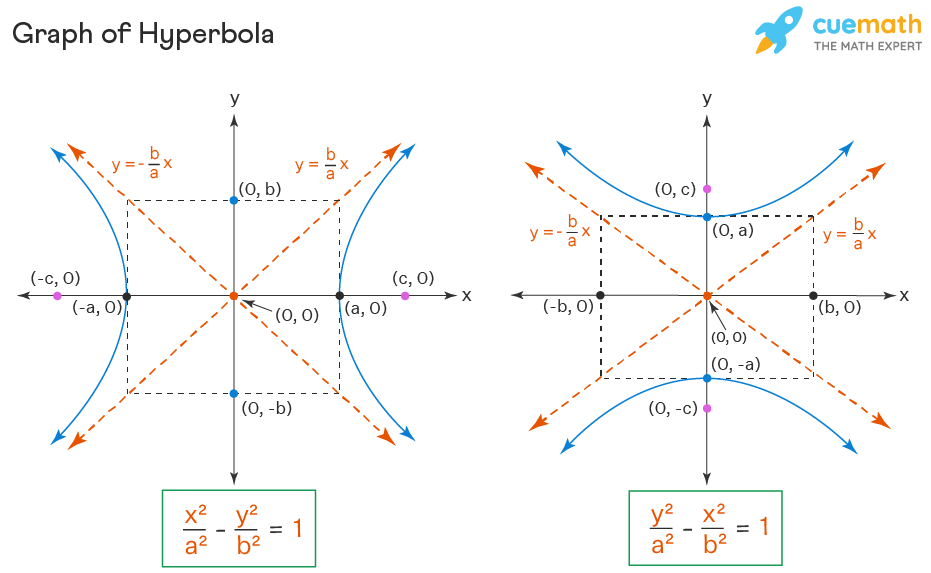
Hyperbola Equation Properties Examples Hyperbola Formula Hyperbola – properties, components, and graph. the hyperbola is a unique type of conic section where we see two disjointed curves representing its equation. these conics are used in describing the pathways of a spacecraft and are even used to model certain seismological events. hyperbolas are conic sections that are the result of a plane. A hyperbola is formed by the intersection of a plane perpendicular to the bases of a double cone. all hyperbolas have an eccentricity value greater than. 1. 1 1. all hyperbolas have two branches, each with a vertex and a focal point. all hyperbolas have asymptotes, which are straight lines that form an x that the hyperbola approaches but never.

Hyperbolas All About Hyperbolas Hw Youtube Learning objectives. by the end of this section, you will be able to: locate a hyperbola’s vertices and foci. write equations of hyperbolas in standard form. graph hyperbolas centered at the origin. graph hyperbolas not centered at the origin. solve applied problems involving hyperbolas. what do paths of comets, supersonic booms, ancient. Then we will turn our attention to finding standard equations for hyperbolas centered at some point other than the origin. hyperbolas centered at the origin. reviewing the standard forms given for hyperbolas centered at (0, 0), (0, 0), we see that the vertices, co vertices, and foci are related by the equation c 2 = a 2 b 2. c 2 = a 2 b 2. Like hyperbolas centered at the origin, hyperbolas centered at a point \((h,k)\) have vertices, co vertices, and foci that are related by the equation \(c^2=a^2 b^2\). we can use this relationship along with the midpoint and distance formulas to find the standard equation of a hyperbola when the vertices and foci are given. Hyperbolas consist of two vaguely parabola shaped pieces that open either up and down or right and left. also, just like parabolas each of the pieces has a vertex. note that they aren’t really parabolas, they just resemble parabolas. there are also two lines on each graph.
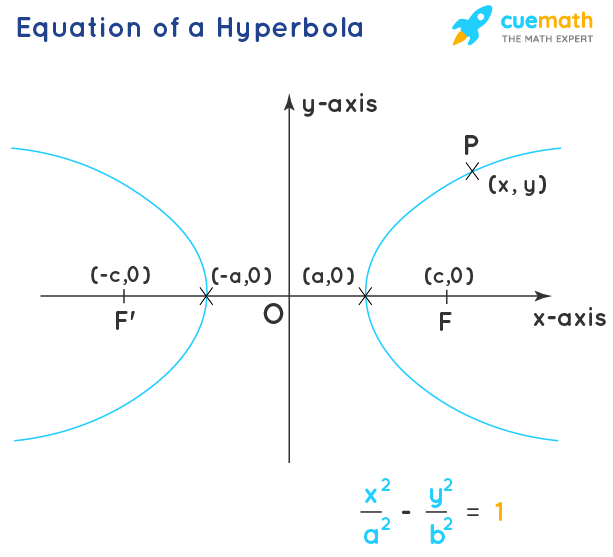
Hyperbola Equation Properties Examples Hyperbola Formula Like hyperbolas centered at the origin, hyperbolas centered at a point \((h,k)\) have vertices, co vertices, and foci that are related by the equation \(c^2=a^2 b^2\). we can use this relationship along with the midpoint and distance formulas to find the standard equation of a hyperbola when the vertices and foci are given. Hyperbolas consist of two vaguely parabola shaped pieces that open either up and down or right and left. also, just like parabolas each of the pieces has a vertex. note that they aren’t really parabolas, they just resemble parabolas. there are also two lines on each graph. Graph a hyperbola with center at (0, 0). the last conic section we will look at is called a hyperbola.we will see that the equation of a hyperbola looks the same as the equation of an ellipse, except it is a difference rather than a sum. Like the ellipse, the hyperbola can also be defined as a set of points in the coordinate plane. a hyperbola is the set of all points [latex]\left(x,y\right)[ latex] in a plane such that the difference of the distances between [latex]\left(x,y\right)[ latex] and the foci is a positive constant.

Comments are closed.