Lean The Waste Of Waiting
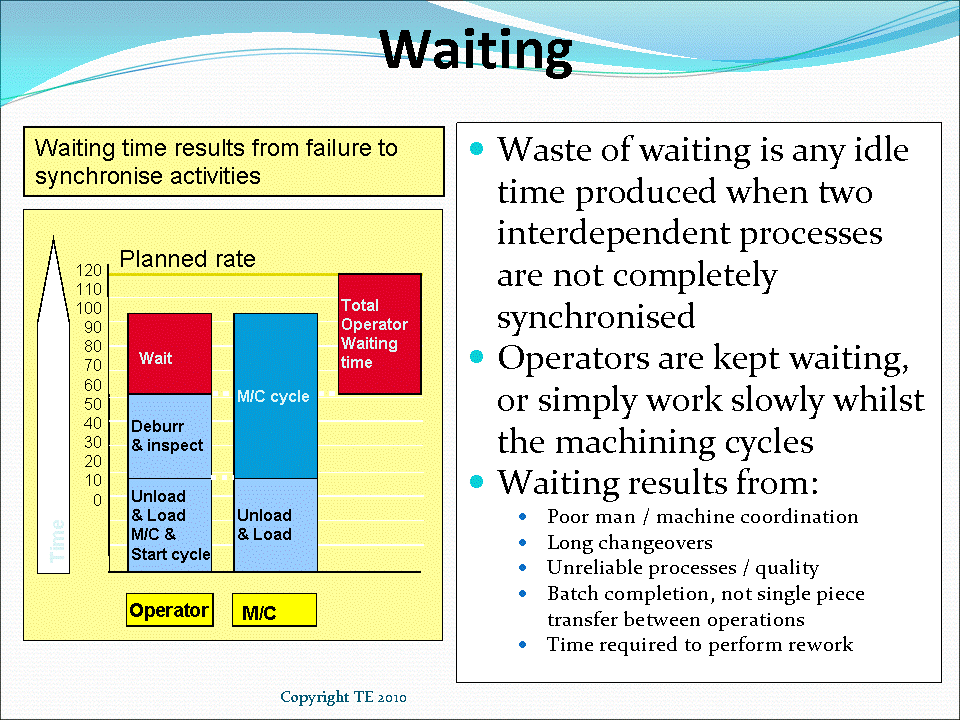
Waste Of Waiting Causes Symptoms Examples And Solutions The original seven wastes (muda) was developed by taiichi ohno, the chief engineer at toyota, as part of the toyota production system (tps). the seven wastes are transportation, inventory, motion, waiting, overproduction, overprocessing and defects. they are often referred to by the acronym ‘timwood’. Examples of wastes of waiting. operators machines standing idle whilst they wait for a previous processes production to be sorted due to quality problems. waiting for a breakdown to be resolved. waiting for a previous process to complete a batch of material prior to movement. waiting for the forklift truck to deliver a batch of components.

8 Wastes Of Lean Manufacturing вђ Greendot Management Solutions Waiting waste can also directly lead to some of the other 8 wastes in lean, such as defect waste and inventory waste, as follows: defect waste: if production falls behind due to waiting time, you may feel pressure to “catch up”. in doing so, you may take shortcuts which lead to the accidental production of additional scrap or rework material. Overproduction. waiting. non utilized talent. transportation. inventory. motion. extra processing. identifying and addressing these wastes is fundamental to lean principles and contributes to streamlined and efficient processes. here’s a more detailed explanation of each of the 8 wastes. This reduces any miscommunication as to what you are talking about when pointing out that something is indeed a waste. 3. the wastes focus on the functioning of the process and not on the people. there will be less resistance and defensiveness if waste is perceived as a process issue rather than a people issue. The lean construction institute has identified eight different kinds of waste that occur during projects: defects, over under production, waiting, not utilizing talent, transportation, inventory, motion, and extra processing.

Comments are closed.