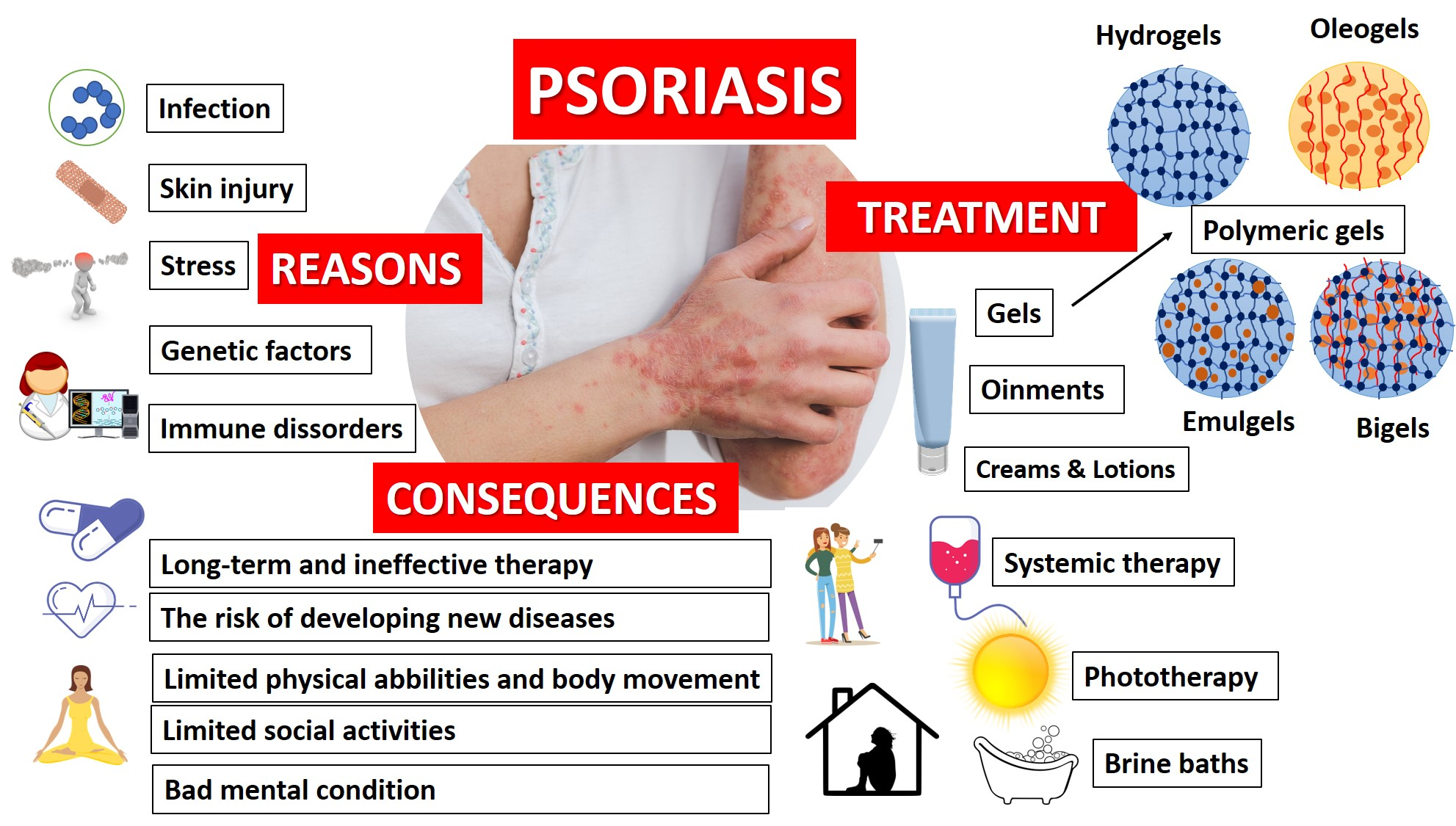
Ijms Free Full Text Polymeric Gels And Their Application In The
Ijms Free Full Text Polymeric Gels And Their Application In The The residence time on the skin and occlusive effect of the polymeric gels can be modified by increasing their strength, viscosity, and abrasion resistance after skin application [50,80,81,82]. this modification is possible by using suitable gels. Search text. search type . add circle outline ijms. volume 22. issue 10. 10.3390 ijms22105124 miastkowska m. polymeric gels and their application in the.
