Larynx Structure Function Cartilages Muscles Blood Supply And Vocal
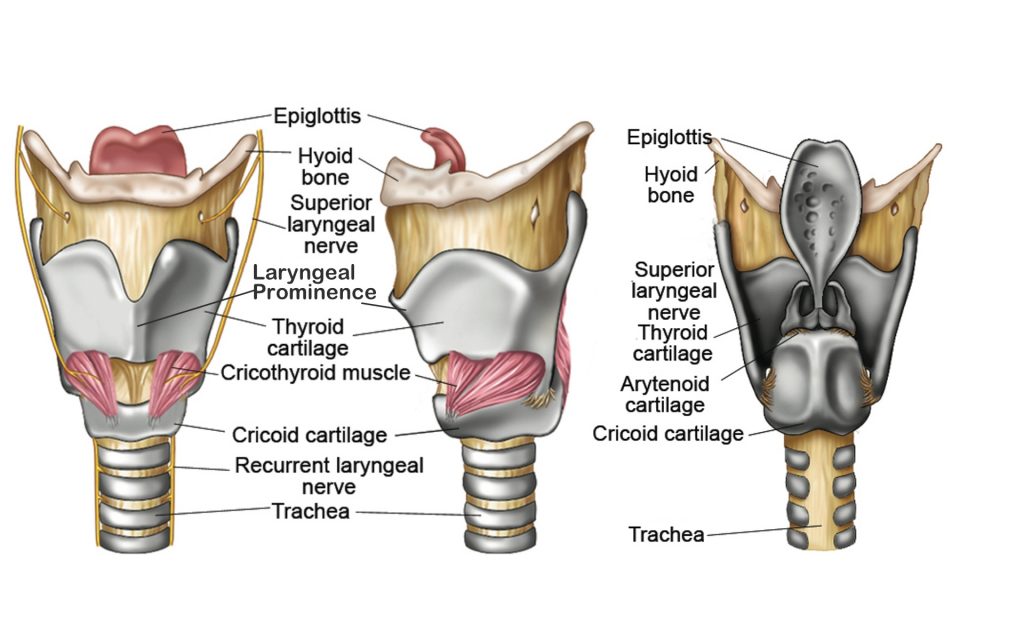
Larynx Structure Function Cartilages Muscles Blood Supply And Vocal The larynx is the organ of phonation (voice production) in addition to its respiratory function (airway). it is formed of a group of cartilages connected by muscles, ligaments, and joints). the larynx lies below the hyoid bone in the midline of the neck at the level of vertebrae. sensory nerves to the larynx are derived from the internal branch. Cartilages, ligaments, membranes and muscles of the larynx. the larynx is a complex hollow structure located in the anterior midline region of the neck. it is anterior to the esophagus and at the level of the third to the sixth cervical vertebrae in its normal position. it consists of a cartilaginous skeleton connected by membranes, ligaments.
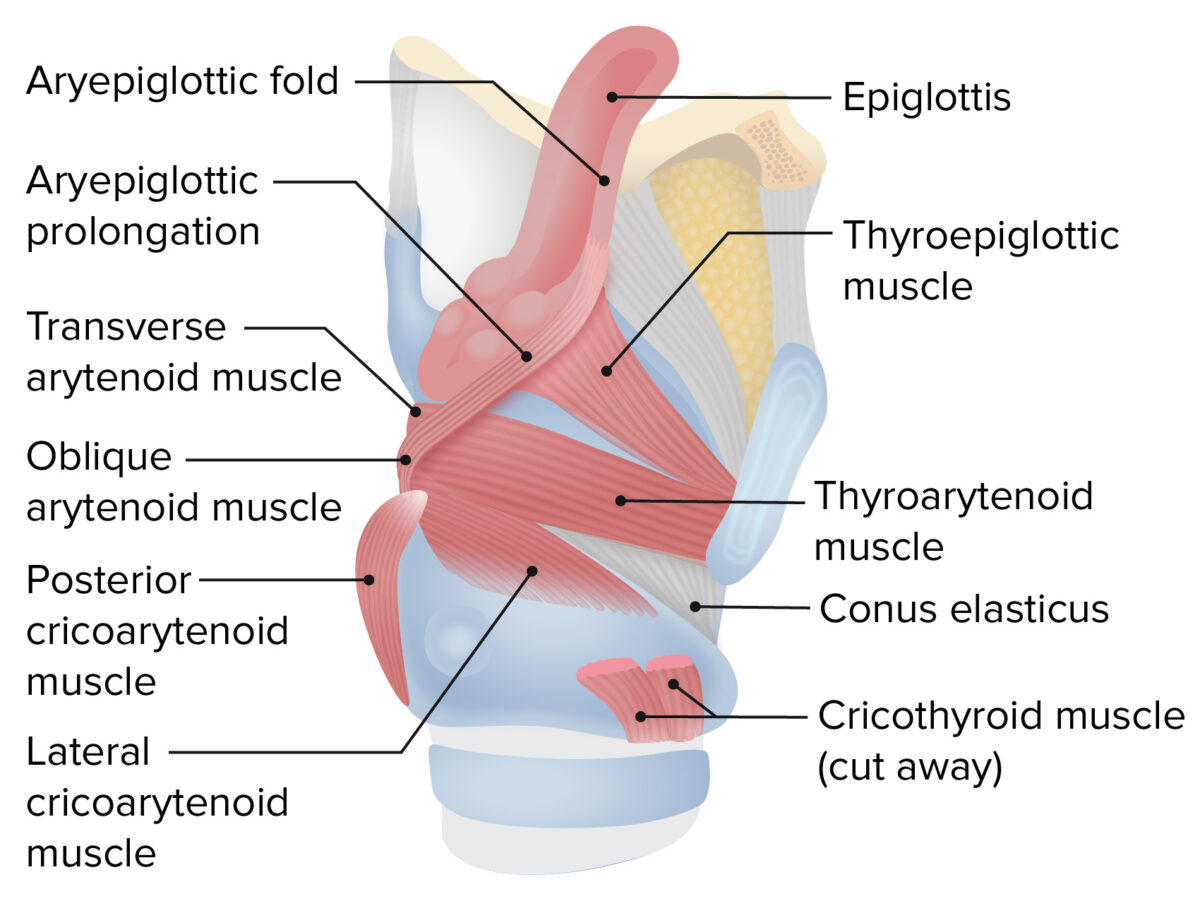
Larynx Anatomy Concise Medical Knowledge The larynx. the larynx (voice box) is an organ located in the anterior neck. it is a component of the respiratory tract, and has several important functions, including phonation, the cough reflex, and protection of the lower respiratory tract. the structure of the larynx is primarily cartilaginous, and is held together by a series of ligaments. There are many muscles that either make up a certain part of the laryngeal structure inside the neck, or that sit adjacent to it and aid in its function. these muscles produce the movements of the larynx and its cartilages, thus enabling the proper air conduction, speech, movements of the epiglottis and airways protection. the muscles of the. The larynx is a cartilaginous segment of the respiratory tract located in the anterior aspect of the neck. the primary function of the larynx in humans and other vertebrates is to protect the lower respiratory tract from aspirating food into the trachea while breathing. it also contains the vocal cords and functions as a voice box for producing sounds, i.e., phonation. from a phylogenetic view. Cartilages in your larynx help to give it structure, the same way interior walls frame a house. muscles in your larynx move your larynx while swallowing, help with breathing and produce vocal sounds. ligaments in your larynx connect cartilages and link your larynx to nearby structures, like your hyoid bone and trachea.
