Indirect Taxes And Producer Surplus Reference Library Economics
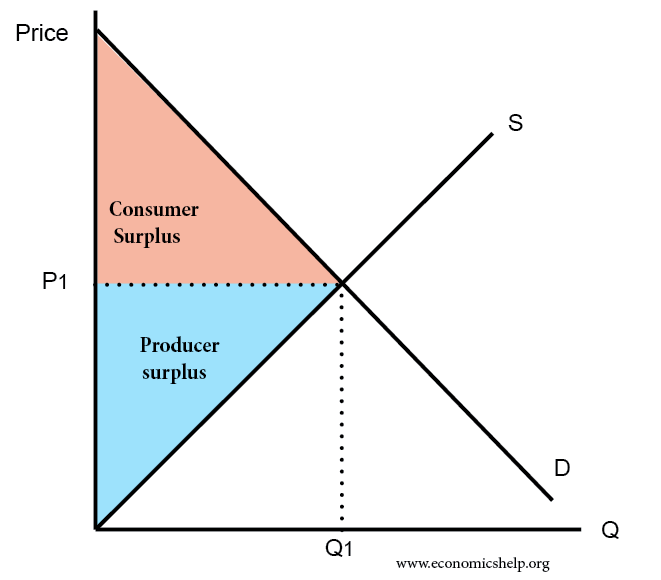
Consumer Surplus And Producer Surplus Economics Help Producer surplus is the difference between the price that producers are willing and able to supply a product for and the price they receive in the market. it is a measure of economic welfare for suppliers to a market or industry. in this revision video we work through step by step the impact of an indirect tax on the level of producer surplus. An indirect tax is a tax imposed by the government that increases the supply costs of producers. the amount of the tax is always shown by the vertical distance between the pre and post tax supply curves. because of the tax, less can be supplied to the market at each price level. consumer surplus. consumer surplus is the difference between the.

