Immunology How Does The Innate Immune System Work
Immunology How Does The Innate Immune System Work The innate immune system utilizes physical barriers such as our skin, mucous, hair, and other epithelial surfaces, including those in the gut, to act as the first line of defense. a simple cough or sneeze is also a useful reaction to expel potentially harmful bacteria, which is all triggered by a tickle of one’s nose hairs or irritation of. The immune system fights germs on the skin, in the tissues of the body, and in bodily fluids such as blood. it is made up of the innate (general) immune system and the adaptive (specialized) immune system. these two systems work closely together and take on different tasks.
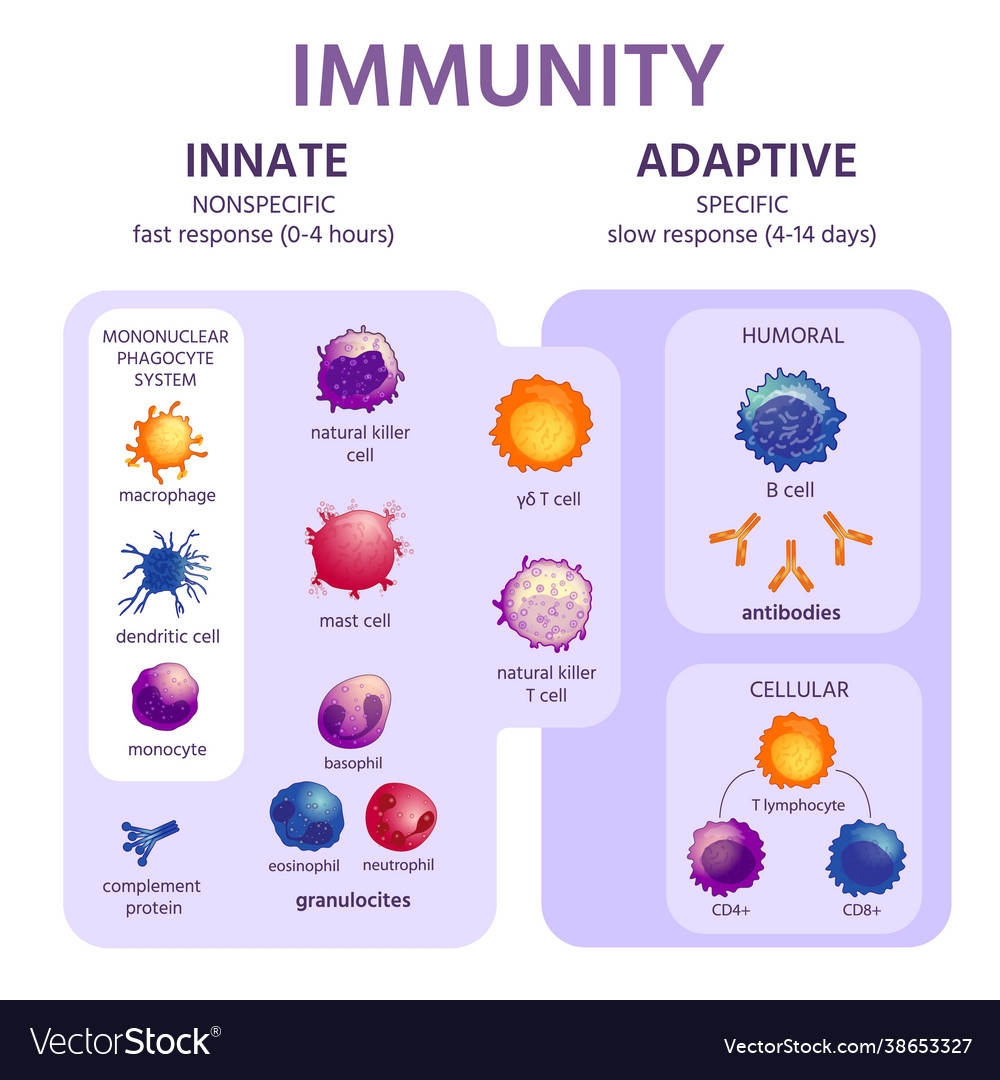
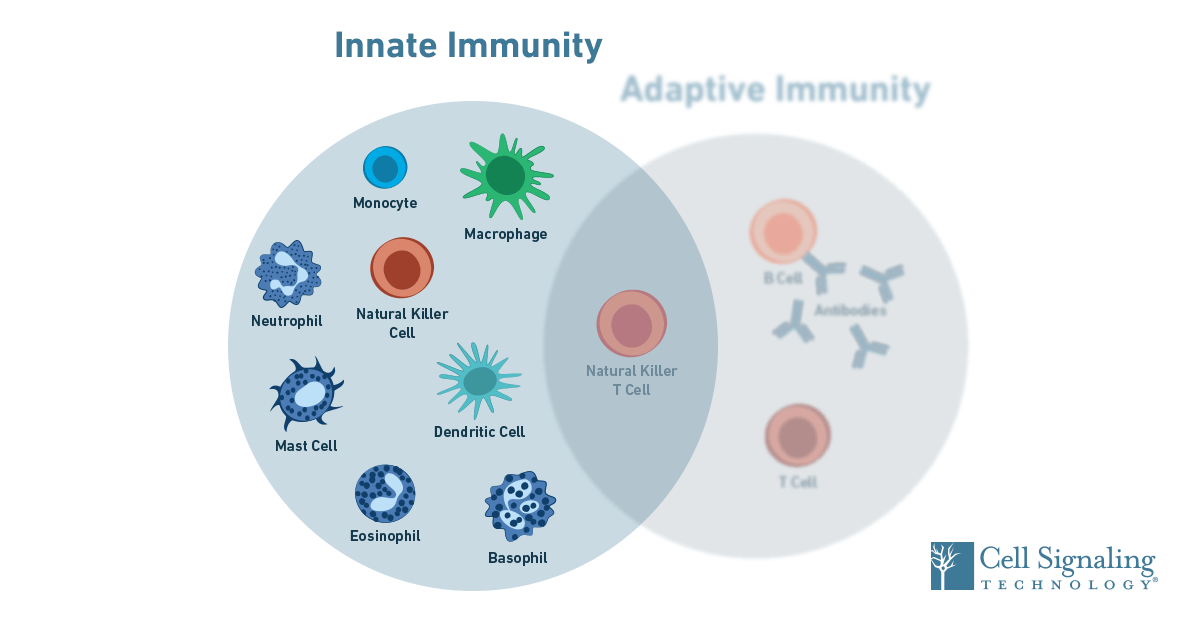
Innate And Adaptive Immune System Immunology Vector Image Innate immunity is an antigen nonspecific defense mechanisms that a host uses immediately or within several hours after exposure to almost any microbe. innate immunity is the immunity one is born with and is the initial response by the body to eliminate microbes and prevent infection. immediate innate immunity begins 0 4 hours after exposure. The innate immune system is an alternate defense strategy and is the dominant immune system response found in plants, fungi, prokaryotes, and invertebrates (see beyond vertebrates). [2] the major functions of the innate immune system are to: act as a physical and chemical barrier to infectious agents; via physical measures such as skin and. The innate immune response is the first mechanism for host defense found in all multicellular organisms. the innate immune system is more ancient than the acquired or adaptive immune response, and it has developed and evolved to protect the host from the surrounding environment in which a variety of toxins and infectious agents including bacteria, fungi, viruses and parasites are found (1). 1 5. most infectious agents induce inflammatory responses by activating innate immunity. microorganisms such as bacteria that penetrate the epithelial surfaces of the body for the first time are met immediately by cells and molecules that can mount an innate immune response. phagocytic macrophages conduct the defense against bacteria by means.

Comments are closed.