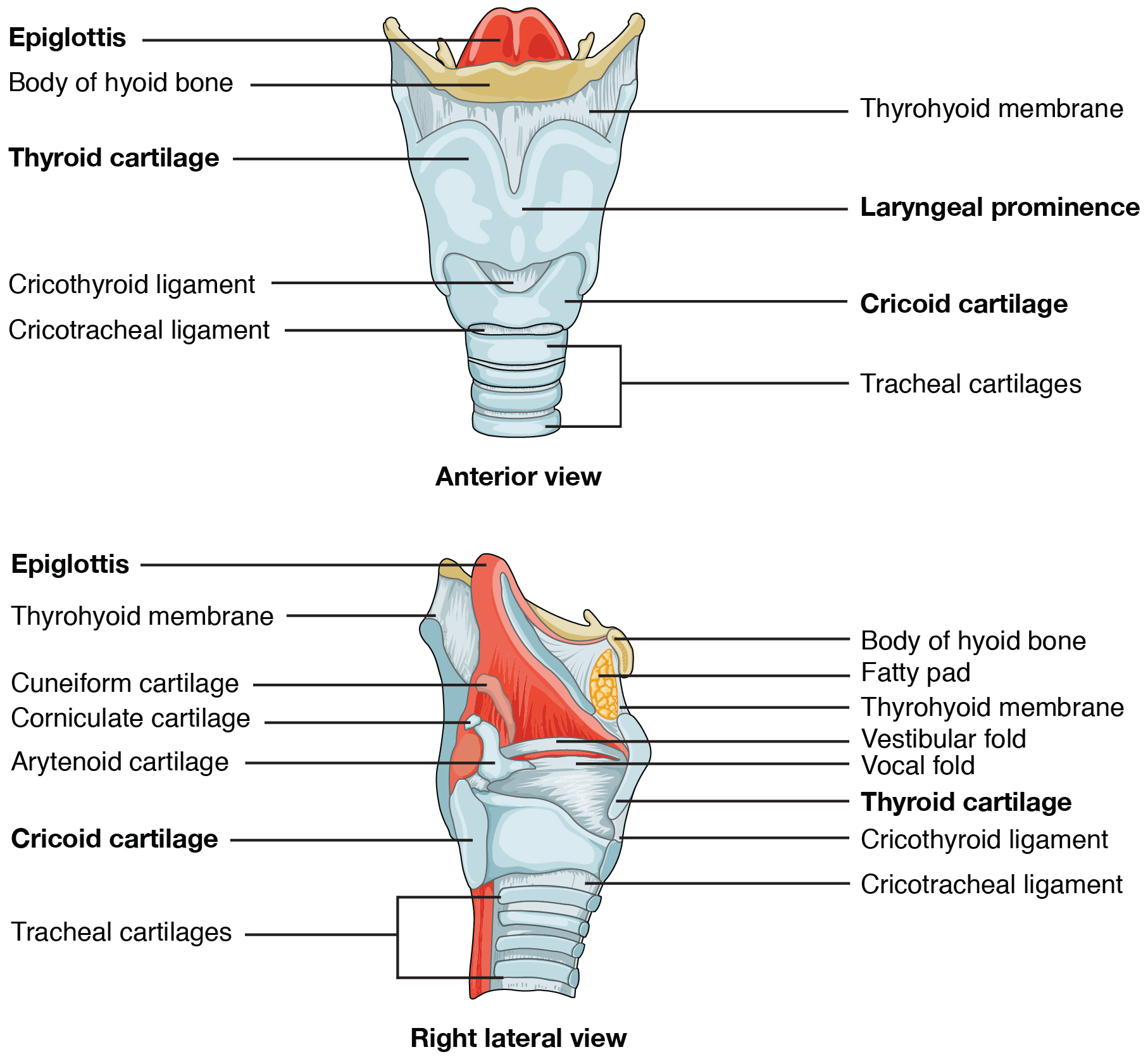
Label The Structures Of The Larynx The larynx is a cartilaginous segment of the respiratory tract located in the anterior aspect of the neck. the primary function of the larynx in humans and other vertebrates is to protect the lower respiratory tract from aspirating food into the trachea while breathing. it also contains the vocal cords and functions as a voice box for producing sounds, i.e., phonation. from a phylogenetic view. Cartilages in your larynx help to give it structure, the same way interior walls frame a house. muscles in your larynx move your larynx while swallowing, help with breathing and produce vocal sounds. ligaments in your larynx connect cartilages and link your larynx to nearby structures, like your hyoid bone and trachea. The larynx splits into three distinct regions known as the supraglottis, glottis, and subglottis. within these three regions the cartilage, neurovascular, and musculature are all intertwined to allow the larynx to function as a unit and carry out its many functions. the primary functions of the larynx are voice production, protection of the airway during respiration, and swallowing. Explore the anatomy and function of the larynx, the voice box that connects the pharynx and the trachea. find out how it works, its disorders and clinical relevance.