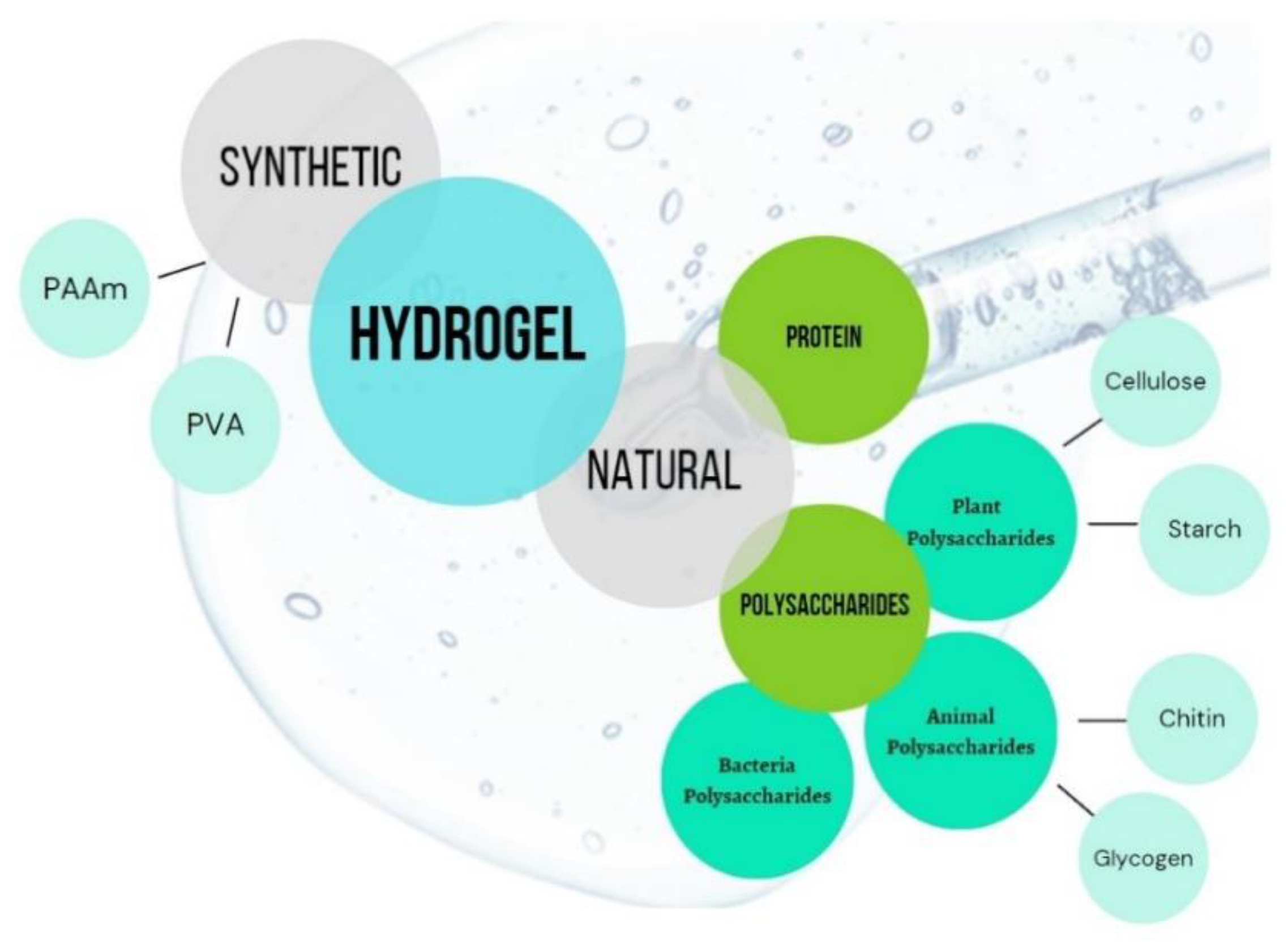
Gels Free Full Text Polymer Gels Classification And Recent 2.1. polymeric gels and their groups. polymeric gels are an important class of soft materials, and they are defined as semi solid formulations (preparations) that are generally composed of at least two components, i.e., a liquid solvent and a solid gelling substance. the solvent forms an external phase and can be hydrophobic or hydrophilic. We discuss the following polymeric gels: hydrogels, oleogels, emulgels, and bigels. in our opinion, they have many characteristics (i.e., safety, effectiveness, desired durability, acceptance by. Nanoparticles are particles that range in size from about 1–1000 nanometers in diameter, about one thousand times smaller than the average cell in a human body. their small size, flexible fabrication, and high surface area to volume ratio make them ideal systems for drug delivery. nanoparticles can be made from a variety of materials including metals, polysaccharides, and proteins. The polymer gel can swell until an equilibrium state is established between the osmotic forces and the ability to expand the polymer chains [14,15,16]. the swelling capacity of the functional polymer gels arises from their hydrophilic functional groups that are attached to polymer chains, and from the cross links between the polymer chains.
