Lecture 6 Polysaccharides

Polysaccharides Diagram Quizlet Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like in polysaccharides many bind glycosidic bonds, in glycoconjugates sugar is connected to , draw fisher projections of > glucose, ribose, fructose and more. Lecture 6 – polysaccharides: learning objectives: definition and classification bond types common disaccharides structural polysaccharides: cellulose, chitin storage polysaccharides: starch, glycogen heteropolysaccharides enzymes of oligosaccharides assembly polysaccharide sequencing carbohydrate recognising proteins.
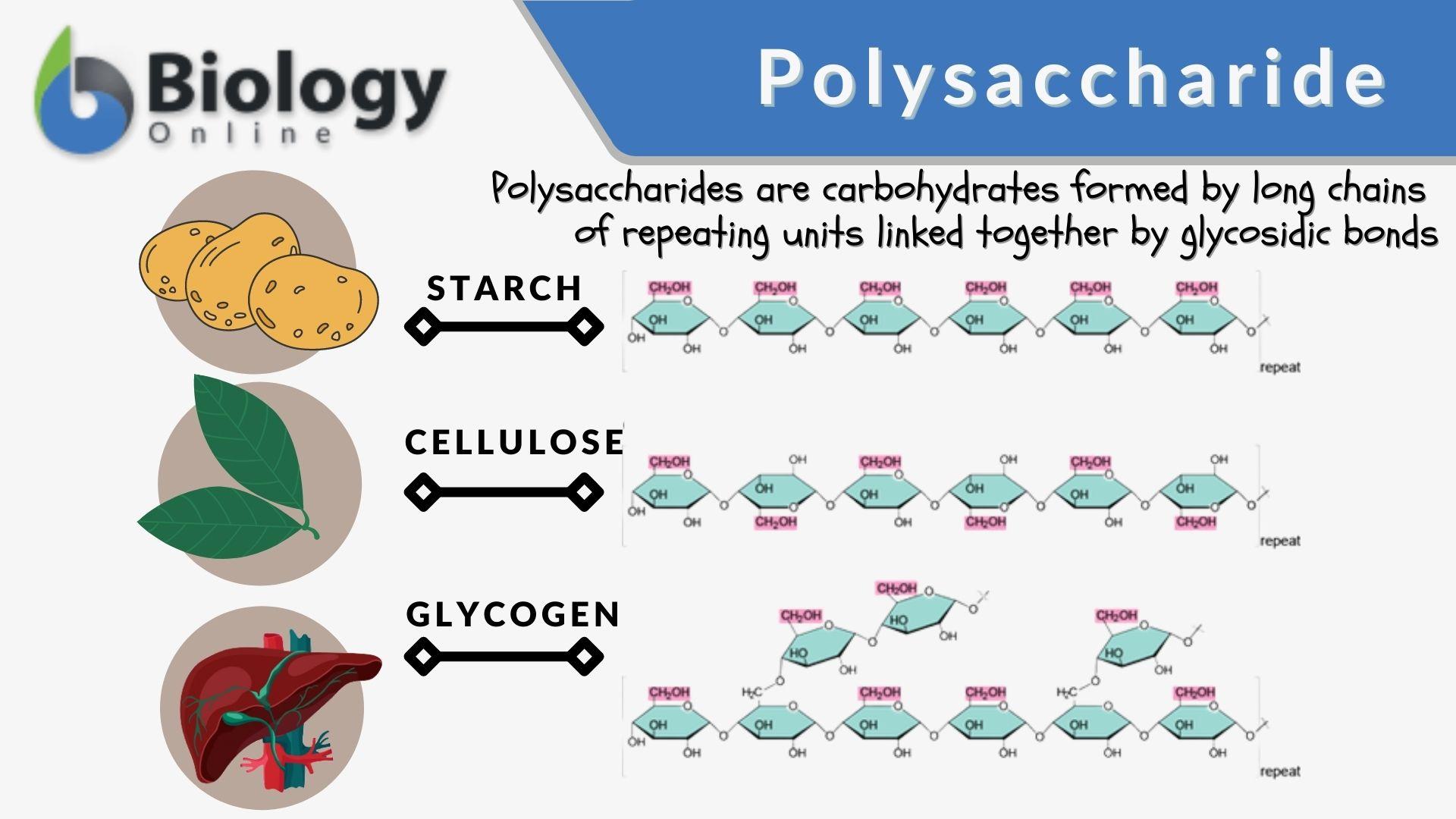
Polysaccharide Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary Ø structural polysaccharides include both homo & hetero polysaccharides. Ø hetero polysaccharides provide extracellular support to the organisms of all kingdoms. Ø polysaccharides are synthesized enzymatically by the cells. Ø unlike proteins, polysaccharides generally do not have definite molecular weights. Polysaccharide synthesis. with numerous –oh groups of similar reactivity, polysaccharides are so structurally complex that their laboratory synthesis has long been a particularly difficult problem. several methods have recently been devised, however, that have greatly simplified the problem. among these approaches is the glycal assembly method. Neet. about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how works test new features nfl sunday ticket. Starch is a storage form of d glucose in plants. it is found in potatoes, beans, rice, wheat, and other grains and roots, as illustrated in figure 7.3.1 7.3. 1. starch is a mixture of two forms, 20% to 25% amylose and 75 to 80% amylopectin. figure 7.3.1 7.3. 1: starch food: sindhi biryani is a delicious dish of sindh.