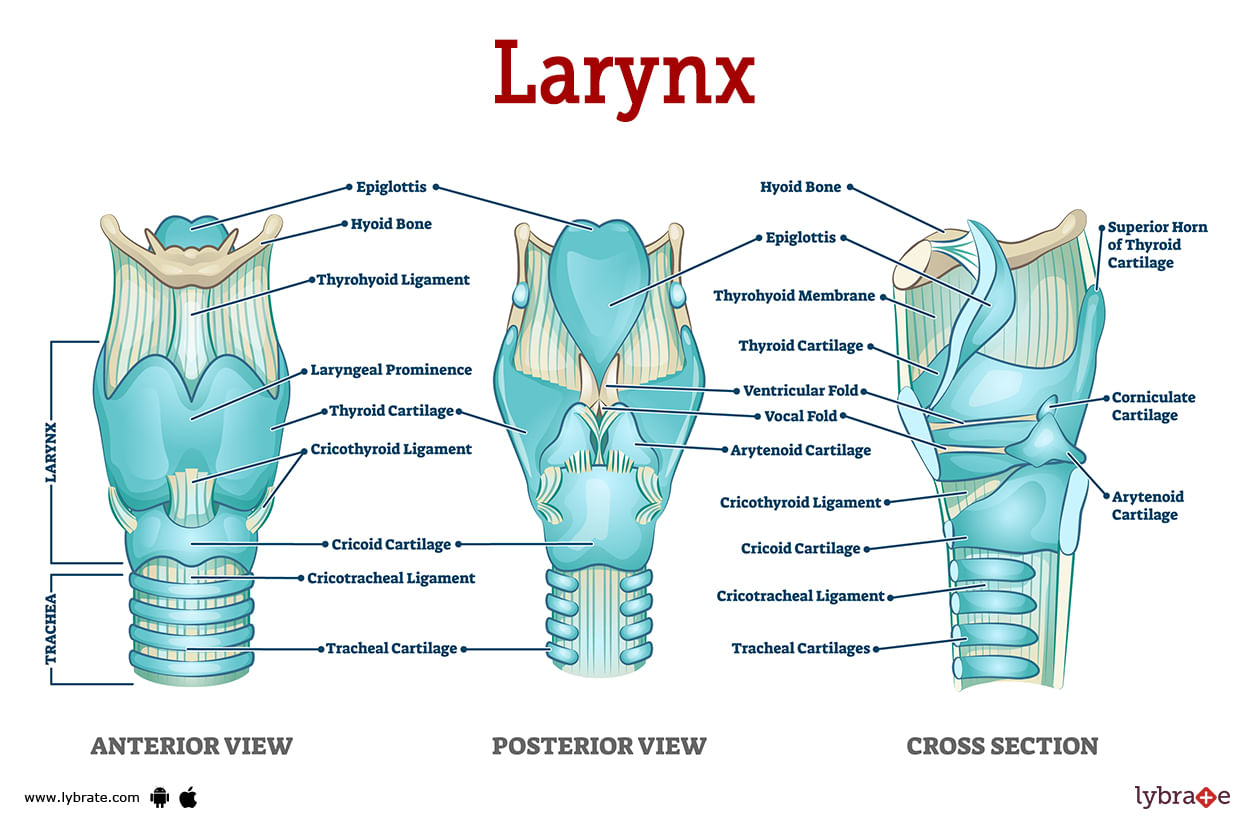
Larynx Human Anatomy Picture Functions Diseases And Treatments The larynx splits into three distinct regions known as the supraglottis, glottis, and subglottis. within these three regions the cartilage, neurovascular, and musculature are all intertwined to allow the larynx to function as a unit and carry out its many functions. the primary functions of the larynx are voice production, protection of the airway during respiration, and swallowing. Explore the anatomy and function of the larynx, the voice box that connects the pharynx and the trachea. find out how it works, its disorders and clinical relevance.

Comments are closed.