Introduction To Heat Transfer Let S Talk Science
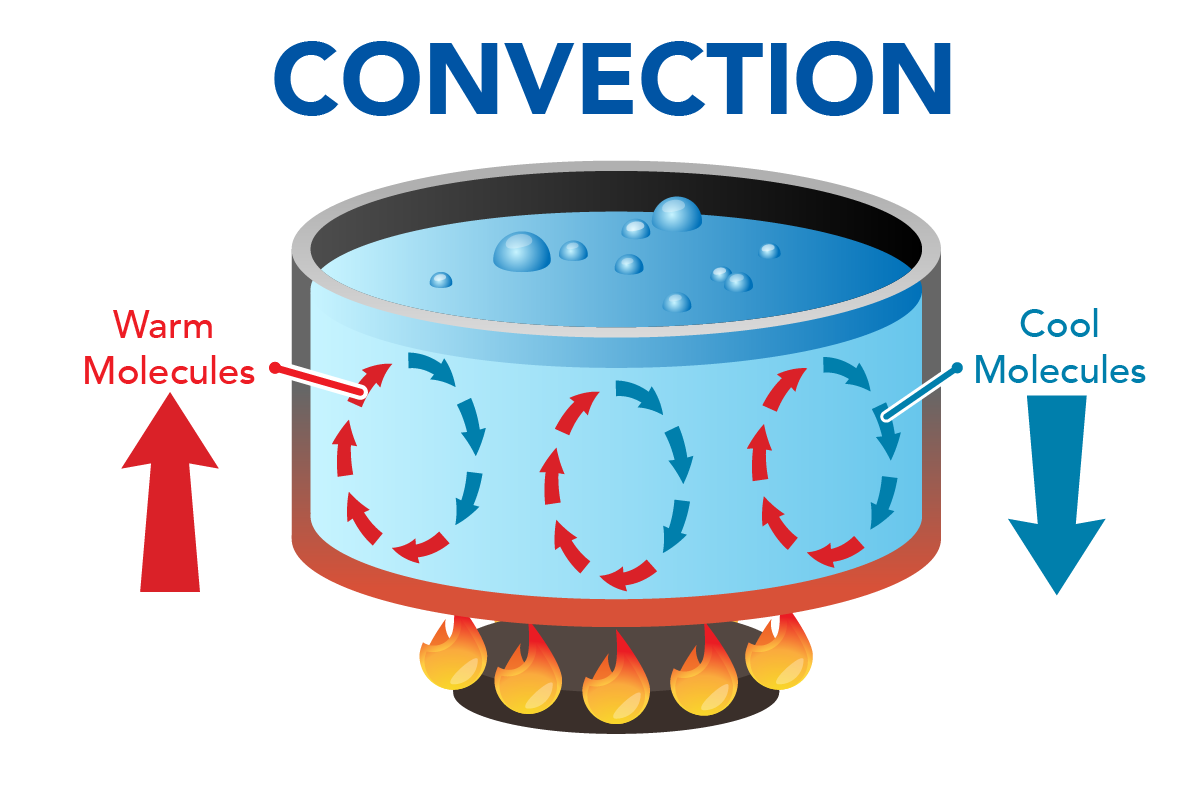
Introduction To Heat Transfer Let S Talk Science Heat can be transferred in three ways: conduction. convection. radiation. boiling water in a kettle on the stove is a good example of the heat transfer processes of conduction, convection and radiation (let’s talk science based on an image from inkoly via istockphoto) image text version. eureka: conduction, convection, radiation. The backgrounder by let’s talk science describes how people control heat in spacecraft such as the iss and orion. how air conditioning works (2018) this video by reactions explains the science of heat transfer and the chemistry of refrigerants. air conditioners: coolest idea ever (2016) this video from scishow explores the history and science.
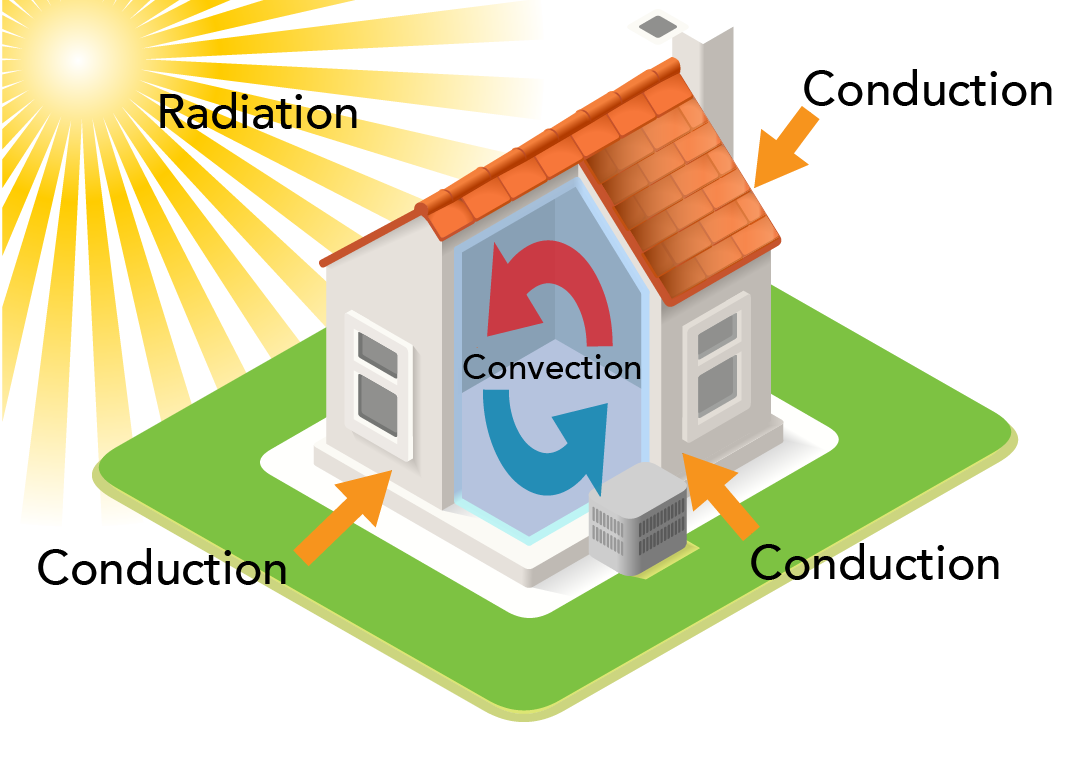
Introduction To Heat Transfer Conduction Convection A Vrogue Co Introduction to heat transfer (2021) this backgrounder by let's talk science describes the three methods that heat is transferred. heat: indoors and outdoors (2024) this backgrounder by let's talk science explores the importance of heat, its sources and how people control it indoors. Updated version available with new content: playlist?list=plzozfx tawahzogn8crjpqrelp5dd gayyou can find the syllabus for the course. The three types of heat transfer with examples. the three types of heat transfer differ according to the nature of the medium that transmits heat: conduction requires contact. convection requires fluid flow. radiation does not require any medium. conduction is heat transfer directly between neighboring atoms or molecules. An introduction to heat transfer including definitioins, terms and units, and the three modes of heat transfer (conduction, convection, and radiation).