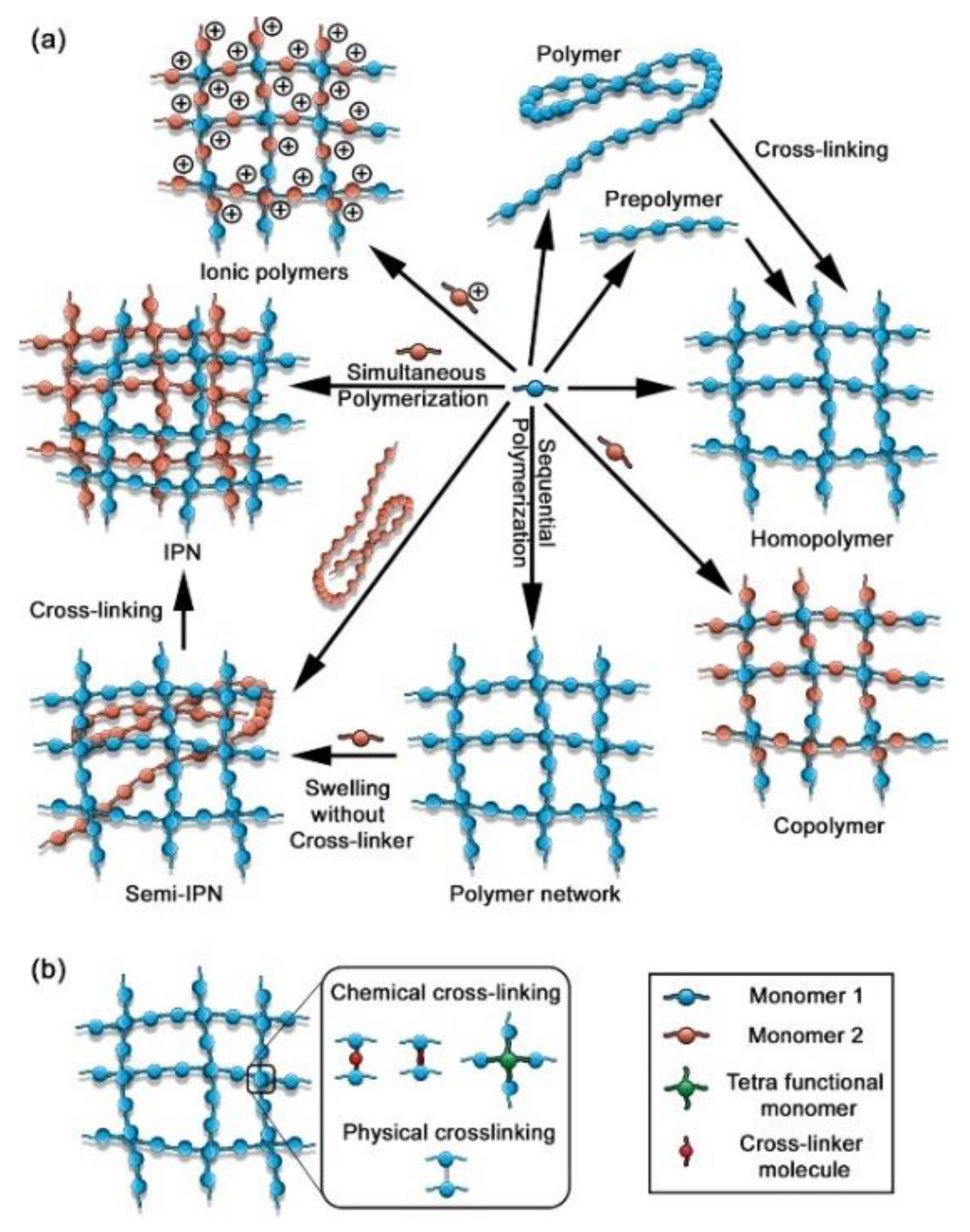
Gels Free Full Text Polymer Gels Classification And Recent Nanoparticles are particles that range in size from about 1–1000 nanometers in diameter, about one thousand times smaller than the average cell in a human body. their small size, flexible fabrication, and high surface area to volume ratio make them ideal systems for drug delivery. nanoparticles can be made from a variety of materials including metals, polysaccharides, and proteins. The polymer gel can swell until an equilibrium state is established between the osmotic forces and the ability to expand the polymer chains [14,15,16]. the swelling capacity of the functional polymer gels arises from their hydrophilic functional groups that are attached to polymer chains, and from the cross links between the polymer chains. Stimuli responsive, biodegradability, and biocompati bility. based on their properties, polymer gels. can be used in a wide range of applications: food industry, agriculture, biomedical, and. In general, polymeric gels are polymer solvent systems (mostly binary systems), in which there subsists a 3 d network made of macromolecules and or their aggregates enabling to retain a larger volume of solvent (s) (rogovina et al., 2008). in some cases, these polymeric gel systems comprise elastic cross linked networks and also fluidfilling.
