Identifying Angles In Inscribed Right Triangles Geometry Study

Identifying Angles In Inscribed Right Triangles Geometry Study Step 1: identify the given and missing angles. step 2: if the missing angle is the angle opposite to the diameter, the missing angle is 90 degrees according to the property of inscribed right. Geometry skills practice. 1. solve for the measure of a ∘ in the illustration below. 2. a triangle is inscribed in the circle as shown in the diagram below. determine the measure of the missing.

Identifying Angles In Inscribed Right Triangles Practice Geometryођ Practice using the inscribed angle theorem with practice problems and explanations. get instant feedback, extra help and step by step explanations. boost your geometry grade with using the. Here's a step by step guide for how to solve inscribed triangles. step 1: label everything. assign letters, tick marks, colors, or symbols to each of the unknown sides and angles to help you keep track of what's what, because you'll need to use a lot of them along the way. step 2: redraw the triangles separately. Angle = (11 × 360°) (2 × 22 7 × 7) angle = 90°. therefore, the angle of the arc is 90°. example 2: find the missing angle x in the diagram below. solution: we need to find the value of x. one angle is given as 80°. by inscribed angle theorem we know that the central angle = 2 × inscribed angle. x = 2 × 80. The total measure of the opposite angles of a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle is 180°. it means that they are supplementary angles. let us say, for example, in the figure below, the points q, u, a, and d form an inscribed quadrilateral. ∠q, ∠u, ∠a, and ∠d are all inscribed angles. ∠q and ∠a are supplementary.
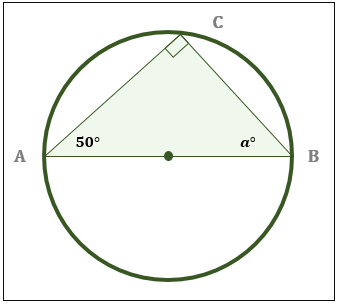
Identifying Angles In Inscribed Right Triangles Practice Geometryођ Angle = (11 × 360°) (2 × 22 7 × 7) angle = 90°. therefore, the angle of the arc is 90°. example 2: find the missing angle x in the diagram below. solution: we need to find the value of x. one angle is given as 80°. by inscribed angle theorem we know that the central angle = 2 × inscribed angle. x = 2 × 80. The total measure of the opposite angles of a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle is 180°. it means that they are supplementary angles. let us say, for example, in the figure below, the points q, u, a, and d form an inscribed quadrilateral. ∠q, ∠u, ∠a, and ∠d are all inscribed angles. ∠q and ∠a are supplementary. According to the inscribed angle theorem, the measure of the inscribed angle is half the measure of the central angle, ∠abc = 2∠cda. hence, ∠abc =2 x 20° = 40°. now, (4x 20)° = 40°. 4x = 40° 20°. x =20° 4 = 5°. what is an inscribed angle of a circle and how to find their measure– its definition in geometry with formula, proof. 1. if a right triangle is inscribed in a circle, then its hypotenuse is a diameter of the circle. 2. if one side of a triangle inscribed in a circle is a diameter of the circle, then the triangle is a right triangle and the angle opposite the diameter is the right angle. these above properties are normally taught in a chapter concerning circles.

Identifying Angles In Inscribed Right Triangles Geometry Study According to the inscribed angle theorem, the measure of the inscribed angle is half the measure of the central angle, ∠abc = 2∠cda. hence, ∠abc =2 x 20° = 40°. now, (4x 20)° = 40°. 4x = 40° 20°. x =20° 4 = 5°. what is an inscribed angle of a circle and how to find their measure– its definition in geometry with formula, proof. 1. if a right triangle is inscribed in a circle, then its hypotenuse is a diameter of the circle. 2. if one side of a triangle inscribed in a circle is a diameter of the circle, then the triangle is a right triangle and the angle opposite the diameter is the right angle. these above properties are normally taught in a chapter concerning circles.

Comments are closed.