Joints Structure And Types Of Motion
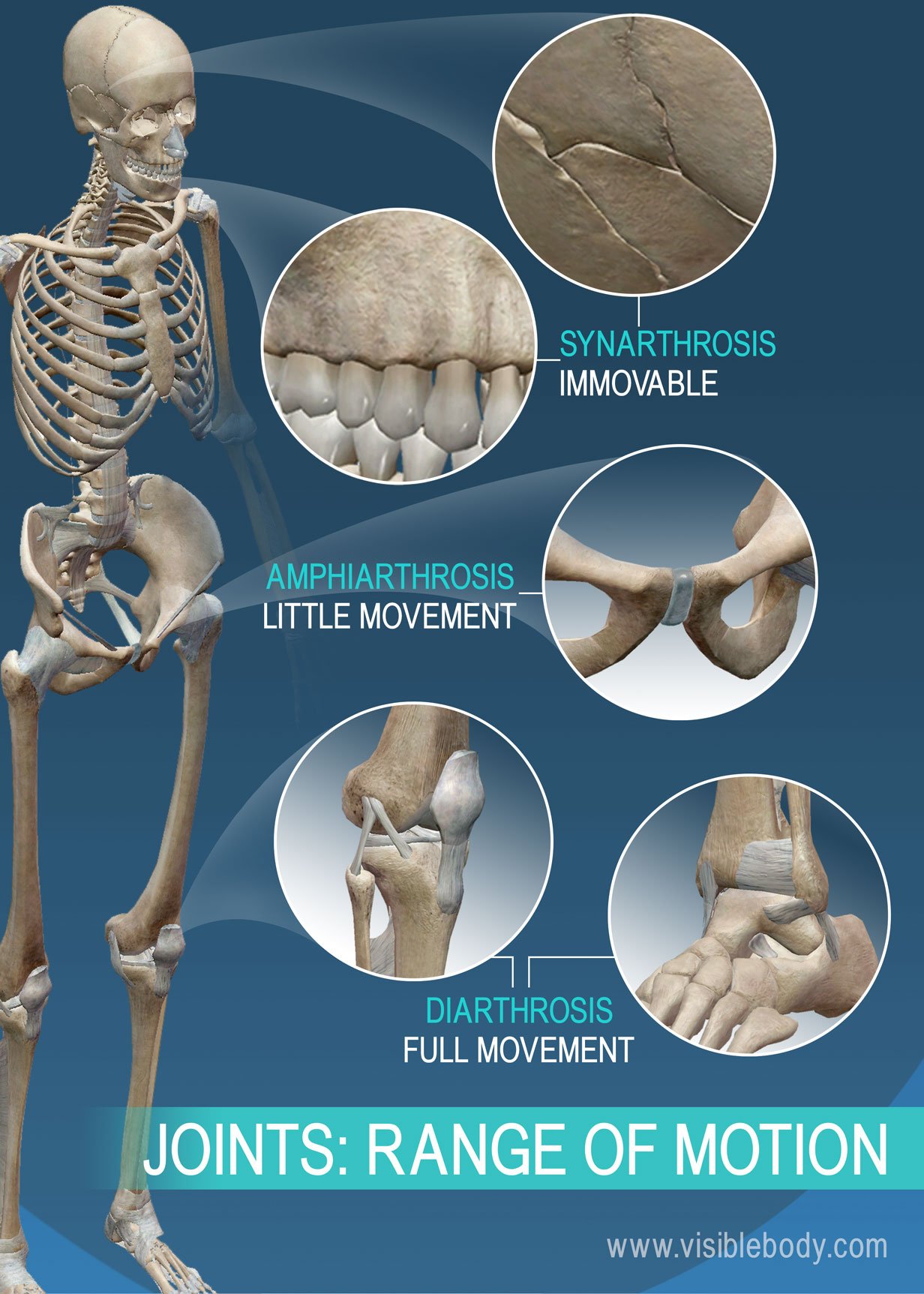
Joints And Ligaments Learn Skeleton Anatomy Sutures: the joints that hold the plates of your skull together. gomphoses: joints that hold your teeth in place in your jaw bones (mandibles). syndesmoses: joints that hold two closely related bones together in place. a syndesmosis joint keeps your tibia (shin bone) connected to your fibula (calf bone). An axis in anatomy is described as the movements in reference to the three anatomical planes: transverse, frontal, and sagittal. thus, diarthroses are classified as uniaxial, biaxial, or multiaxial joints. a uniaxial joint only allows for a motion in a single plane (around a single axis). the elbow joint, which only allows for bending or.