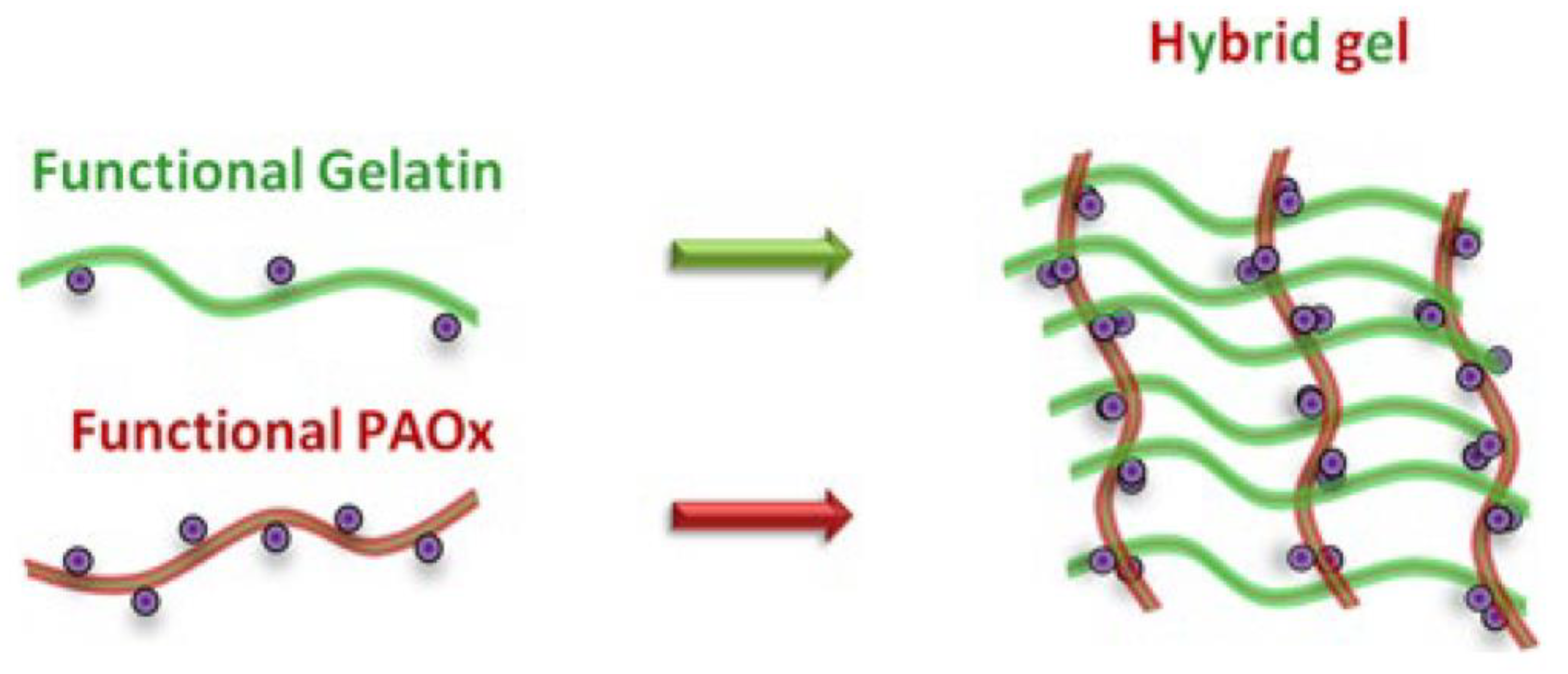
Gels Free Full Text Polymer Gels Classification And Recent Stimuli responsive, biodegradability, and biocompati bility. based on their properties, polymer gels. can be used in a wide range of applications: food industry, agriculture, biomedical, and. In general, polymeric gels are polymer solvent systems (mostly binary systems), in which there subsists a 3 d network made of macromolecules and or their aggregates enabling to retain a larger volume of solvent (s) (rogovina et al., 2008). in some cases, these polymeric gel systems comprise elastic cross linked networks and also fluidfilling.

Comments are closed.