Introduction To Heat Transfer Let S Talk Science Vrogue Co The three types of heat transfer with examples. the three types of heat transfer differ according to the nature of the medium that transmits heat: conduction requires contact. convection requires fluid flow. radiation does not require any medium. conduction is heat transfer directly between neighboring atoms or molecules. An introduction to heat transfer including definitioins, terms and units, and the three modes of heat transfer (conduction, convection, and radiation). Course description. this course is an introduction to the principal concepts and methods of heat transfer. the objectives of this integrated subject are to develop the fundamental principles and laws of heat transfer and to explore the implications of these principles for system behavior; to formulate the models necessary to study, …. show more. Heat transfer definition. heat transfer is a process by which internal energy from one substance transfers to another substance. thermodynamics is the study of heat transfer and the changes that result from it. an understanding of heat transfer is crucial to analyzing a thermodynamic process, such as those that take place in heat engines and.

Introduction To Heat Transfer Let S Talk Science Vrogue Co Course description. this course is an introduction to the principal concepts and methods of heat transfer. the objectives of this integrated subject are to develop the fundamental principles and laws of heat transfer and to explore the implications of these principles for system behavior; to formulate the models necessary to study, …. show more. Heat transfer definition. heat transfer is a process by which internal energy from one substance transfers to another substance. thermodynamics is the study of heat transfer and the changes that result from it. an understanding of heat transfer is crucial to analyzing a thermodynamic process, such as those that take place in heat engines and.

Comments are closed.