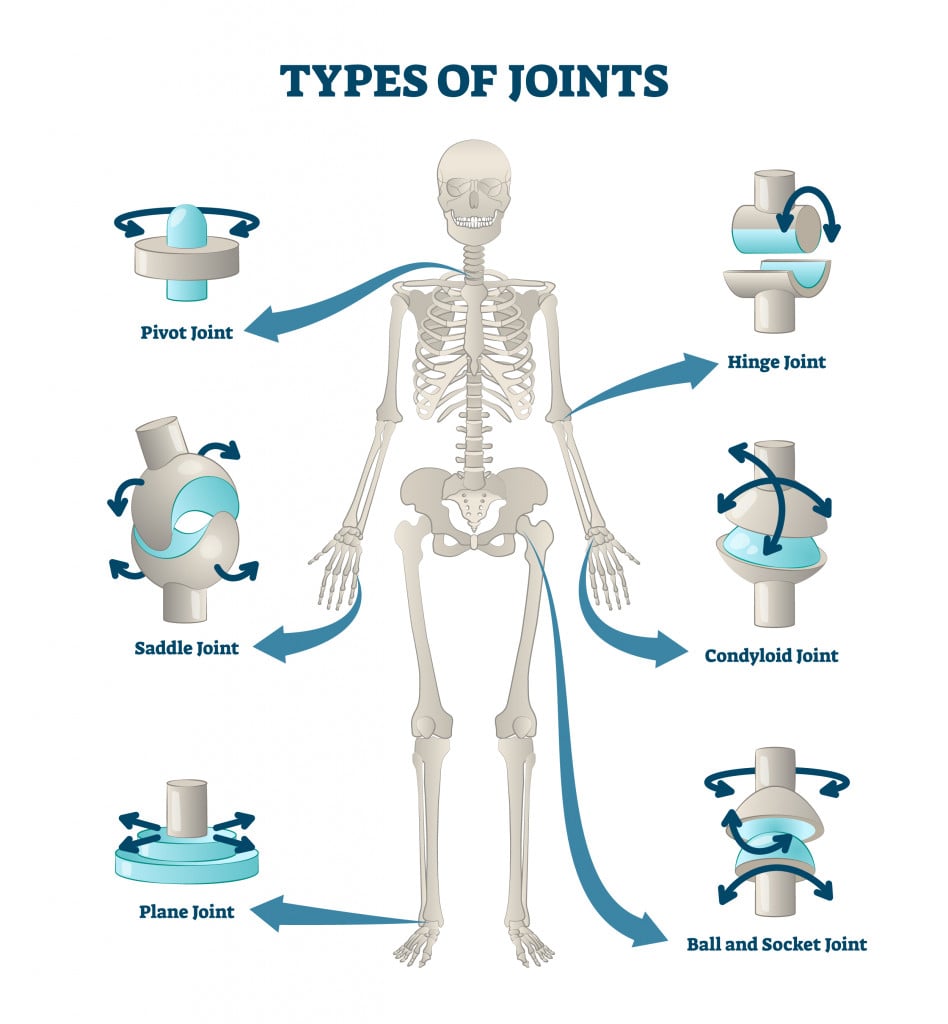
What Are The Different Types Of Joints In Our Body в Scienceabc We've learned about bones and the skeletal system, but bones are so hard, so why are our bodies so bendy and flexible? the answer is joints! joints let our b. Joint, in humans and other animals, structure connecting two or more adjacent parts of the skeleton. not all joints move, but, among those that do, motions include spinning, swinging, gliding, rolling, and approximation. learn about the different types of joints and their structure and function. These types of joints include all synovial joints of the body, which provide the majority of body movements. most diarthrotic joints are found in the appendicular skeleton and thus give the limbs a wide range of motion. these joints are divided into three categories, based on the number of axes of motion provided by each. Joints hold the skeleton together and support movement. there are two ways to categorize joints. the first is by joint function, also referred to as range of motion.the second way to categorize joints is by the material that holds the bones of the joints together; that is an organization of joints by structure.
