Larynx Location Anatomy Function And More

Larynx Location Anatomy Function And More Summary. the larynx is a small structure of cartilage that connects the throat to the windpipe. it is located in the front of the neck and houses the vocal cords, producing speech sounds and. What is the larynx (voice box)? your larynx is part of your respiratory system. it’s a hollow tube that’s about 4 to 5 centimeters (cm) in length and width. it lets air pass from your throat (pharynx) to your trachea on the way to your lungs. your larynx is also the reason you’re able to make sounds, so it’s often called your voice box.
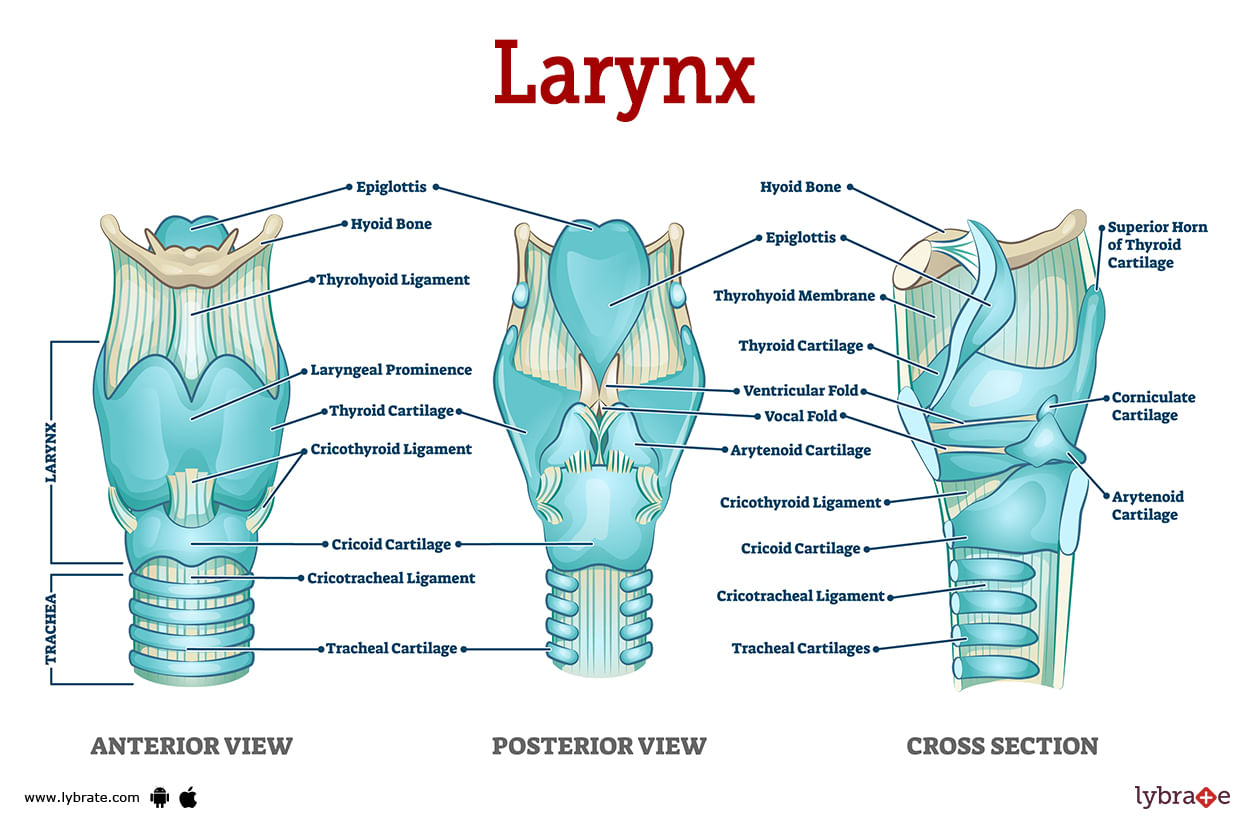
Larynx Human Anatomy Picture Functions Diseases And Treatments The anatomy of the larynx. the larynx sits on the top of the neck and plays a role in vocalizing. commonly called the voice box, the larynx is located on top of the neck and is essential for breathing, vocalizing, as well as ensuring food doesn’t get stuck in the trachea and cause choking. sitting just in front of the esophagus, the vocal. The larynx is a short (= 1.5 inch) tube that is located in the throat, inferior to the hyoid bone and tongue and anterior to the esophagus. forming the larynx are nine (9) supportive cartilages, several intrinsic and extrinsic muscles, and a mucous membrane lining. as a primary function, the larynx provides a carefully guarded air passageway. Cartilages, ligaments, membranes and muscles of the larynx. the larynx is a complex hollow structure located in the anterior midline region of the neck. it is anterior to the esophagus and at the level of the third to the sixth cervical vertebrae in its normal position. it consists of a cartilaginous skeleton connected by membranes, ligaments. The larynx is a cartilaginous segment of the respiratory tract located in the anterior aspect of the neck. the primary function of the larynx in humans and other vertebrates is to protect the lower respiratory tract from aspirating food into the trachea while breathing. it also contains the vocal cords and functions as a voice box for producing sounds, i.e., phonation. from a phylogenetic view.

Comments are closed.