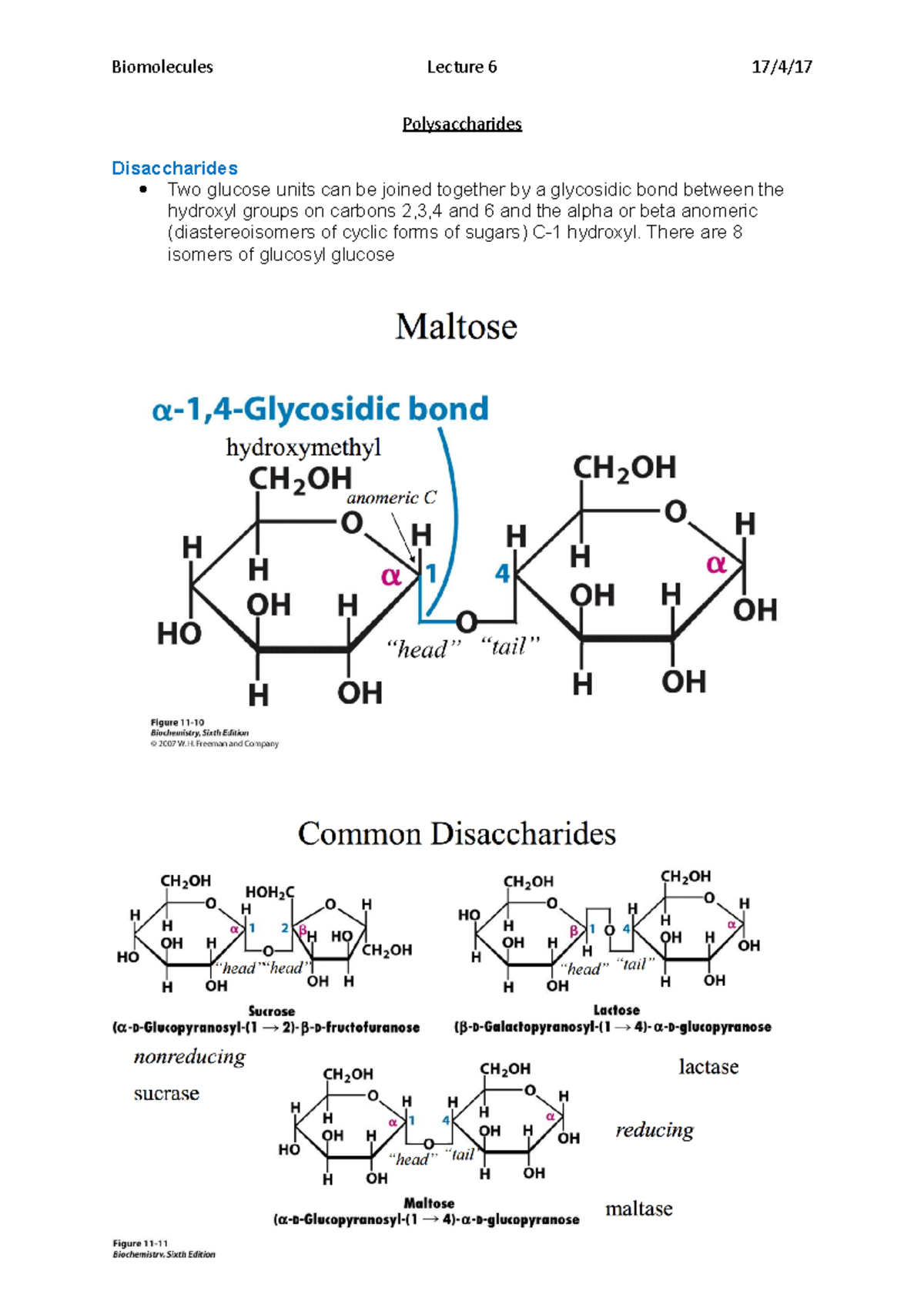
Polysaccharides Lecture Notes 6 Biomolecules Lecture 6 17 4 17 Neet. about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how works test new features nfl sunday ticket. Starch is a storage form of d glucose in plants. it is found in potatoes, beans, rice, wheat, and other grains and roots, as illustrated in figure 7.3.1 7.3. 1. starch is a mixture of two forms, 20% to 25% amylose and 75 to 80% amylopectin. figure 7.3.1 7.3. 1: starch food: sindhi biryani is a delicious dish of sindh. 25.9 • polysaccharides and their synthesis polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates in which tens, hundreds, or even thousands of simple sugars are linked together through glycoside bonds. because they have only the one free anomeric –oh group at the end of a very long chain, polysaccharides aren’t reducing sugars and don’t show. Figure 6.10.1 6.10. 1: amylose. (a) amylose is a linear chain of α d glucose units joined together by α 1,4 glycosidic bonds. (b) because of hydrogen bonding, amylose acquires a spiral structure that contains six glucose units per turn.

Carbohydrates Lecture 6 Polysaccharides Join 2 Monosaccharides To 25.9 • polysaccharides and their synthesis polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates in which tens, hundreds, or even thousands of simple sugars are linked together through glycoside bonds. because they have only the one free anomeric –oh group at the end of a very long chain, polysaccharides aren’t reducing sugars and don’t show. Figure 6.10.1 6.10. 1: amylose. (a) amylose is a linear chain of α d glucose units joined together by α 1,4 glycosidic bonds. (b) because of hydrogen bonding, amylose acquires a spiral structure that contains six glucose units per turn.

Comments are closed.