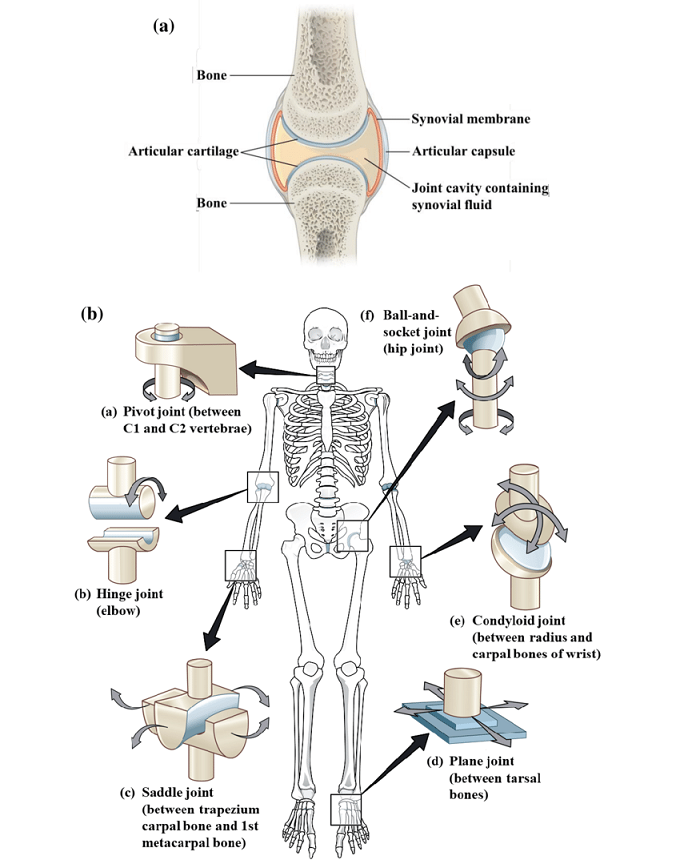
Six Types Of Synovial Joints And Examples These types of joints include all synovial joints of the body, which provide the majority of body movements. most diarthrotic joints are found in the appendicular skeleton and thus give the limbs a wide range of motion. these joints are divided into three categories, based on the number of axes of motion provided by each. Joints hold the skeleton together and support movement. there are two ways to categorize joints. the first is by joint function, also referred to as range of motion.the second way to categorize joints is by the material that holds the bones of the joints together; that is an organization of joints by structure. Cartilaginous joints. cartilaginous joints are chiefly characterized by the fact that they connect with neighboring bones via cartilage. they exhibit a range of motion that falls between synovial and fibrous joints. there are two types of cartilaginous joints, synchondrosis and symphysis joints. sternochondral joints. These types of joints include all synovial joints of the body, which provide the majority of body movements. most diarthrotic joints are found in the appendicular skeleton and thus give the limbs a wide range of motion. this type of multiaxial diarthrotic joint allows for movement along three axes (figure 11.3). the shoulder and hip joints are.

Joints And Skeletal Movement Biology For Majors Ii Cartilaginous joints. cartilaginous joints are chiefly characterized by the fact that they connect with neighboring bones via cartilage. they exhibit a range of motion that falls between synovial and fibrous joints. there are two types of cartilaginous joints, synchondrosis and symphysis joints. sternochondral joints. These types of joints include all synovial joints of the body, which provide the majority of body movements. most diarthrotic joints are found in the appendicular skeleton and thus give the limbs a wide range of motion. this type of multiaxial diarthrotic joint allows for movement along three axes (figure 11.3). the shoulder and hip joints are.

Comments are closed.