Producer Surplus Definition Formula How To Calculate Indirect taxes normally cause a deadweight loss of economic welfare. consumers face higher prices and producers experience a loss of revenue after tax has been paid. a key issue is what is done with thegovernment tax revenue – might it be ring fenced for socially beneficial purposes. Likewise, a tax on consumers will ultimately decrease quantity demanded and reduce producer surplus. this is because the economic tax incidence, or who actually pays in the new equilibrium for the incidence of the tax, is based on how the market responds to the price change – not on legal incidence. tax – shifting the curve. Types of indirect tax: specific tax: is where a fixed amount of tax is imposed upon a product. i.e. a tax of $1 per unit → supply shifts $1 unit upward. figure 3.1 the effect of a specific tax on the supply curve. 2. ad valorem tax: is where the tax is a percentage of the selling price. gap between s & s tax gets bigger. Indirect taxes tend to take a higher percentage of income from those on low income. for example, a smoker who pays £1,000 a year in smoking duties. for a smoker on low income (£10,000), this will be a high percentage of income 10%. for someone on high income, £120,000 – this same tax will be much smaller percentage 0.8%.
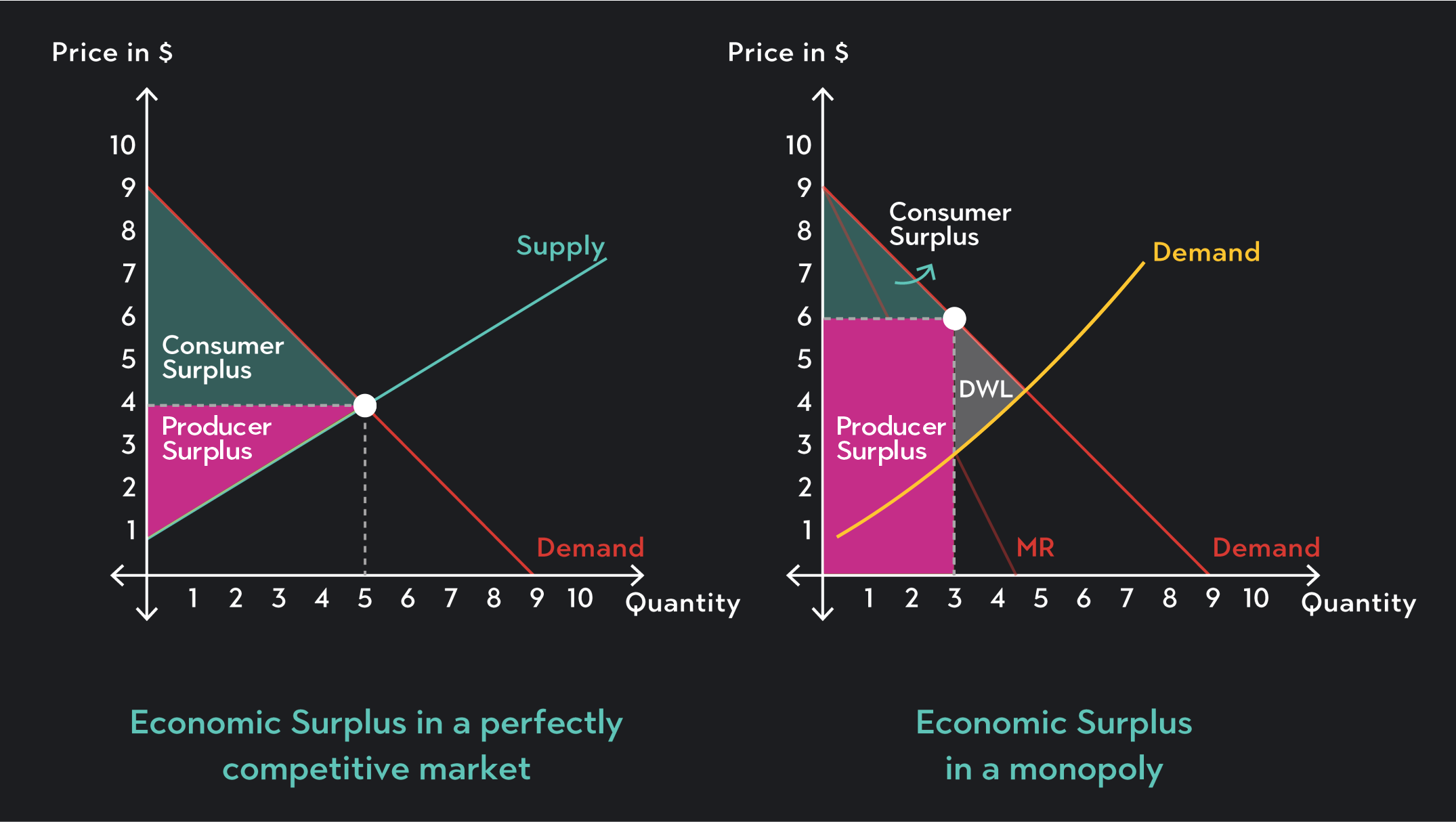
Economic Surplus Definition How To Calculate It Outlier Types of indirect tax: specific tax: is where a fixed amount of tax is imposed upon a product. i.e. a tax of $1 per unit → supply shifts $1 unit upward. figure 3.1 the effect of a specific tax on the supply curve. 2. ad valorem tax: is where the tax is a percentage of the selling price. gap between s & s tax gets bigger. Indirect taxes tend to take a higher percentage of income from those on low income. for example, a smoker who pays £1,000 a year in smoking duties. for a smoker on low income (£10,000), this will be a high percentage of income 10%. for someone on high income, £120,000 – this same tax will be much smaller percentage 0.8%. At the higher price, the domestic quantity supplied increases from qs to q at point e. because producers are selling more quantity at a higher price, the producer surplus increases to the area of the triangle p notrade, e, and d. step 7. compare the areas of the two triangles and you will see the increase in the producer surplus. step 8. • the revenue the government collects from the tax is part of the total surplus. in the diagram, area a is the sum of producer and consumer surplus, and area b is government revenue. • a tax distorts production away from the competitive equilibrium, so at the resulting level of production and consumption mb>mc.
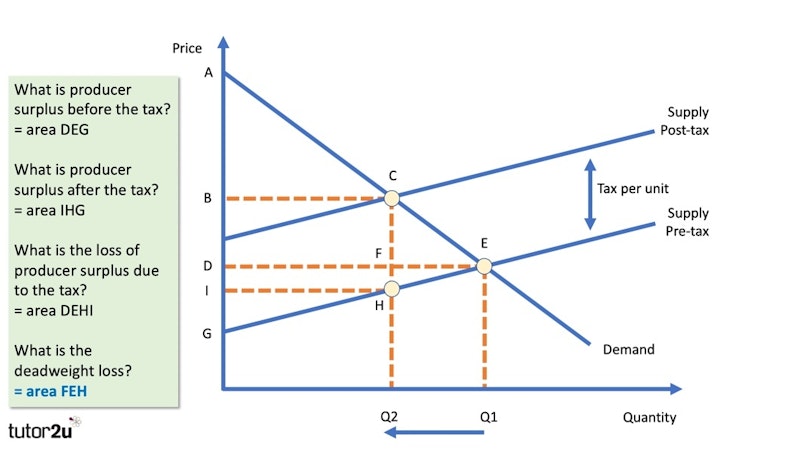
Indirect Taxes And Producer Surplus Reference Library Economics At the higher price, the domestic quantity supplied increases from qs to q at point e. because producers are selling more quantity at a higher price, the producer surplus increases to the area of the triangle p notrade, e, and d. step 7. compare the areas of the two triangles and you will see the increase in the producer surplus. step 8. • the revenue the government collects from the tax is part of the total surplus. in the diagram, area a is the sum of producer and consumer surplus, and area b is government revenue. • a tax distorts production away from the competitive equilibrium, so at the resulting level of production and consumption mb>mc.

Consumer And Producer Surplus Edexcel Economics Revision

Comments are closed.